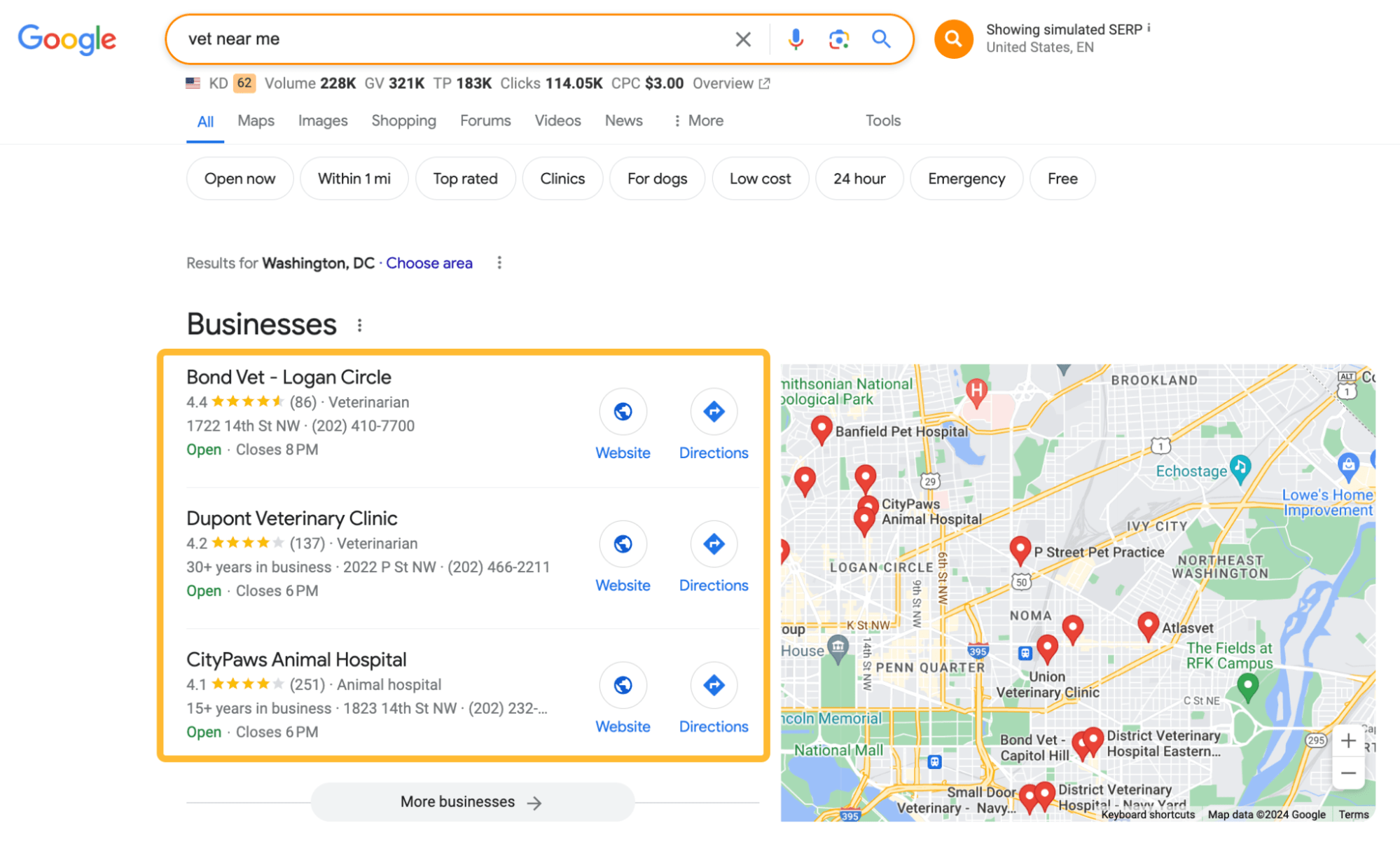
The goal of SEO is to increase visibility in search results, making it easier for people to find relevant, trustworthy, and useful content when they search for information, products, or services. This involves optimizing webpages, improving technical performance, and building credibility through links and engagement—so that both search engines and users see your site as valuable.
For example, if you sell coffee, SEO can help your website show up on the first page of Google when people search for “buy coffee”. Higher rankings lead to more clicks to your website, and that means more potential customers for your business.
There are two main reasons why SEO is important:
- People use Google to find all kinds of things, including products, services, and any helpful information about them. That creates search demand, which many websites compete for. The outcome of effective SEO is outranking the competition to take advantage of that search demand.
- Unlike online advertising, the traffic you get through SEO is free.
Overall, SEO benefits include free, sustainable, and passive traffic to your website month after month.
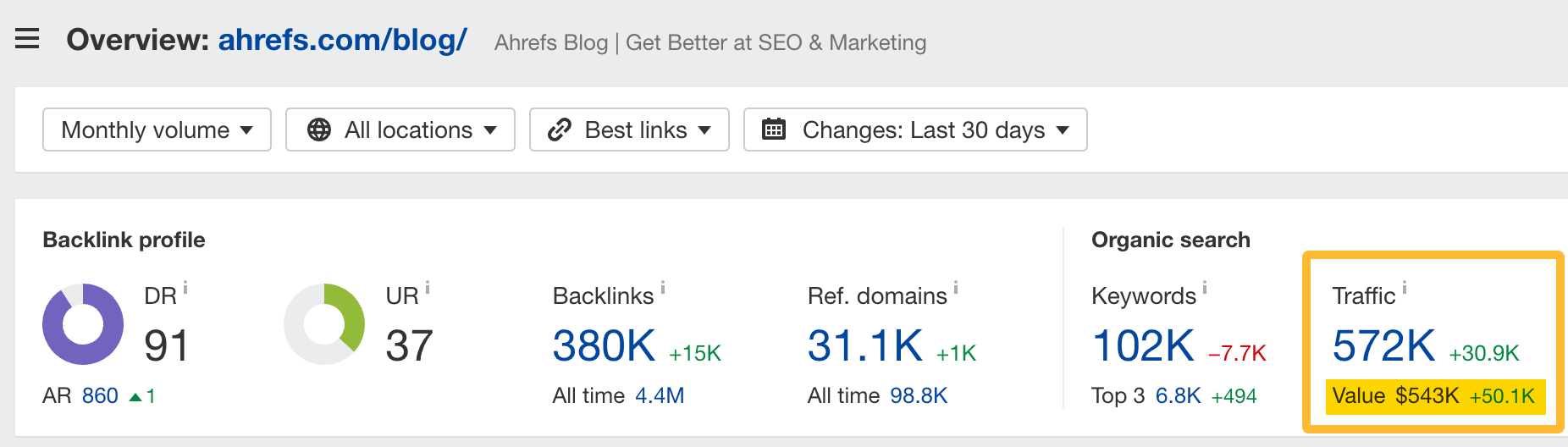
To illustrate, our blog generates an estimated 572K visits per month from Google. Without SEO, we’d have to spend over $0.5M on ads to get that traffic.
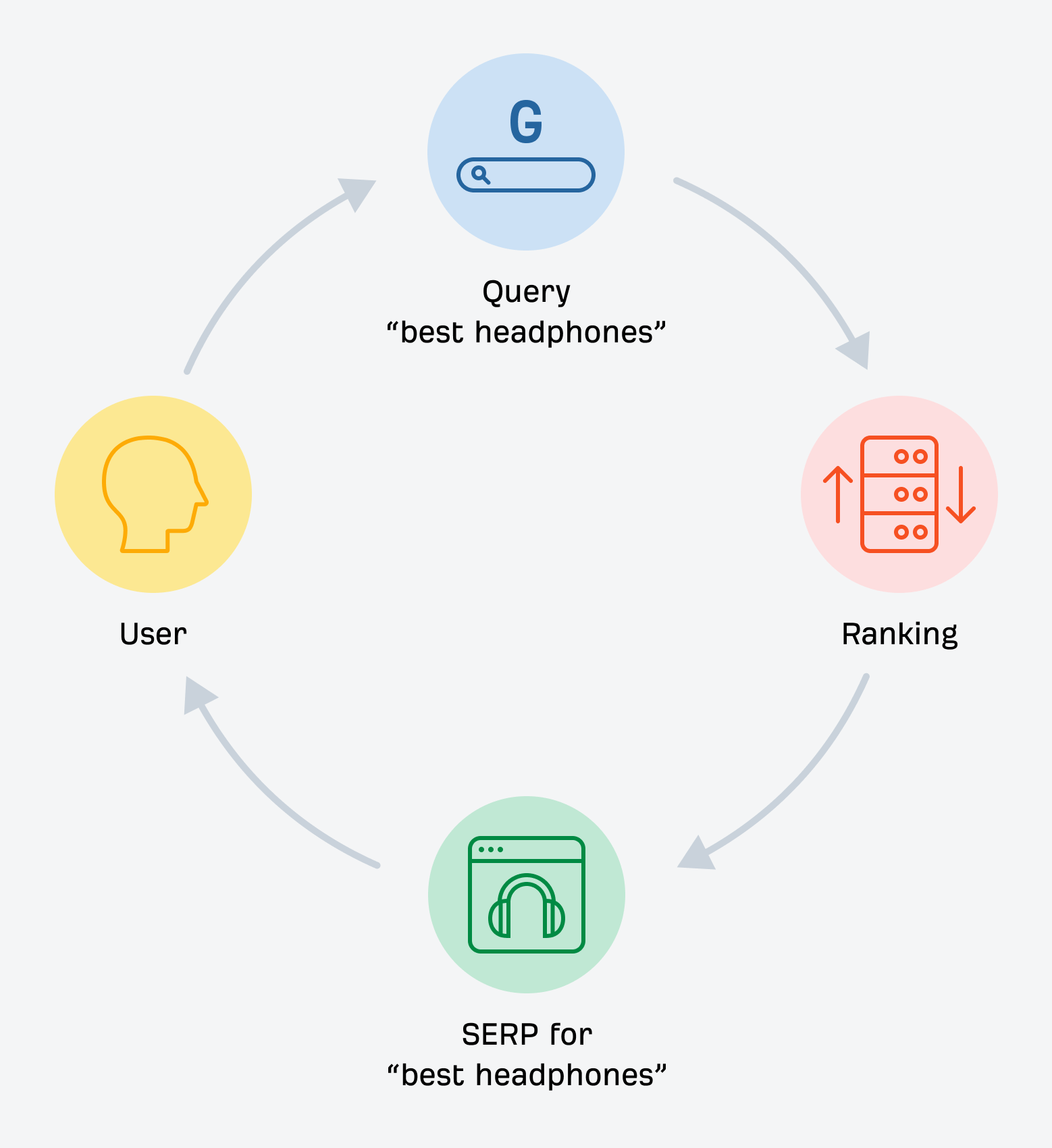
Search engines are designed to help you find information on the internet. They use two main components:
- Search index. A digital library of information about web pages.
- Search algorithms. Programs that match and rank results from the index based on your search query.
Search engines work in three phases:
- Crawling: Web crawlers (or spiders) visit and download webpages by following links from known pages.
- Indexing: The information from crawled pages is processed and added to the search index.
- Ranking: When you perform a search, the algorithm ranks relevant results based on various factors to provide the best answers.
So, in a nutshell, when you search, search engines look through all the pages in the index for relevant results. They then rank them using a computer program called an algorithm to put the best results at the top and display a search engine result page (SERP) to the user.
What poses the main difficulty for SEOs here is that, except for some privy people at Google, nobody really knows how this ranking algorithm(s) works, so there is a lot of trial and error in the SEO industry.
Google holds a number of patents related to how their search works in order to prevent manipulating search results and copying the secret formula of their multibillion-dollar business.
That said, they still leave clues through their spokespeople and pages like “How Search Works”:
To give you the most useful information, Search algorithms look at many factors, including the words of your query, relevance and usability of pages, expertise of sources and your location and settings. The weight applied to each factor varies depending on the nature of your query – for example, the freshness of the content plays a bigger role in answering queries about current news topics than it does about dictionary definitions.
We also have evidence of some of the ranking signals Google uses. Here are the seven they already confirmed:
- Backlinks.
- Relevance (search intent).
- Freshness.
- HTTPS (site security).
- Mobile-friendliness.
- Page speed.
- Intrusive interstitials.
But that’s not all. Google likes to “stir things up” a bit by personalizing search results based on:
- Location. Shows results relevant to your geographical area.
- Language. Ranks content in the language you understand.
- Search history. Tailors results based on your past searches.
SEO works by creating high-quality, relevant content with good UX about things people search for, and then proving to Google it deserves to rank.
To do SEO effectively, these four things matter the most:
- Keyword research.
- Search intent.
- Content quality.
- User experience and usability of the page.
1. Keyword research
To drive organic traffic, your content needs to be created specifically for topics that people actually search for. Otherwise, no one will be able to find your page on Google’s search result pages (SERPs), and you won’t get any organic traffic.
At the same time, the best kind of topics are the ones that hold business value to you. Otherwise, you’re unlikely to attract potential customers through SEO.
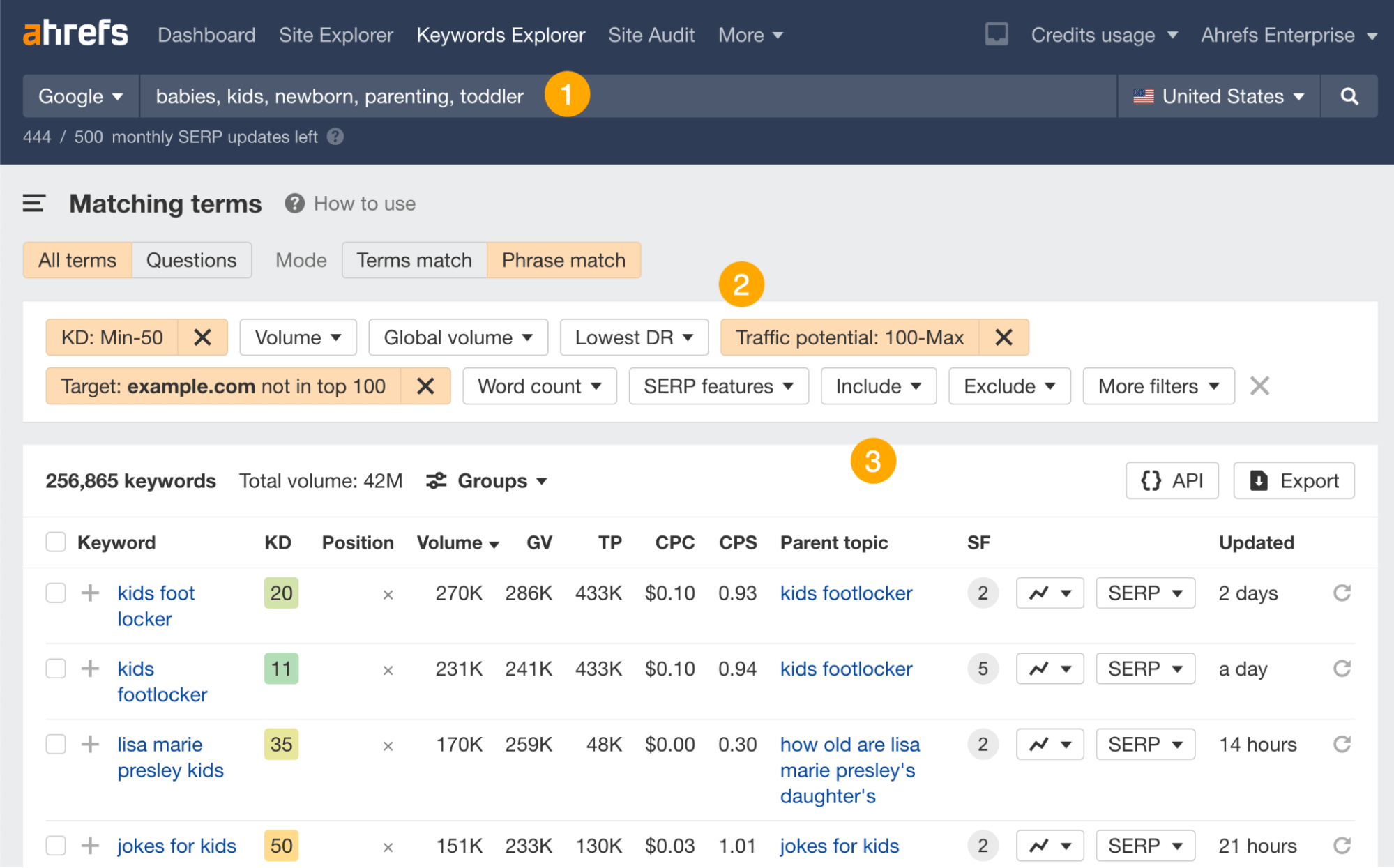
To find topics that meet both criteria, you need a keyword research tool like Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer.
The general process of keyword research goes like this:
- Enter a few industry-related “seed” phrases. For instance, “parenting”, “newborn”, “toddler”, “babies”, “kids”.
- Refine the list with filters such as keyword difficulty, minimum traffic potential, or excluding keywords you already rank for.
- Pick keywords that fit your website best.
2. Search intent
Search intent is the reason behind the search. In other words, why did the person make this search? Was it to buy something, to learn something, or maybe to find a particular site?
These are important questions to answer before you start creating content because Google evaluates content relevancy based on how well a page serves search intent. Irrelevant content won’t get far.
For example, interactive tools dominate the first page for “days between dates” whereas videos dominate for “excel for beginners.” This is a clear indication of what searchers want and the best type of content to create for each keyword.
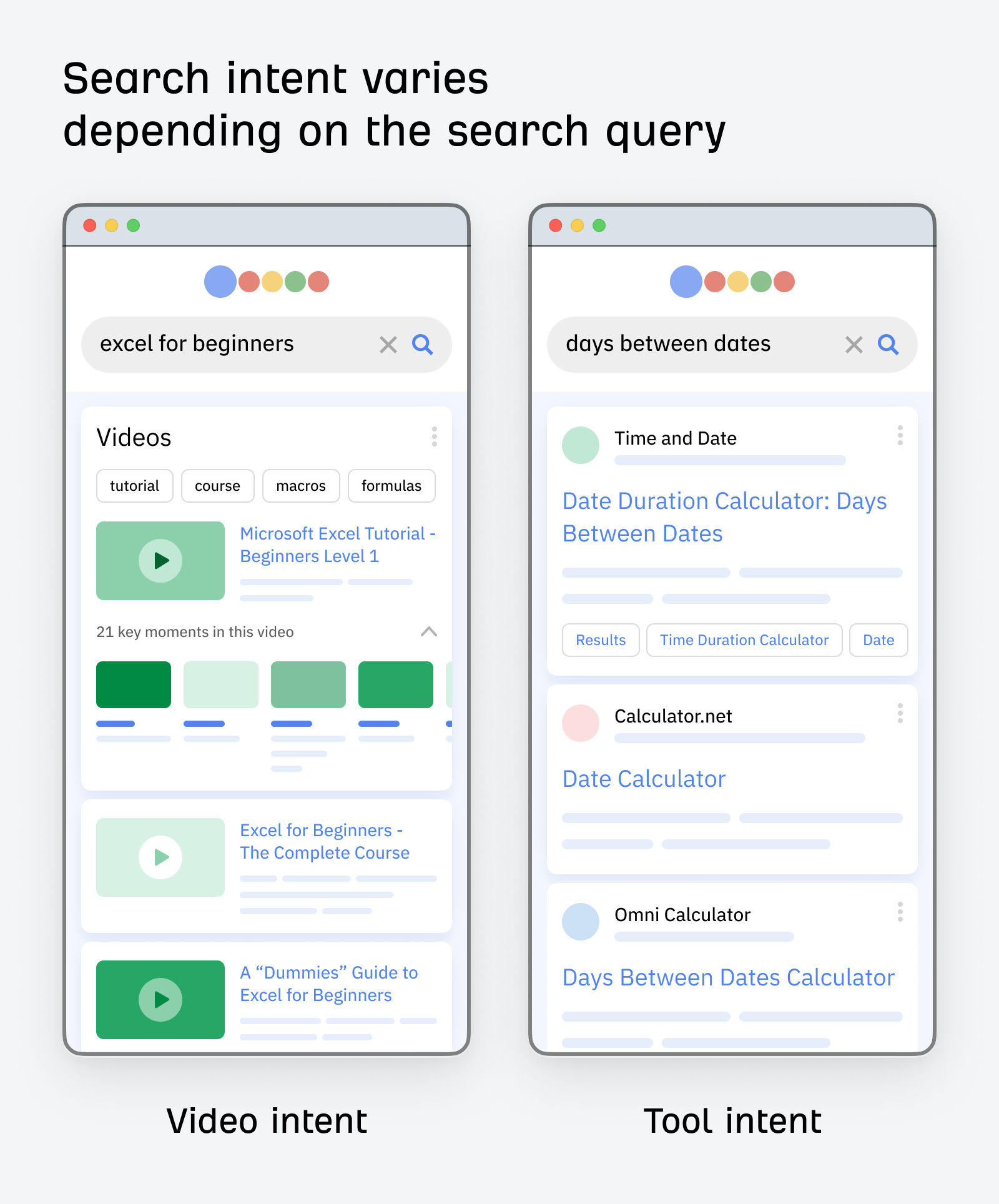
The reason why this is happening is that Google interprets the motive behind the query and shows the results the user wants to see.
Search intent is not always that obvious. In some cases, it can be mixed or fractured. But to make their jobs easier, SEOs typically classify possible reasons behind the search into four categories:
- Informational. The searcher is looking for information, e.g., “who invented the mouse”.
- Navigational. The intent is to find a specific website, e.g., “facebook login”.
- Commercial investigation. The searcher wants to buy a specific product but needs to do more research, e.g., “ahrefs review”.
- Transactional. Pure buying mode, e.g., “buy iphone 15”.
How do you optimize for search intent? Look at the top-ranking pages and ask yourself questions to identify the “3 C’s of search intent.”
- Content type: Are most of the results blog posts, product pages, category pages, landing pages, or something else?
- Content format: Is Google mainly ranking how-to guides, list-style articles, tutorials, comparisons, opinion pieces, or something entirely different?
- Content angle: Is there a common theme or unique selling point across the top-ranking pages? If so, this gives you some insight into what might be important to searchers.
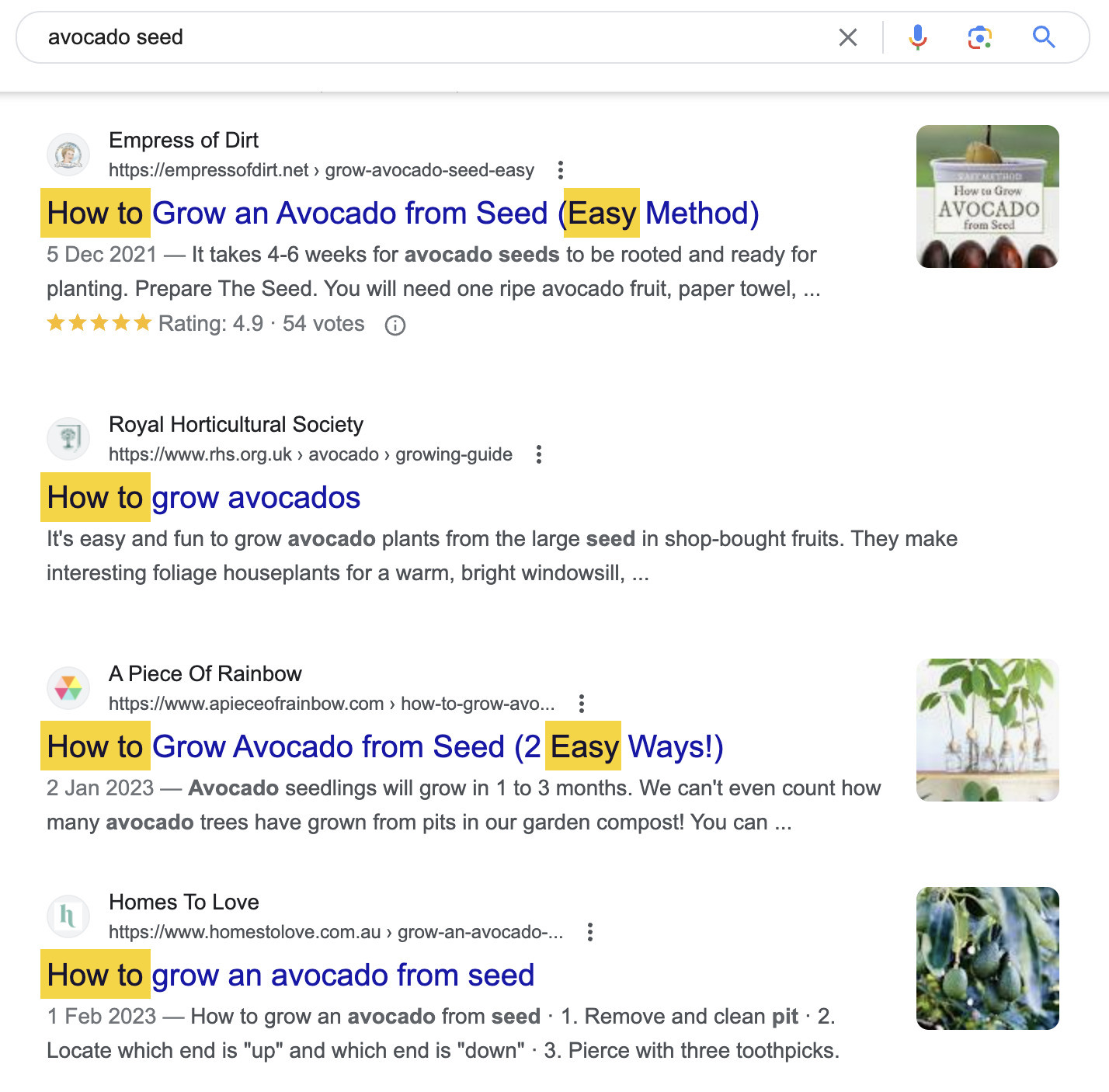
For example, most top-ranking pages for “avocado seed” are blog posts serving as how-to guides for planting the seed. The use of “easy” and “simple” angles indicates that searchers are beginners looking for straightforward advice.
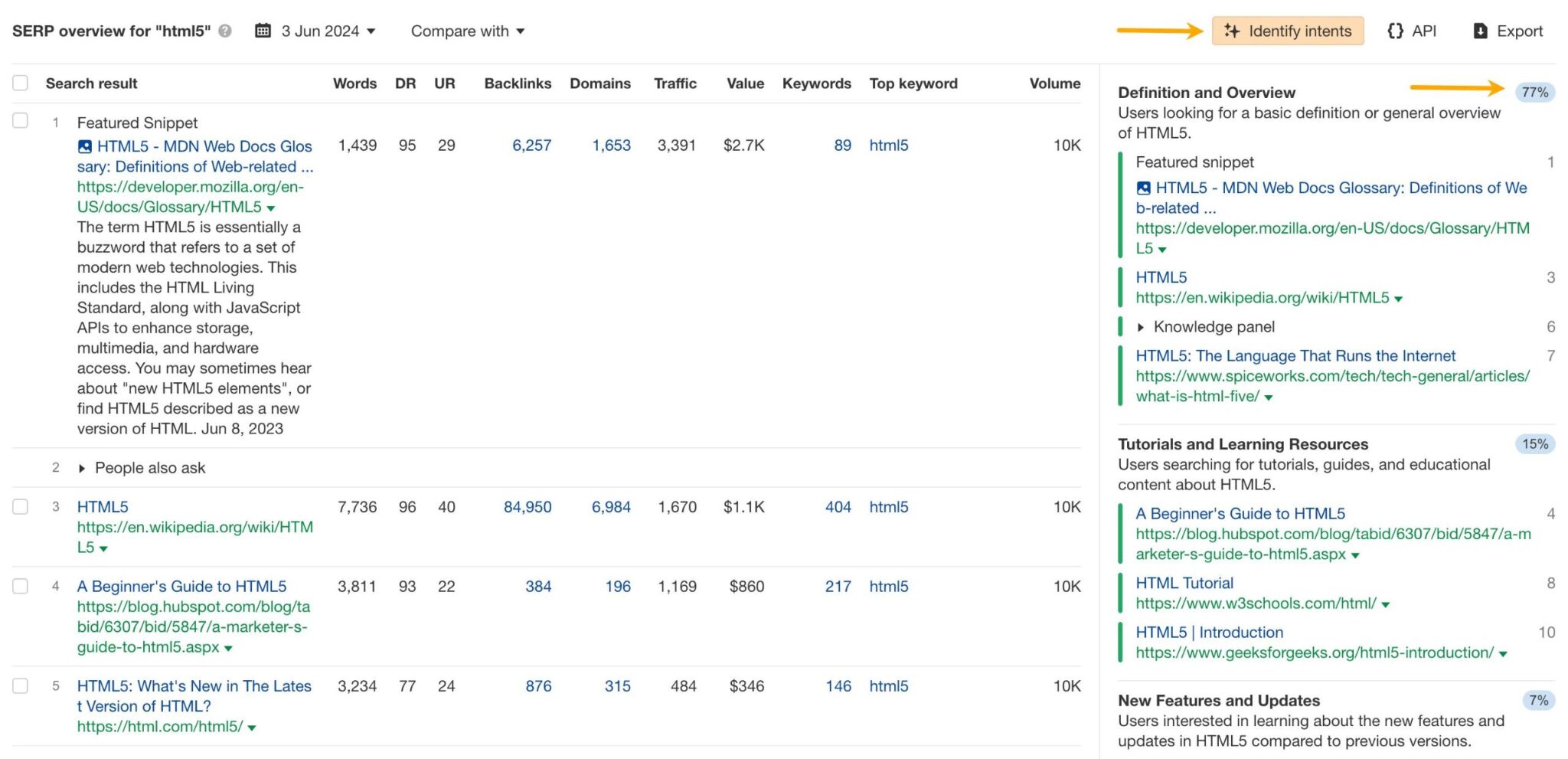
If you’re an Ahrefs user, you can also use the Identify intents AI feature to see the type of search intent that gets the most traffic.
3. Content quality
Google ranks pages, not entire websites. And over the years, it has developed guidelines and ranking factors to test pages for signs of quality.
In short, there are three things key to demonstrating content quality in the eyes of Google:
- Optimized content.
- E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness).
- Backlinks.
Optimized content
Content optimization concerns the information you provide on any given page. If you want to outrank your competitors, your content has to be:
- Helpful. Offer relevant, thorough answers; give searchers what they expect.
- Easy to digest. Use simple language with uncomplicated sentences to improve readability (about half of Americans read at a below 6th-grade reading level). Use images where you can make the content more comprehensible.
- Well-structured. Follow a logical structure, use headings to separate different sections.
- Unique. You can increase your chances of ranking if you bring something new and interesting to the SERPs, such as original research.
- Fresh. More important in search queries that require up-to-date information.
On top of that, you need to follow some simple on-page SEO best practices. Page elements like title tags, image alt text, or schema markup can help Google better understand your content.
These on-page SEO techniques are easy to use so whenever you need to, just check out our beginner’s guide on-page SEO to get some tips and use our free AI writing tools to streamline the process.
E-E-A-T (previously E-A-T)
E-E-A-T (aka Double-E-A-T) is a set of guidelines that Google’s quality raters use to assess the quality of search results. And it looks beyond the information on your website.
E-E-A-T applies to all topics, but it’s more impactful on YMYL topics (Your Money or Your Life) - topics that can potentially impact a person’s future happiness, health, financial stability, or safety.
Basically, Google looks for signs of overall trustworthiness on your pages before it serves them to searchers. Specifically, it looks for:
- Experience. As in first-hand experience with the subject matter (product, problem, event, place, etc.)
- Expertise. Formal expertise, qualifications, and education of the content creator.
- Authoritativeness. The extent to which the content creator or the website is known as a go-to source for the topic. In other words, reputation.
- Trustworthiness. Legitimacy, transparency, and accuracy of the website and its content. It’s the most important criterion out of them all.
Arguably the most impactful way of improving E-E-A-T on your pages is getting more quality links from other websites - backlinks. And this brings us to one of the most powerful ranking factors.
Backlinks
Backlinks (or inbound links, incoming links) are links from a page on one website to another.
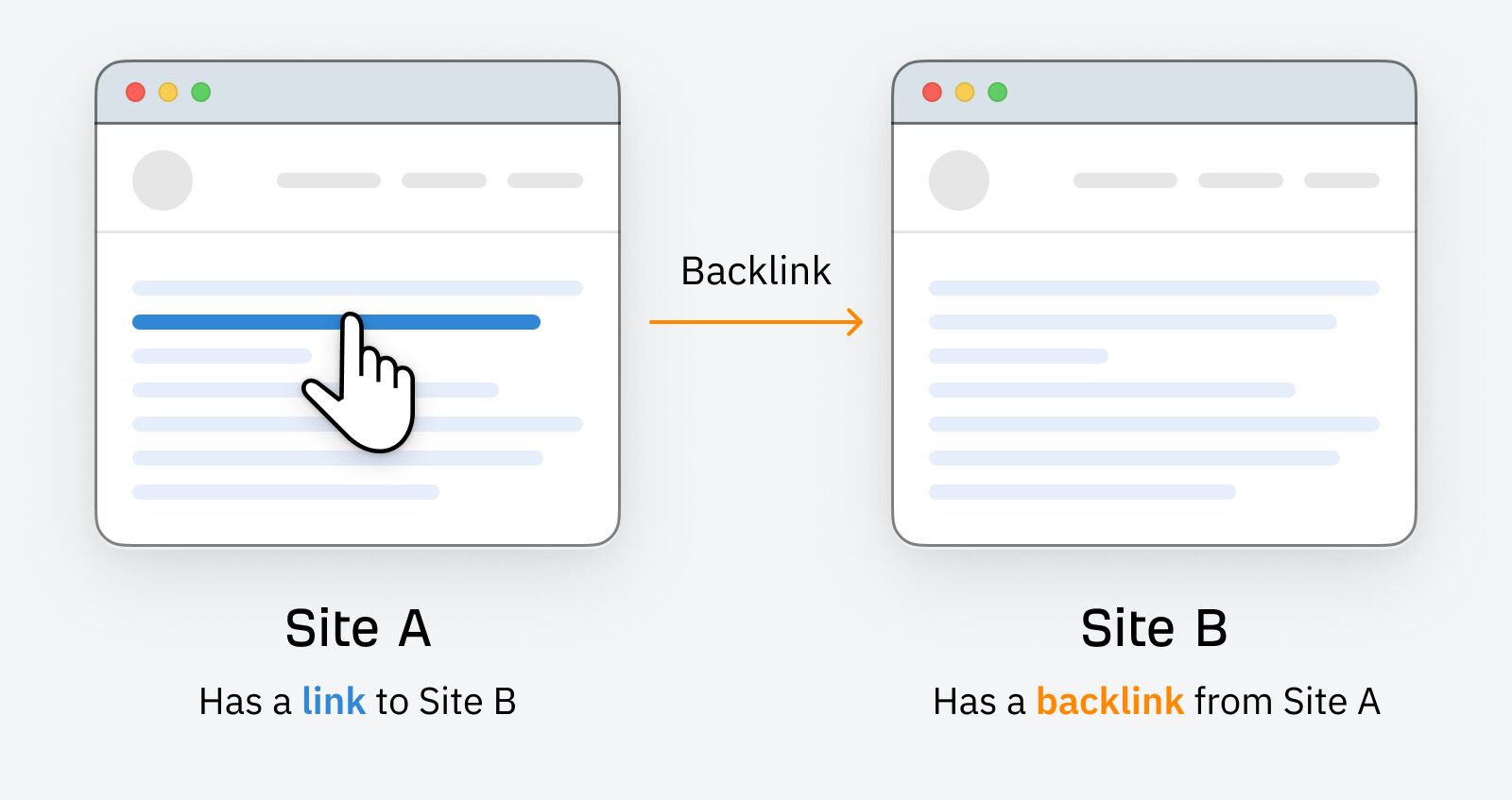
Backlinks act as votes. Generally speaking, pages with more votes tend to rank higher.
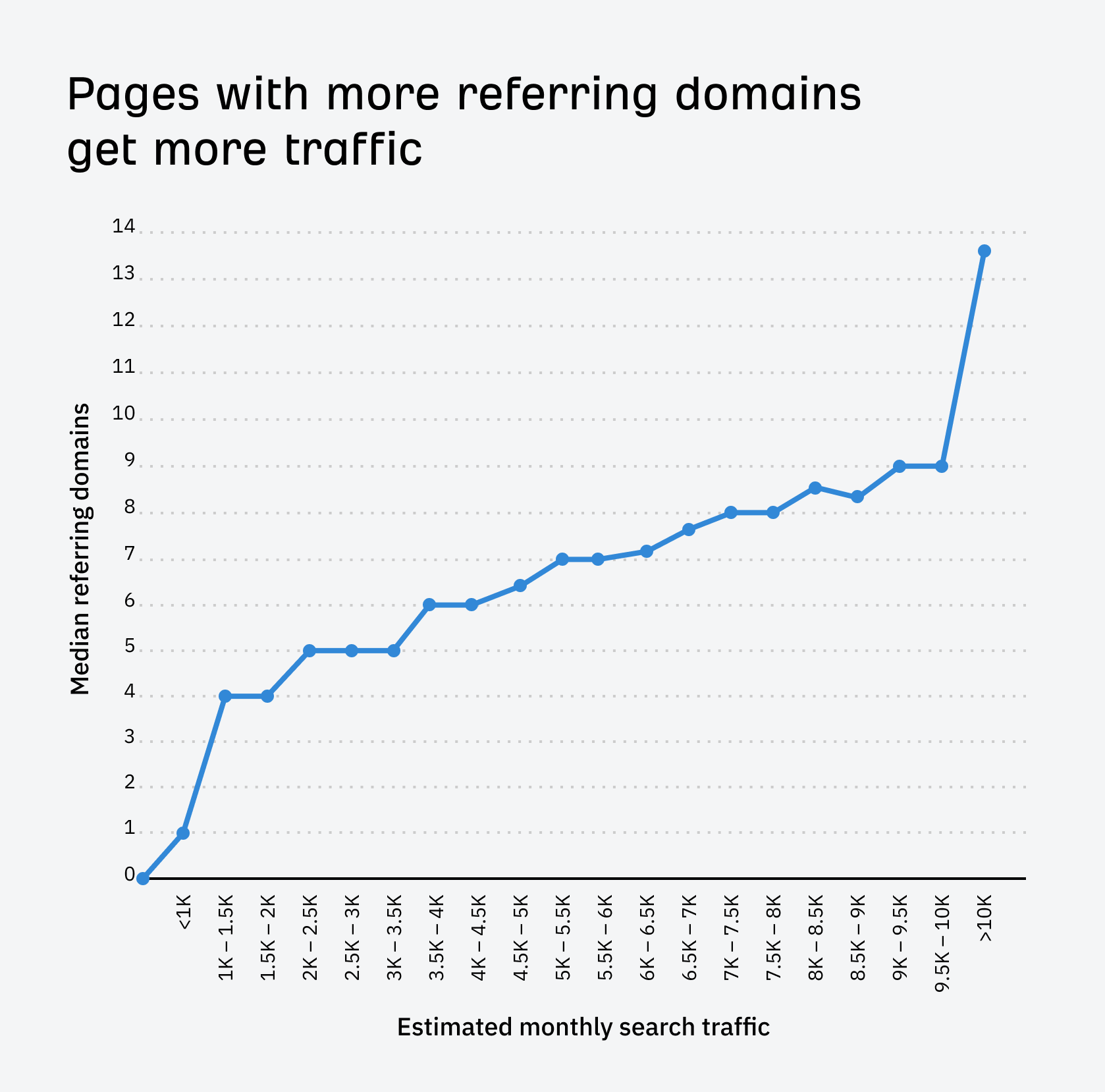
How do we know? We studied almost one billion web pages and found a clear correlation between referring domains (links from unique websites) and organic search traffic.
Getting more links to your pages is called link building. Overall, there are three ways to get backlinks, and you can (even should) use all of them:
- Earn backlinks by creating compelling content with assets designed to attract backlinks, such as original studies, free resources, infographics, or a unique view on a topic.
- Create backlinks by manually adding them to popular directories and resource pages.
- Build backlinks by reaching out to people who can include links to your pages on their website.
Link building is something that preoccupies the SEO industry. In fact, many SEOs and agencies specialize in that alone. To give you an idea of how this works, here’s a quick overview of a few popular backlink building techniques.
- Broken link building: Find a “dead page” and ask linkers to swap the links to a working page on your site.
- Guest blogging: Write a blog post for another website and earn a link back to your site in return.
- The Skyscraper Technique: Find content with lots of backlinks, create something better, then ask everyone linking to the content you improved to link to you instead.
- Resource page link building: Get backlinks from webpages that curate and link out to useful industry resources.
- HARO (and similar services): Use services like HARO to find relevant journalist requests for quotes. You can usually earn a link to your site if your quote gets published.
What you want, though, is not just any kind of backlinks. The consensus in the SEO community is that there are five factors that make up a backlink’s quality:
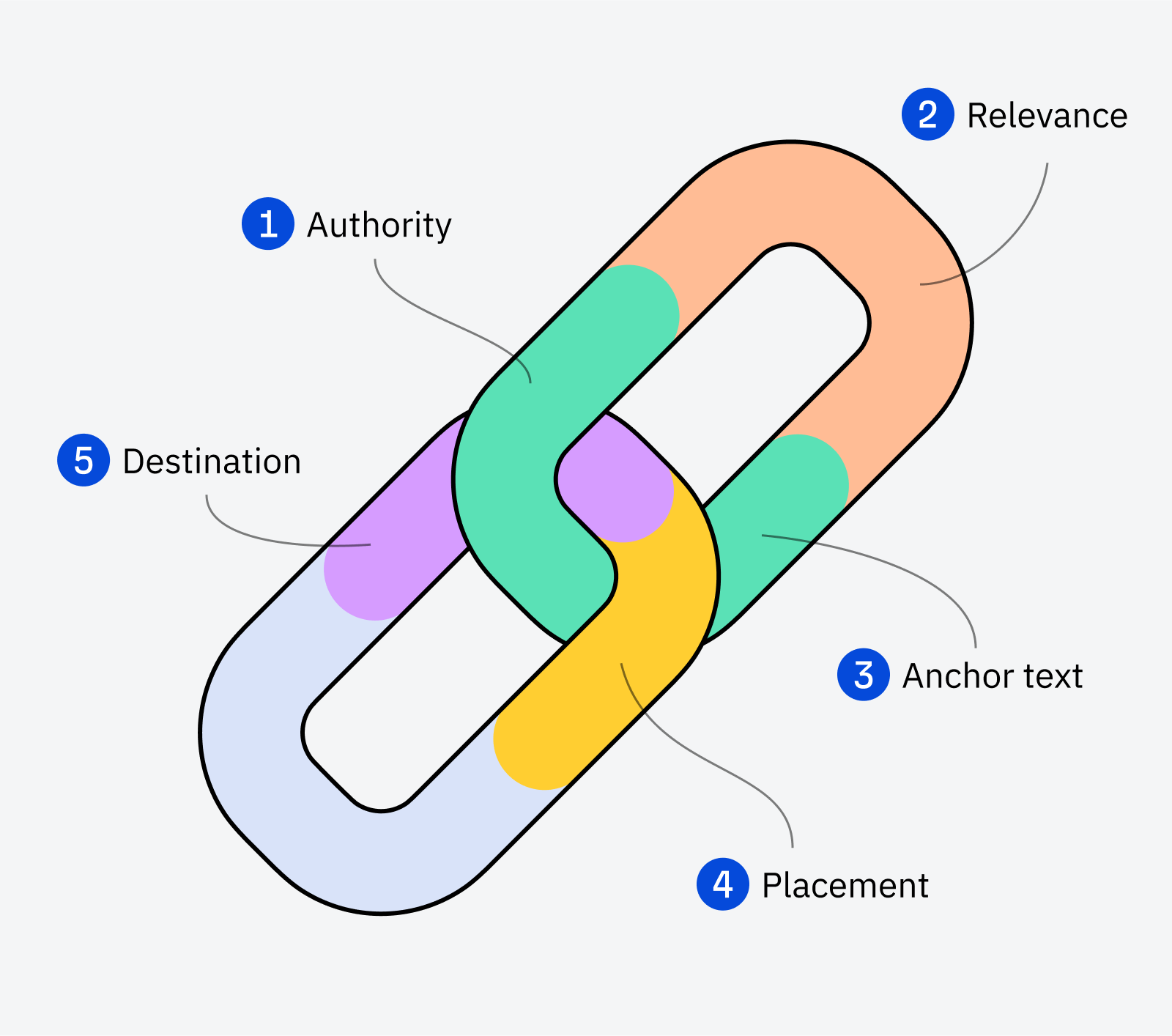
We cover all of them in detail in our link building guide for beginners. But here’s the takeaway to remember: the best links come from relevant, authoritative websites and are placed within the main content.
Since these kinds of links are so valuable, they became sort of the currency of the web. That’s why it’s so challenging to get good quality links.
What is the difference between SEO, SEM, and PPC?
SEM (Search Engine Marketing) has the broadest scope of those three, encompassing generating traffic from organic search (SEO) and paying for traffic with PPC search ads. Learn more about the difference in our guide to SEO vs. SEM.
What are the types of SEO?
There are 3 main types of SEO:
- On-page SEO concentrates on ranking factors occurring on a page, such as aligning with search intent or improving content quality.
- Off-page SEO concentrates on ranking factors occurring outside of a page, such as building backlinks, or optimizing a Google Business Profile.
- Technical SEO is the process of optimizing a website to help search engines find, crawl, understand, and index your pages.
There are also a few subtypes of SEO focusing on specific business conditions such as local SEO, ecommerce SEO, or enterprise SEO. But if you want a full list of all the types of SEO, we compiled one here (67 types of SEO to date).
How can I learn SEO?
There are many good resources you can find online, and a good portion of them are free. You can start with our guide on SEO for beginners or take free courses in Ahrefs’ Academy.
Can I do SEO on my own?
The short answer is yes if you run a small to medium-sized website. All you need is some time to learn and practice SEO, plus good SEO tools that offer vast and accurate data.
For bigger sites, more than one SEO specialist may be needed. You may need to hire someone or outsource to freelancers or an agency.
SEO tools - which ones do I need?
There are two basic types of tools for SEO:
- Google Search Console is a free tool that provides click, click-through rate and SERP impression data straight from Google and notifies you of technical issues and manual actions. The data is limited but it’s considered to be the most accurate so pretty much every SEO professional uses the Search Console.
- An all-in-one SEO tool like Ahrefs compensates for Google Search Console’s data limitations and provides additional features that SEO would be impossible without. All-in-one tools allow you to analyze your competitors’ organic performance, do keyword research, track your rankings across many locations, analyze backlinks and find backlink opportunities, audit and optimize your website for over 160 technical issues, and more.
If you just want to try with free tools first, you will find lots of them online. Ahrefs provides fourteen free SEO tools, one for every aspect of SEO, including your central SEO dashboard called Webmaster Tools. Want even more options? Check out our list of 31 free SEO tools.
How much time does SEO take?
SEO is usually a lengthy process. We learned from over 4k respondents that it typically takes between 3-6 months to see results.
How much does SEO cost?
If you’re looking to hire someone for SEO instead of doing it yourself, your options are:
- Hiring an agency. Probably the most expensive option, costing $134.66/hour (+ retainer) on average.
- Hiring freelancers/consultants. On average, SEO consultants cost $122.33/hour (+ retainer), and freelancers cost $68/hour (+ retainer).
- Building an in-house team. On average, an in-house SEO specialist costs $71K/year (in the U.S.). Naturally, the salary will largely depend on the experience of the employee.
The cost estimates are based on our study.
What latest SEO trends are worth following?
In a recent article, we analyzed ten influential SEO trends for 2024. Based on our research, we think these four trends are definitely worth implementing and keeping an eye on for further development:
- Video SEO. Video SEO is essential due to steady search trends and can significantly boost visibility.
- SGE (Search Generative Experience, now “AI Overview”). Google recently rolled out a feature that uses AI to generate exhaustive answers to search queries. Follow Google’s search essentials guidelines to appear in those AI overviews.
- AI SEO. AI tools improve efficiency and save time in various SEO tasks.
- Information Gain. Google’s patented way to assign a score to your content to determine its uniqueness. For instance, original content could be something that offers a unique perspective or original research.
Read the full article to learn more, and see which other trends could be worth following under some circumstances and which are best avoided.