A backlink is a link created when one website links to another. Backlinks are important for both helping people discover your website and improving your ranking on search engines like Google.

Learn how to check and analyze backlinks, which backlinks will be worth your time, and where to get them.
Acquiring backlinks (link building) is the cornerstone of search engine optimization (SEO). More backlinks from unique domains can improve your search ranking. And we confirmed this in a study.
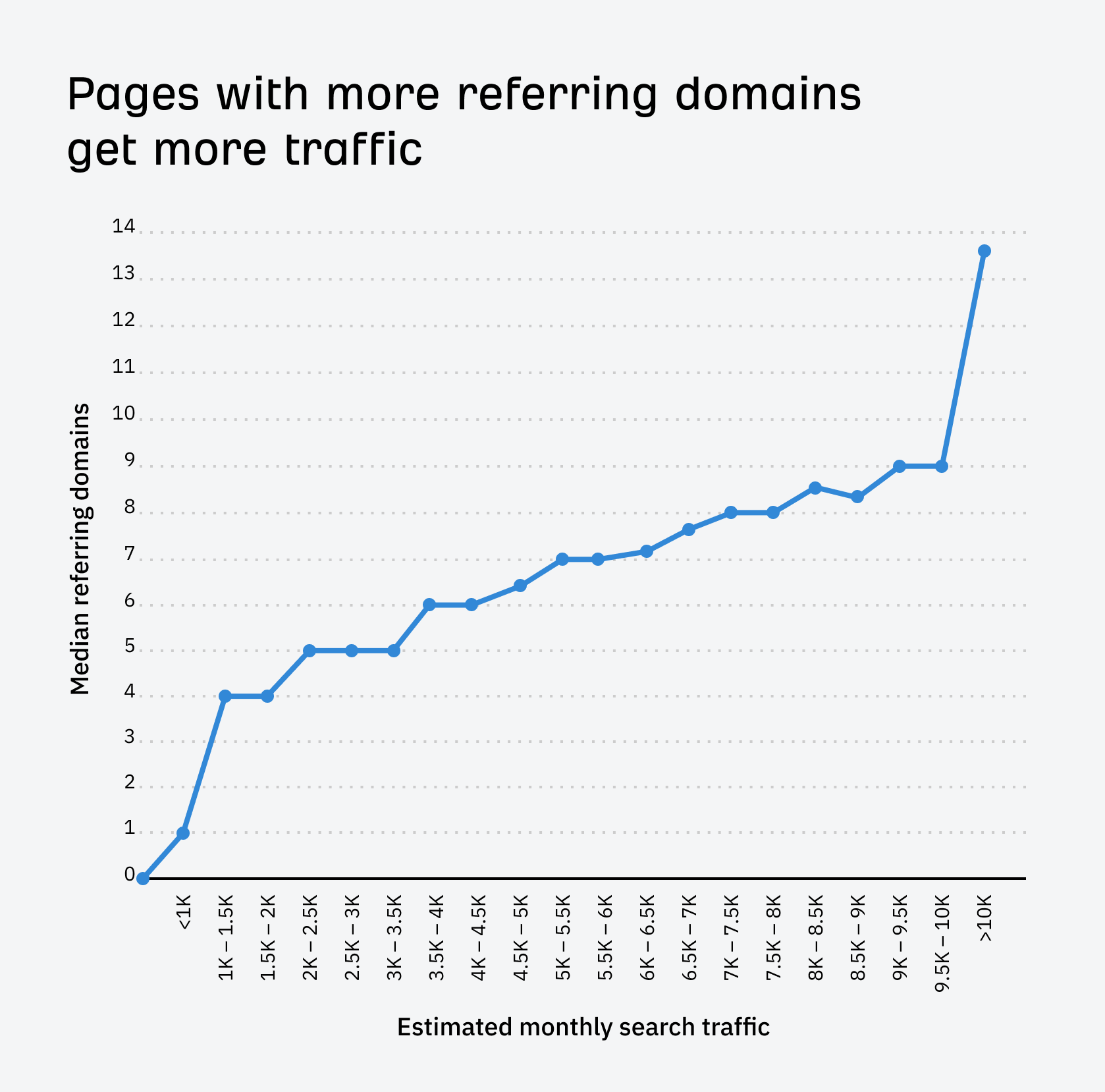
We also ran an experiment. It tested if removing backlinks to a few pages would affect their traffic. Traffic fell after we disavowed the backlinks (told Google to ignore them). Traffic then rose after we removed the disavow file.
There is another reason why backlinks are so important. Backlinks boost the discoverability of the pages on your site. This means search engines may find your content faster if you get more quality backlinks.
A few high-quality, relevant backlinks will likely boost your rankings more than many low-quality ones. If all links had the same weight, Google would struggle to rank pages, and their algorithms could be easily manipulated.
Interestingly, on SEO Office Hours, Google’s John Mueller said the number of links doesn’t matter at all. It’s all about their quality.
There could be one really good link from one website out there that is, for us, a really important sign that we should treat this website as something that is relevant because it has that one link. I don’t know, maybe from like a big news site’s home page, for example. So the total number essentially is completely irrelevant.
That’s why it’s so important to know which backlinks could impact your rankings more. Here are some of the main attributes that will help you identify the best-quality links:
- Authority: backlinks from popular websites are more valuable.
- Relevance: backlinks from closely related websites could be more valuable.
- Anchor Text: the words that people click on to get to your website matter to Google.
- Placement: backlinks in important parts of a website are more valuable.
- Destination: ideally, get backlinks to the page you want to optimize.
- Follow vs. nofollow: some backlinks have a tag that tells Google not to pass on any of their influence to the linked page.
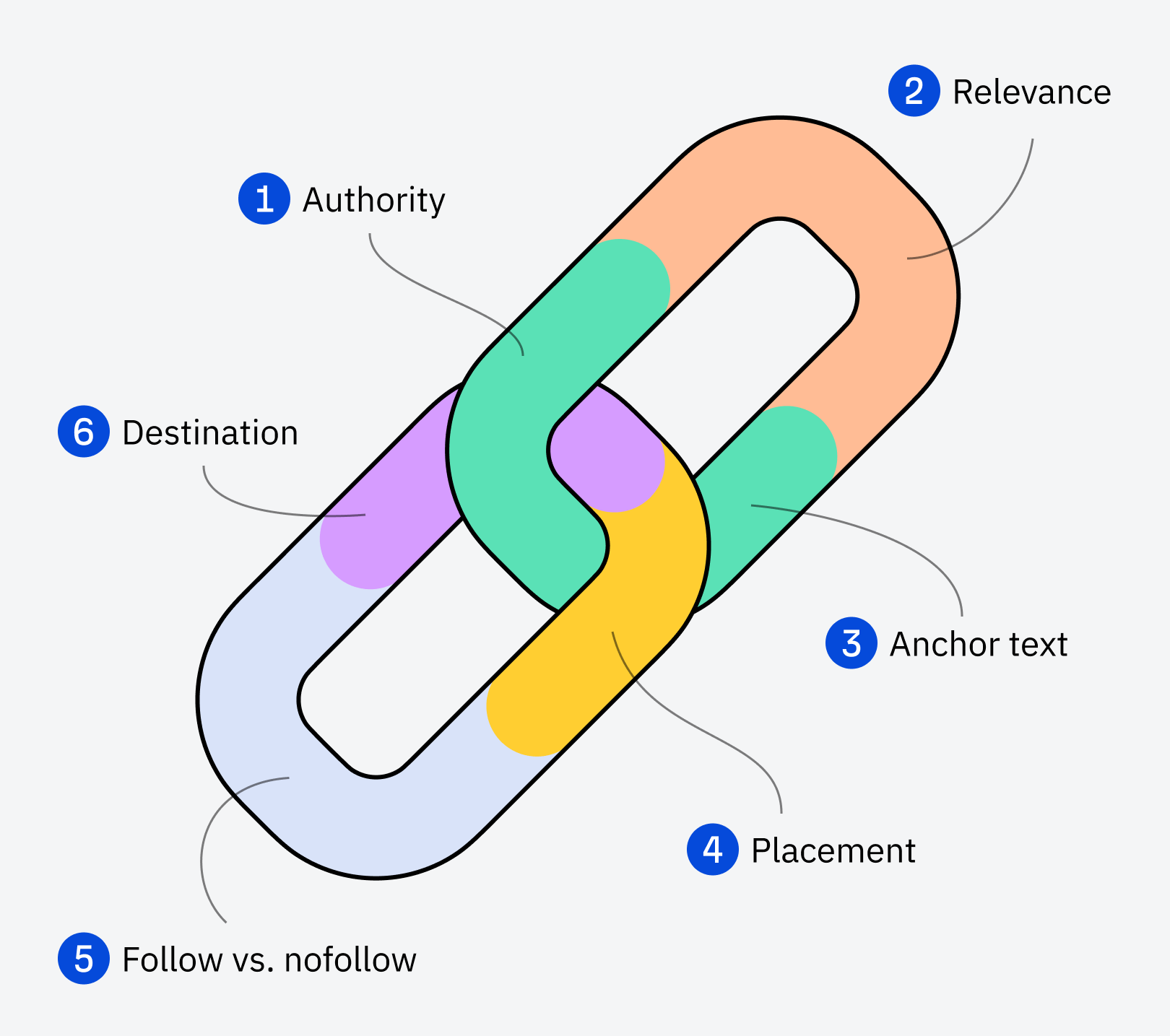
Let’s look at these in more detail.
Authority
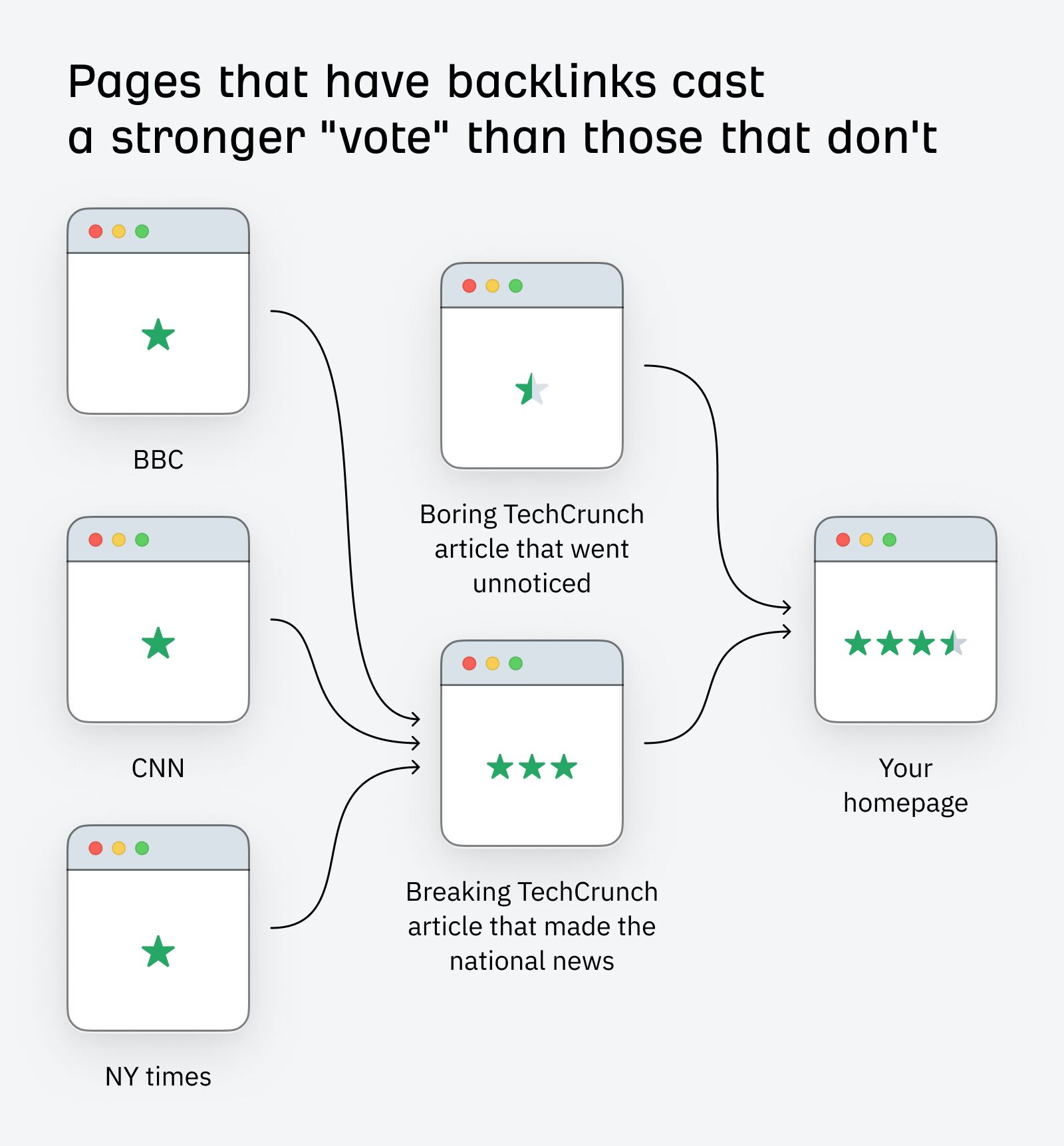
Pages with more quality backlinks have more authority in Google. It shows that people find those pages valuable and trustworthy. For instance: BBC, CNN, and NY Times are authoritative sites in that sense. A piece of that authority is passed on to the sites they link to.
That’s why, backlinks from strong web pages are better than weak ones. They simply have more authority to be passed on.
We studied page-level authority a few times. We found a clear link to organic search traffic.
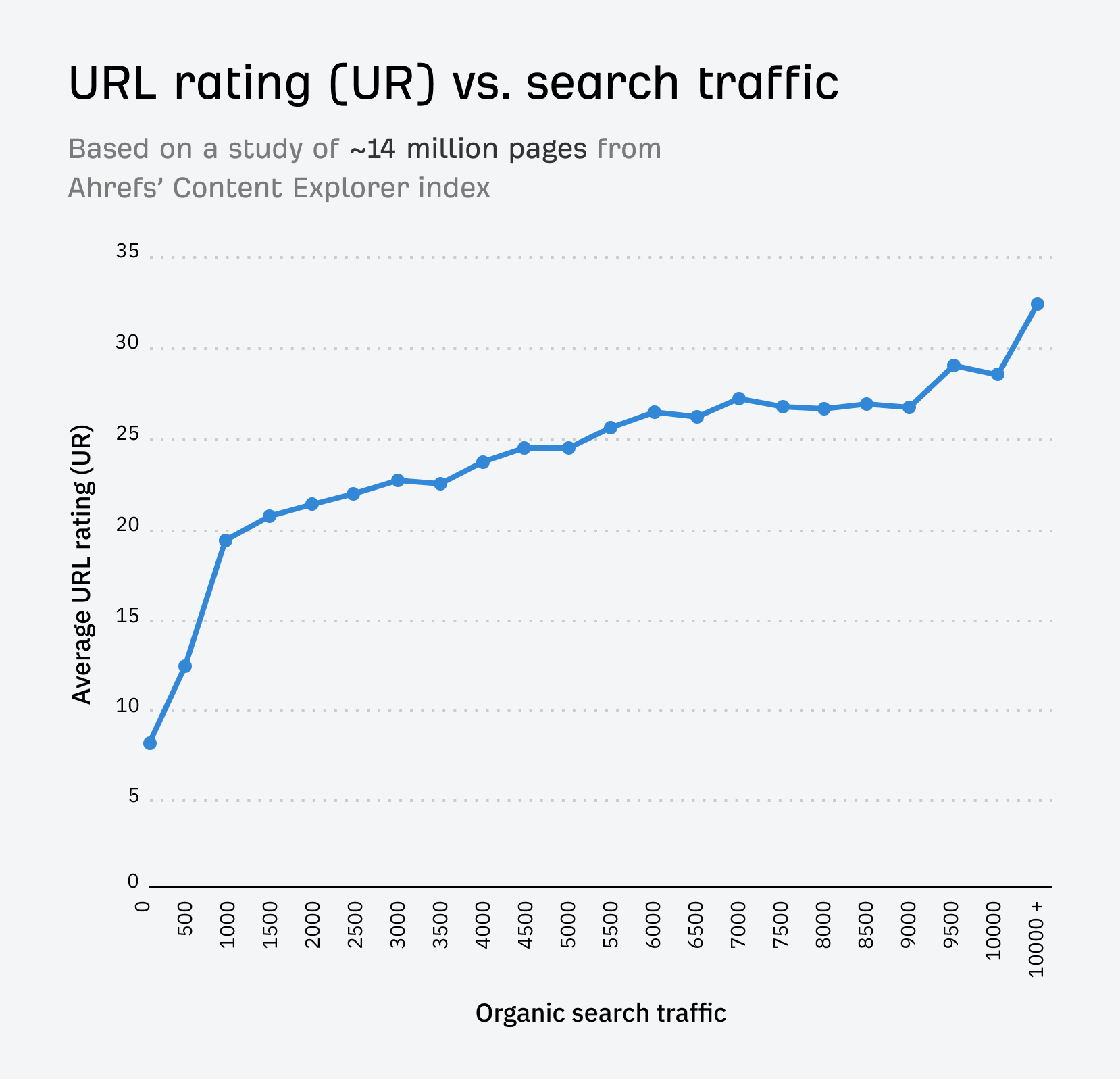
URL Rating (UR) is Ahrefs’ page-level authority metric. It’s scored on a scale from 0 to 100.
That said, backlinks from high-authority websites don’t always transfer more authority.
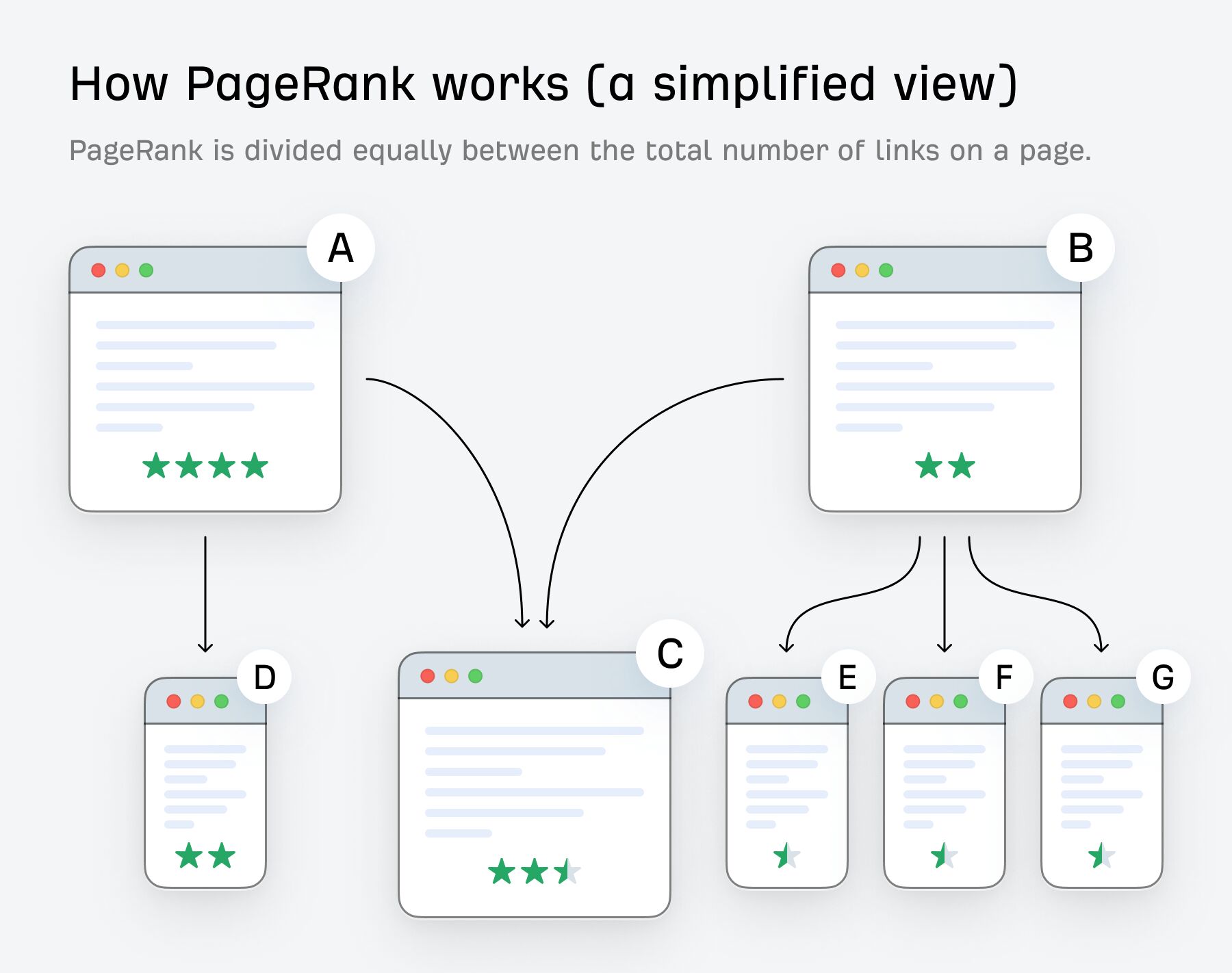
The more links there are on the page that link to you, the less authority will be transferred. The PageRank algorithm shares it between all those pages. It’s a program that ranks web pages in search results. It does this by assessing the number and quality of links to each page.
To illustrate Page Rank (PR), consider two pages, A and B. A links to two pages, and B links to four. The PR flow would look like this:
You can gauge a backlink’s authority by using the UR metric in the Backlinks report in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer. The higher the UR, the better.
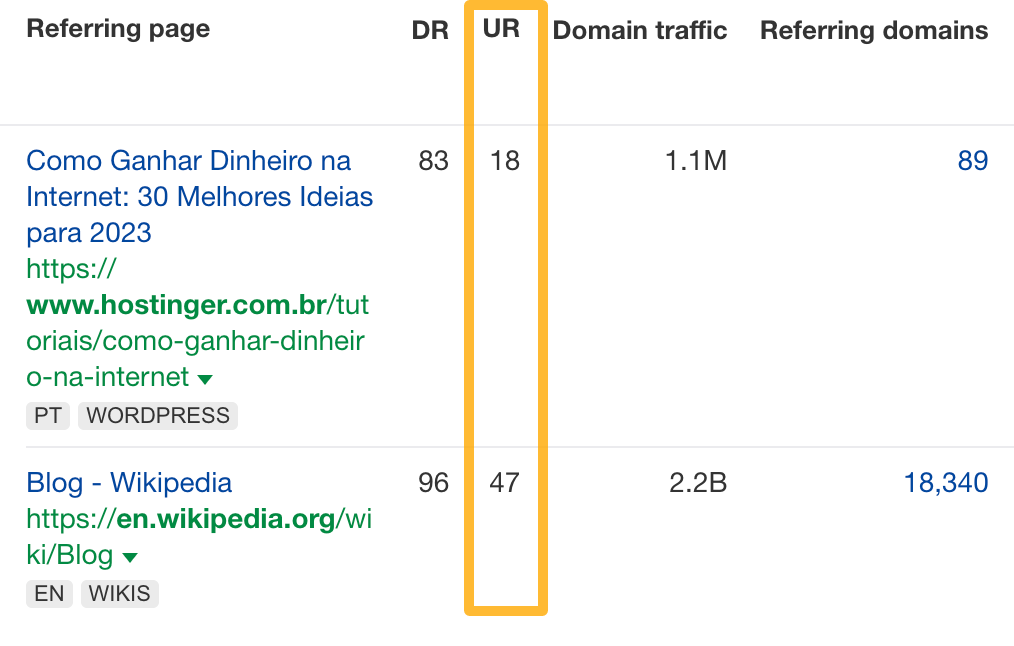
Don’t confuse page-level authority (UR in Ahrefs) with domain authority (DR in Ahrefs). DR measures a site’s backlink profile strength against all others in its index. It is expressed in on a logarithmic scale of 0 - 100 (i.e., it’s harder to go from 69 - 70 than 1 - 10).
Since you Google ranks pages and not websites, it’s more important to focus on boosting the pages that you want to rank rather than achieving a higher authority score for the site.
You can see the difference between those two types of authority in their correlation with organic traffic.
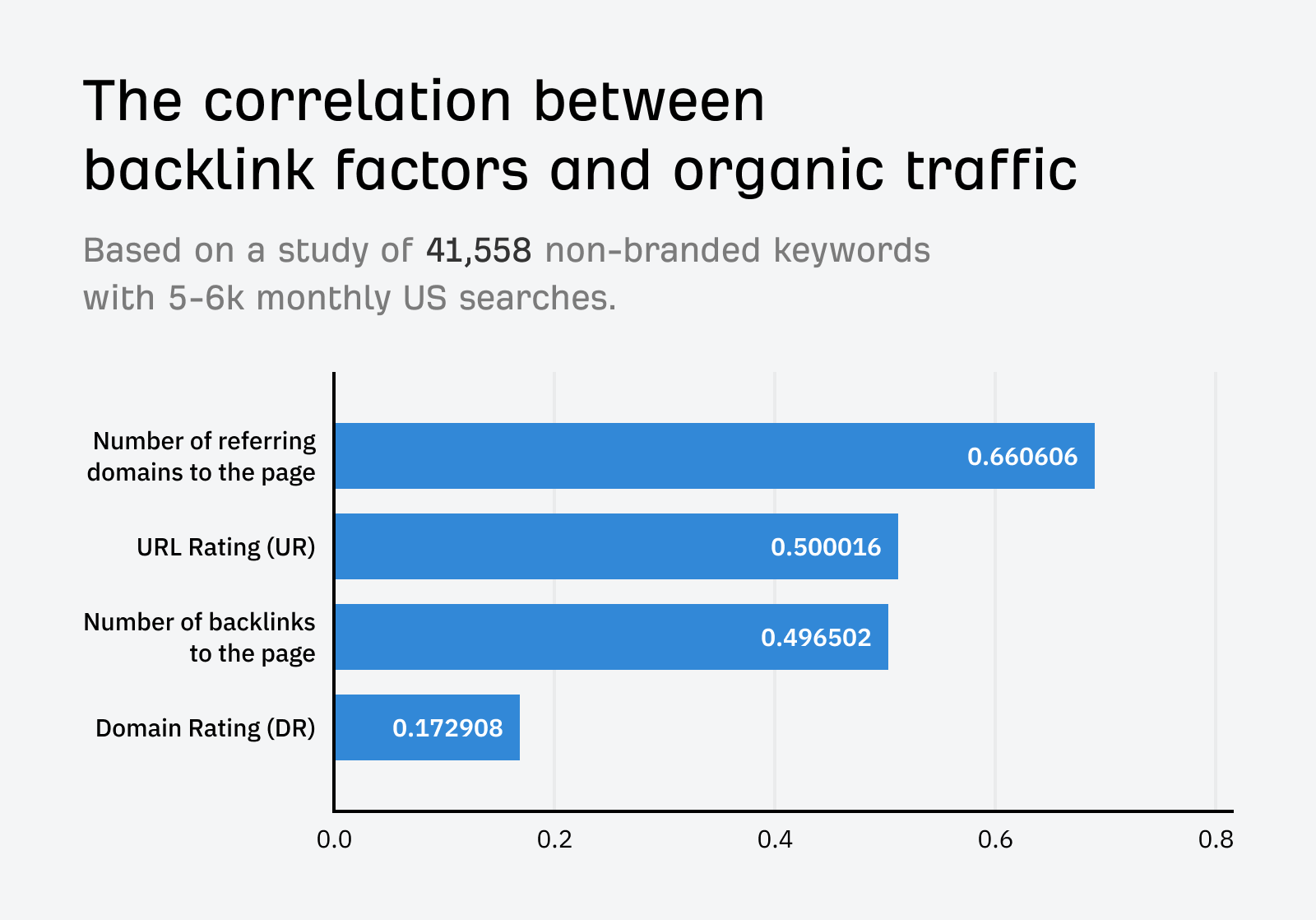
So, is domain authority something you should ignore, then? Definitely not. A higher DR means a stronger link profile. You can then compete for keywords with more authoritative pages. Find out more about domain authority, aka domain rating, in this guide.
Relevance
Google is said to consider a website’s main topic when evaluating backlinks. They used to state this in How Search Works back in 2021 (bolding mine):
If other prominent websites on the subject link to the page, that’s a good sign that the information is of high quality.
Also, a few more documents mention evaluating the topical relevance of backlinks. These are Google’s Reasonable Surfer patent and research on topic-sensitive PageRank.
Also, Google supposedly reduced the effect of irrelevant backlinks in the Penguin update.
So, with all else equal, backlinks from related sites may matter more. For example, a plumber has backlinks from two pages: one about cats and one about installing boilers. Chances are the latter link is most valuable.
Anchor text
Anchor text refers to the clickable words that form a backlink. Here’s what an anchor text looks like:

Google says that anchor text influences rankings in its original patent (bolding mine):
Google uses several techniques to improve search quality. These include page rank, anchor text, and proximity information.
If this sounds too mysterious, here’s a video. Google’s Matt Cutts explains how anchor text helps find relevant pages for “Katy Perry” searches on Google.
You can see the anchor text of any backlink using a backlink analysis tool like Site Explorer.
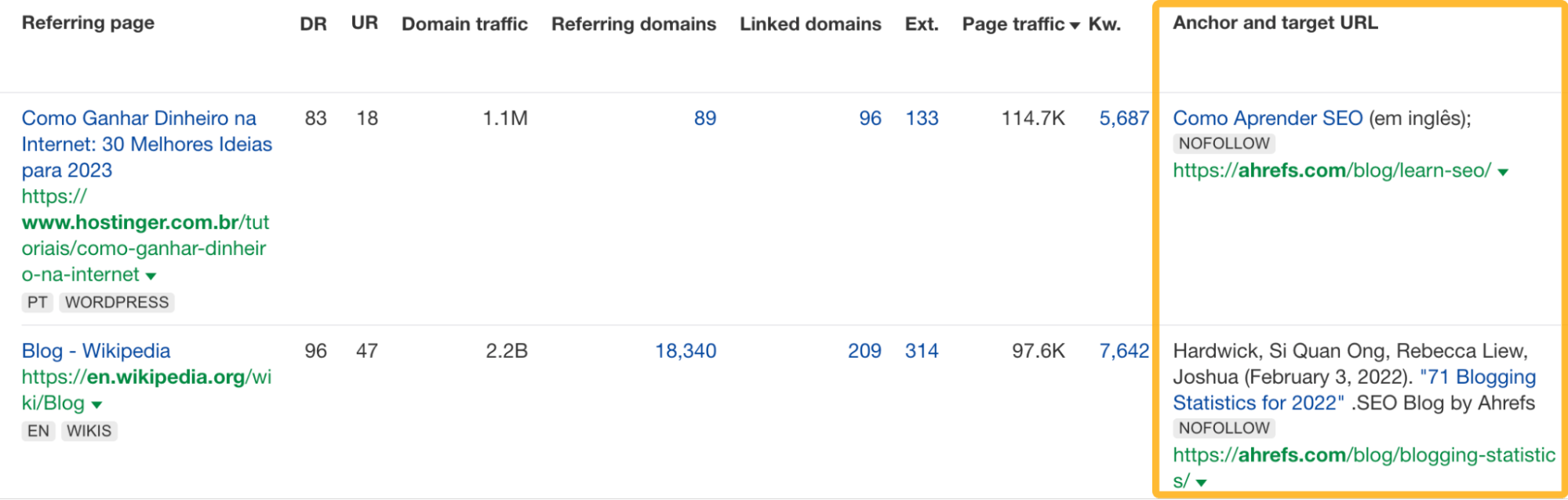
You can also filter for certain words in the anchor text to get more specific results.
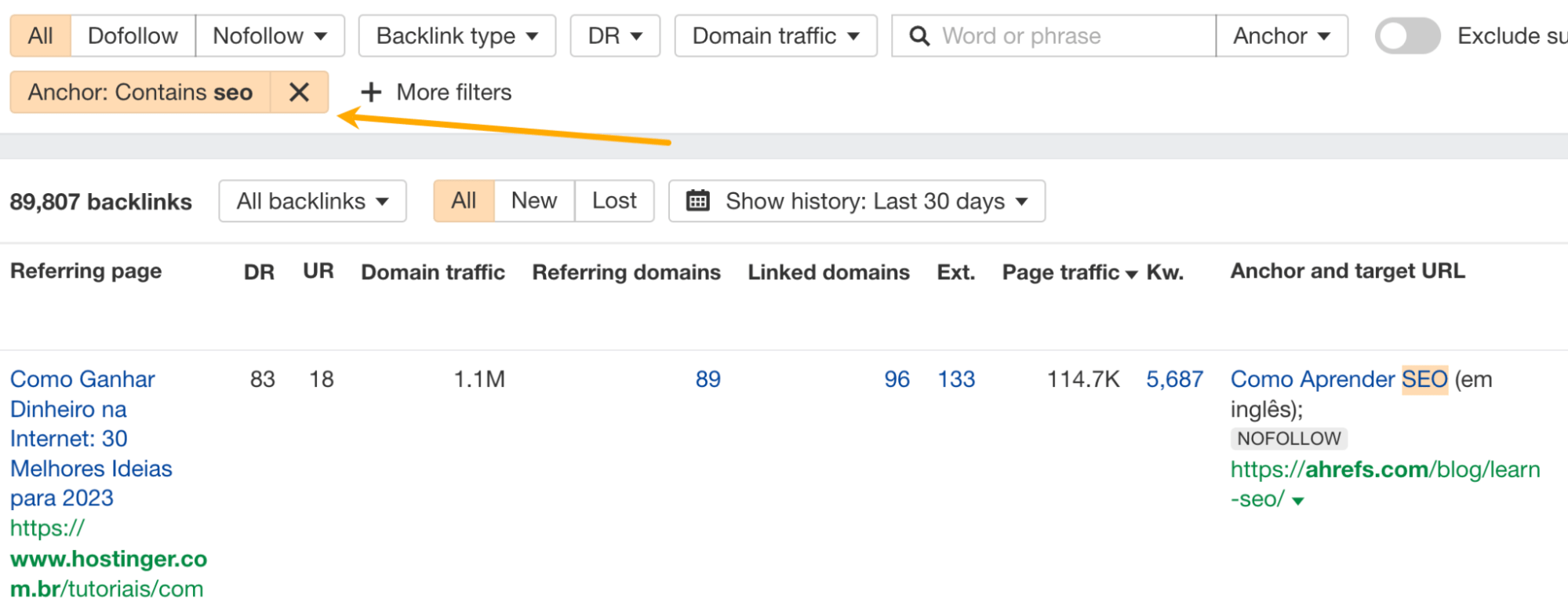
Placement
Some links on web pages likely pass more authority than others. This is because people are more likely to click links that are prominently placed.
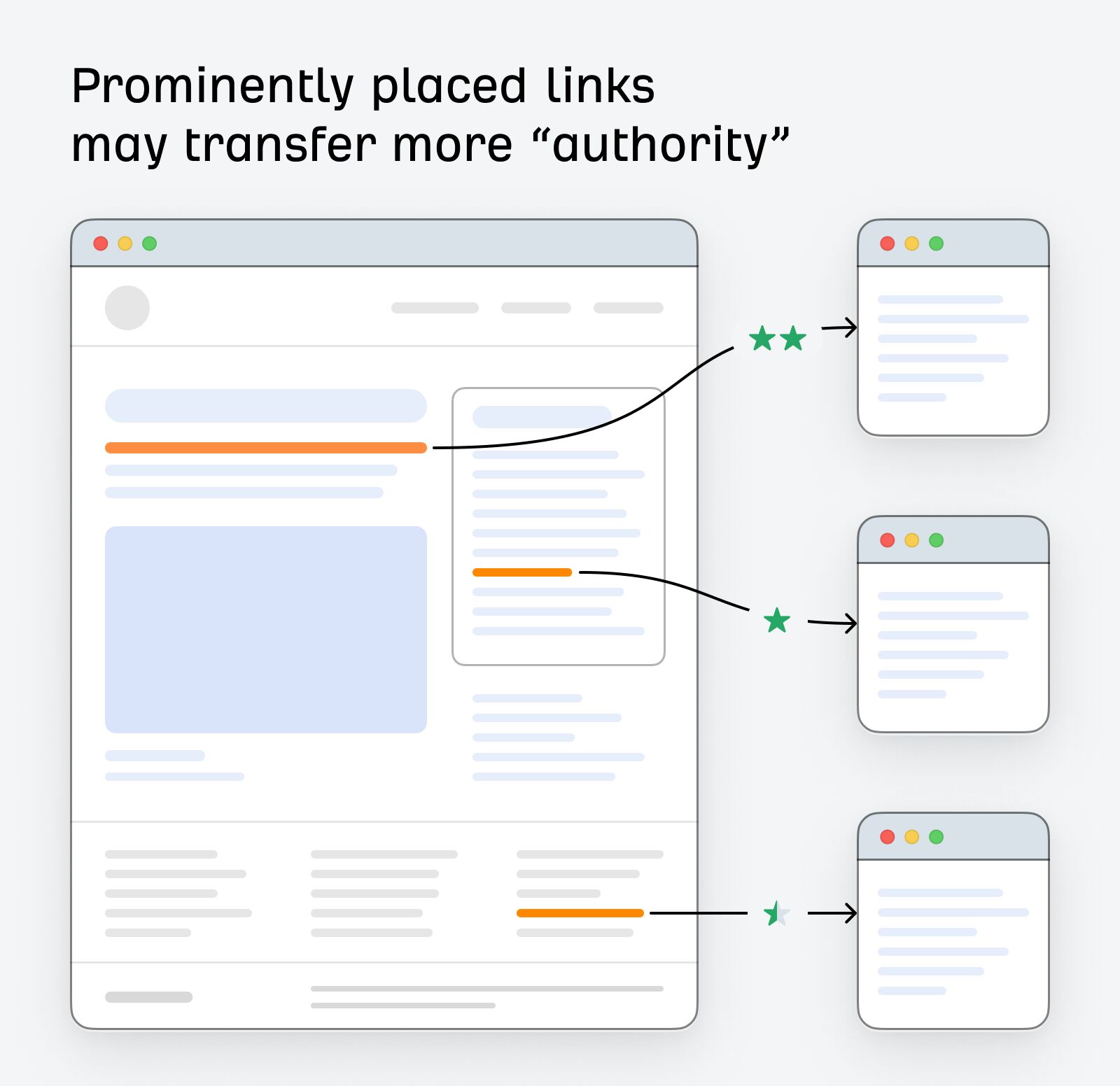
Bill Slawski talks about this in his analysis of Google’s updated “reasonable surfer” patent:
If a link is in the main content area of a page, uses a font and color that might make it stand out, and uses text that may make it something likely that someone might click upon it, then it could pass along a fair amount of PageRank. On the other hand, if it combines features that make it less likely to be clicked upon, such as being in the footer of a page, in the same color text as the rest of the text on that page, and the same font type, and uses anchor text that doesn’t interest people, it may not pass along a lot of PageRank.
Consider this when pursuing links. If a website links to you with many other sites in the sidebar or footer, focus on other opportunities.
To find backlinks in content, use the “Backlink type” filter in the Backlinks report of Site Explorer. It filters out less prominent links.

Follow vs. nofollow links
A nofollow is a link attribute that hints to Google not to pass authority (as of 2019).

Conversely, a followed link lacks the “sponsored” and “UGC” attributes.
Nofollow backlinks usually don’t affect rankings. So, prioritize getting followed links.
That said, “nofollow” is now a hint. So, it may be good to pursue a nofollow link from a relevant, high-authority page.
You can find these types of backlinks using filters in Site Explorer’s Backlinks report.
Destination
Google ranks pages, not websites. So, it’s best to get links to the page you want to rank.
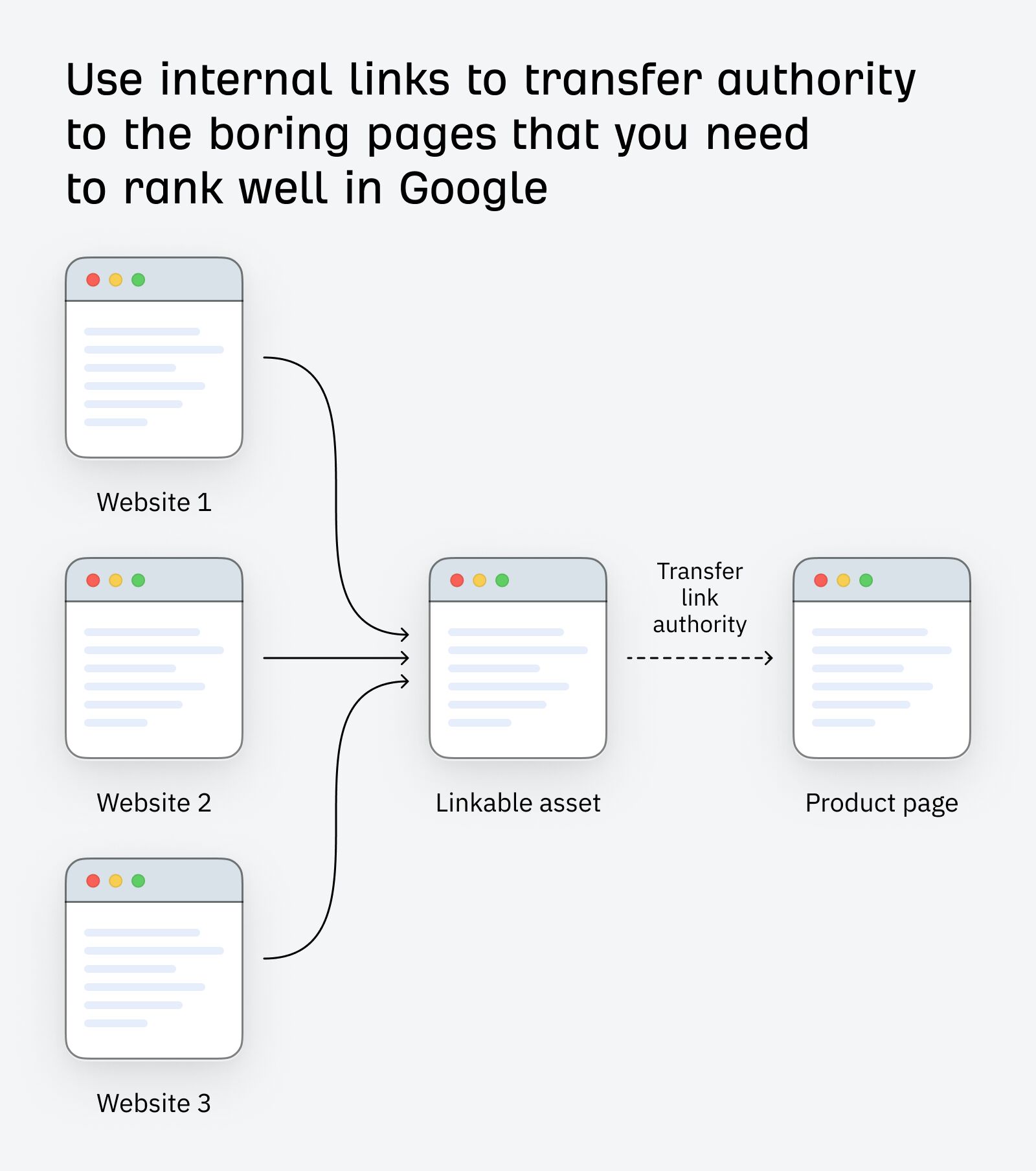
However, getting links to some types of pages is harder. For example, it’s often hard to get links to commercial pages. People prefer to link to informative content.
To fix this, use internal links. They will pass authority from high-link pages to your important but “boring” pages.
If you want to check backlinks to your site quickly, you can do it for free right here:
Below you’ll find other tools that will allow you do learn even more about your and your competitors’ backlinks.
Checking backlinks to your website
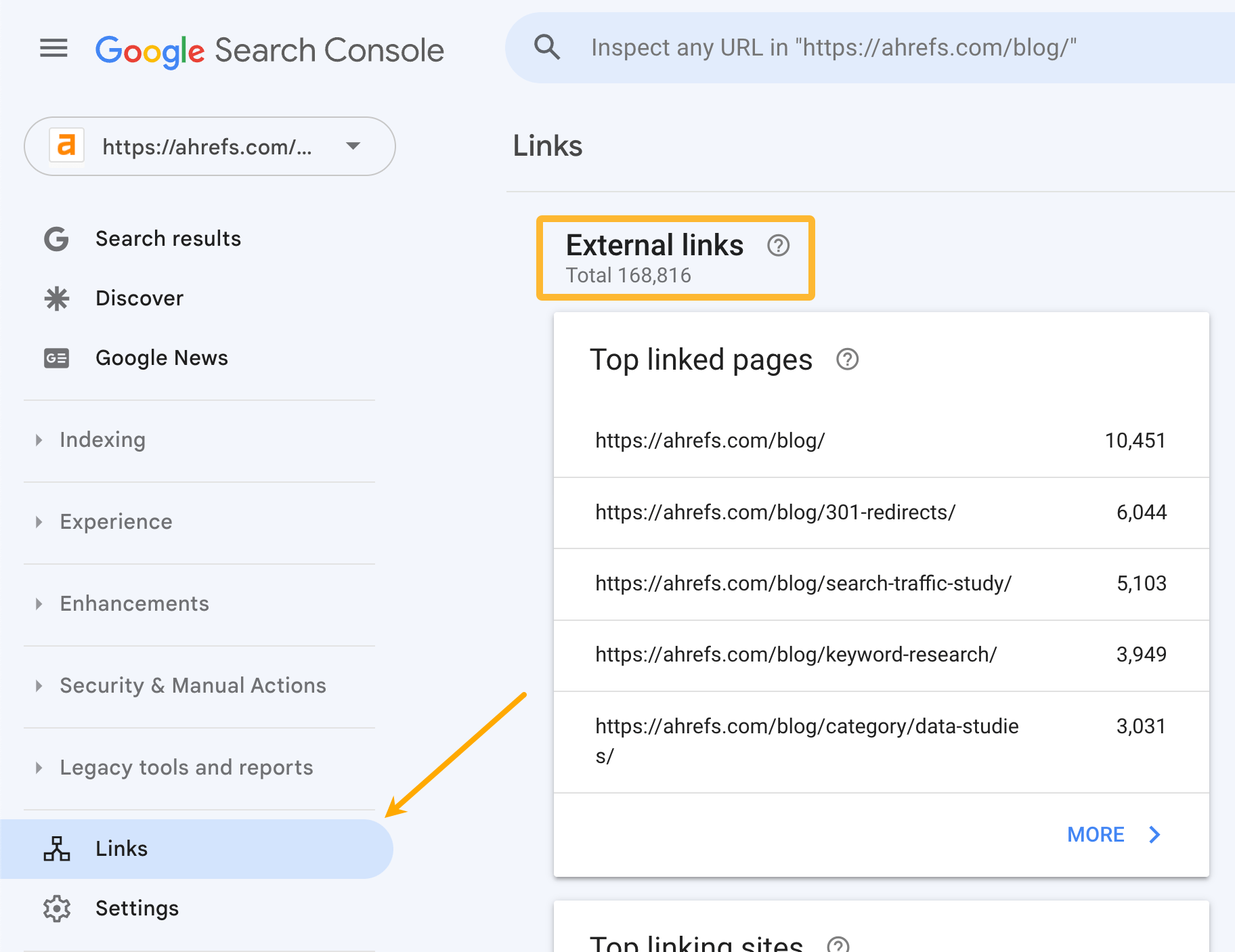
The basic tool for checking your website backlinks is the free Google Search Console.
Once signed in, click Links on the sidebar. The number below External links shows the total unique backlinks to the website.
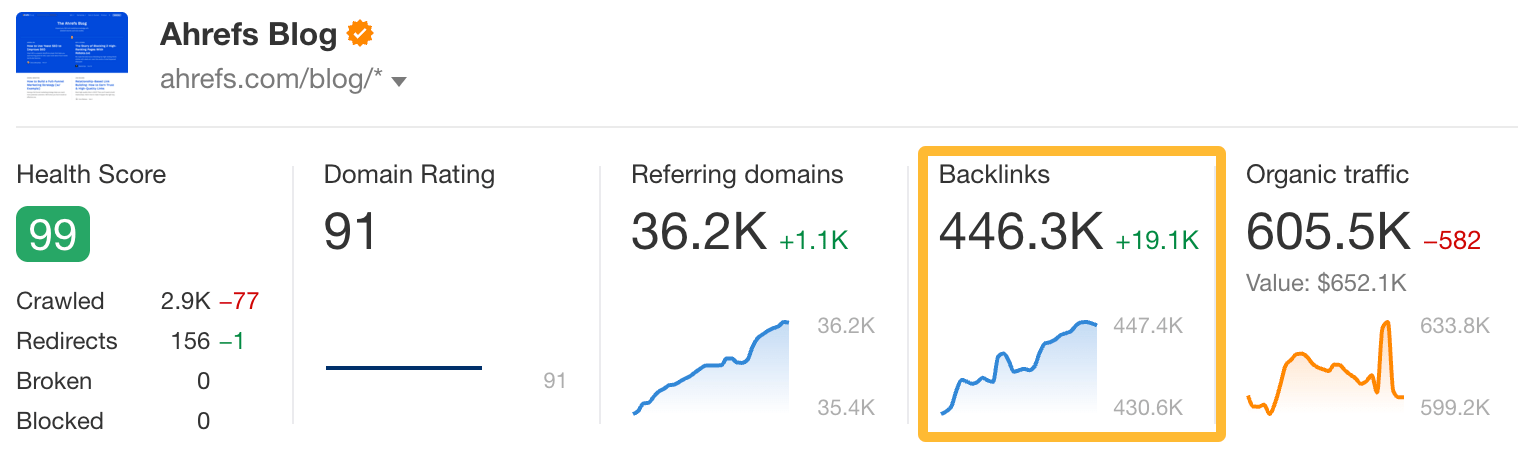
Google Search Console shows limited data in the app (top 1,000 links). It won’t show some useful SEO metrics for analyzing your backlinks. To get more data for free, you can use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools.
Once you set up a project, click on Backlinks in the dashboard.
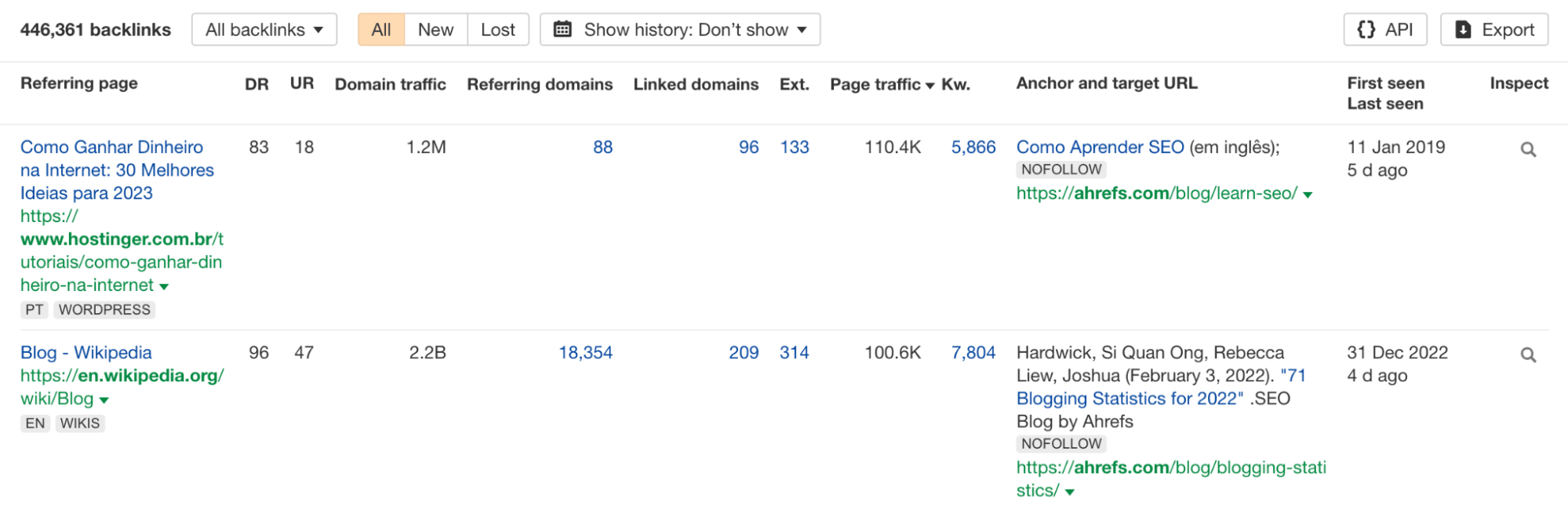
This will take you to the Backlinks report. This report will show all your backlinks and relevant backlink data.
How to check backlinks to your competitors (and any other site)
To see all backlinks, including to your competitors, use a paid tool like Ahrefs’ Site Explorer.
You can check backlinks to the entire website, a directory on that website, or a single page. Just enter the address and choose the correct mode. Ahrefs will usually pick the right mode automatically.
To see all backlinks to Apple.com, a site I don’t own, I could paste the domain in the address bar, hit Search, and go to the Backlinks report.
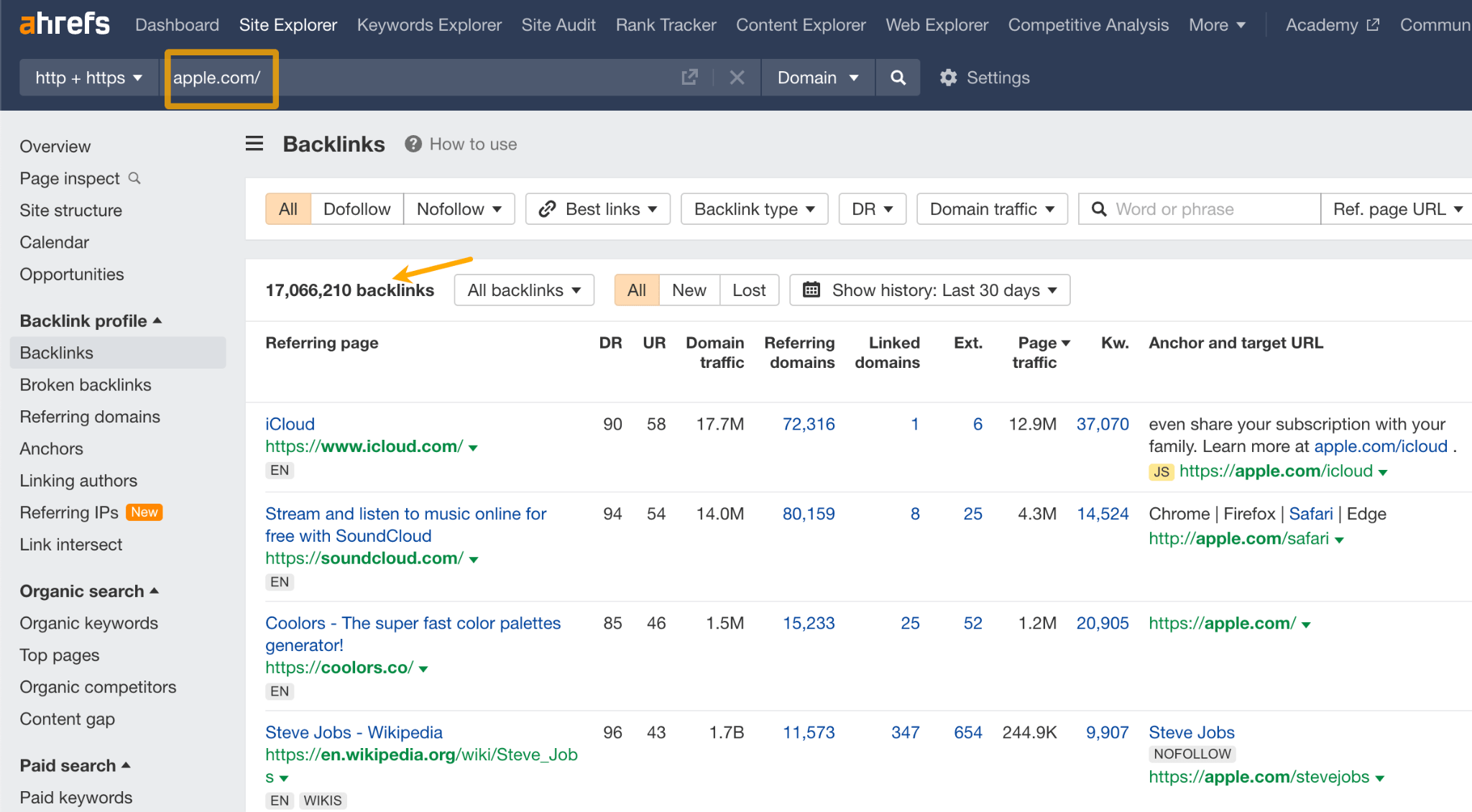
SEO tools like Ahrefs allow you to examine backlinks by giving you access to useful data points. You can use that info to track your link building. Or, find backlinks to pursue. Here are some of the backlink data you should look at:
- Follow status: use it to find links that pass authority. Or, find ones that usually don’t (nofollow or sponsored tags).
- Type of backlink: use to find links in the main content of the page.
- Domain rating: an indicator of a linking website’s authority.
- Domain traffic: high-traffic sites typically have more authority with search engines. Moreover, you may get some of that traffic if people click on the link to your site.
- Words or phrases related to backlinks: they will help you if you search for specific words in the link’s anchor text or its surrounding text.
Of course, you can filter through this data to find the kind of backlink you’re looking for: 
Let’s look at an example. Here’s how you can find and analyze your competitors’ best links.
First, you can let the tool find your organic competitors. These are sites that compete with you for the same keywords. This will uncover a comprehensive list of competitors, some of which you might not have been aware of previously.
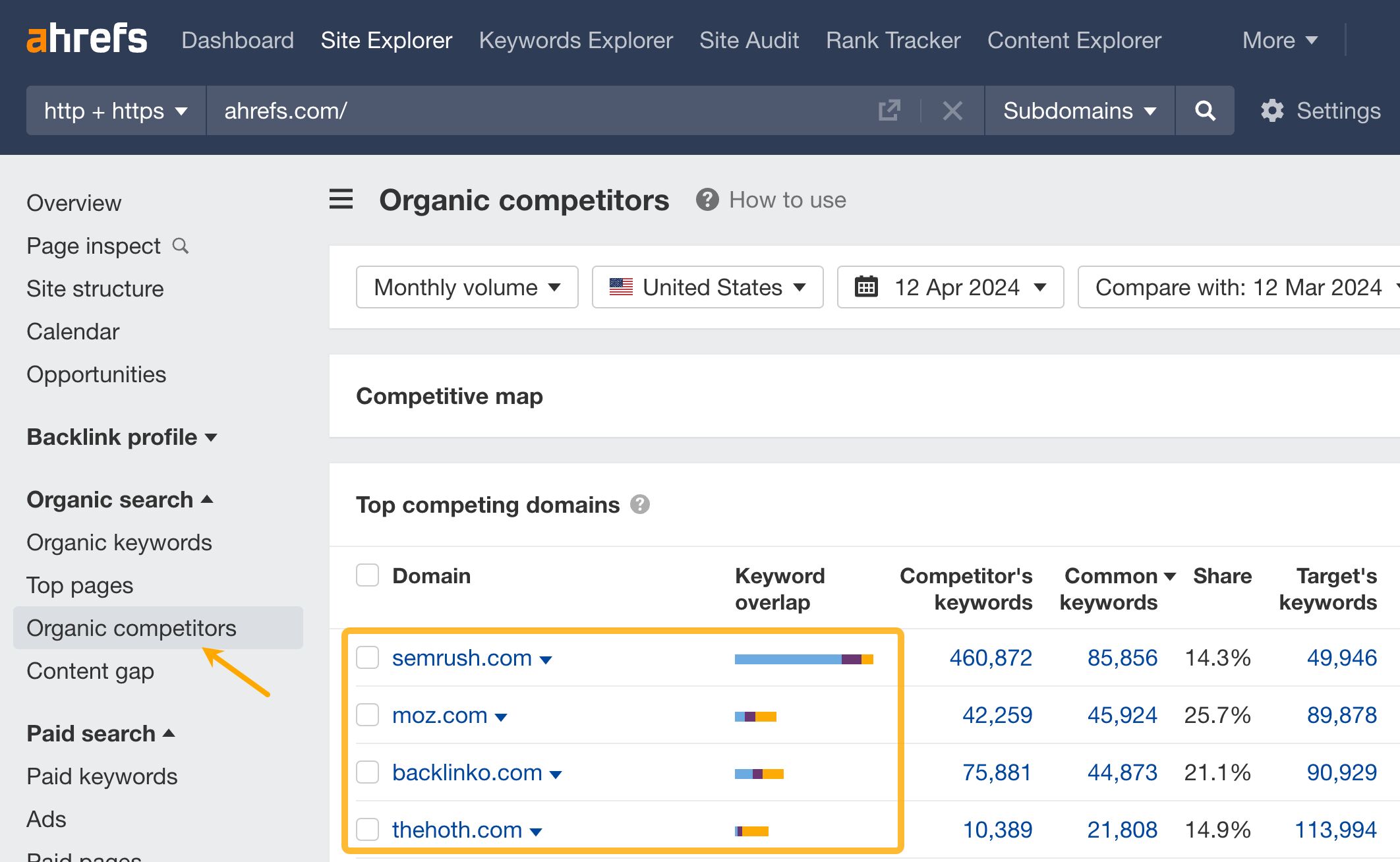
Now, click on the caret next to your competitor’s domain to view all of their backlinks in the Backlinks report.
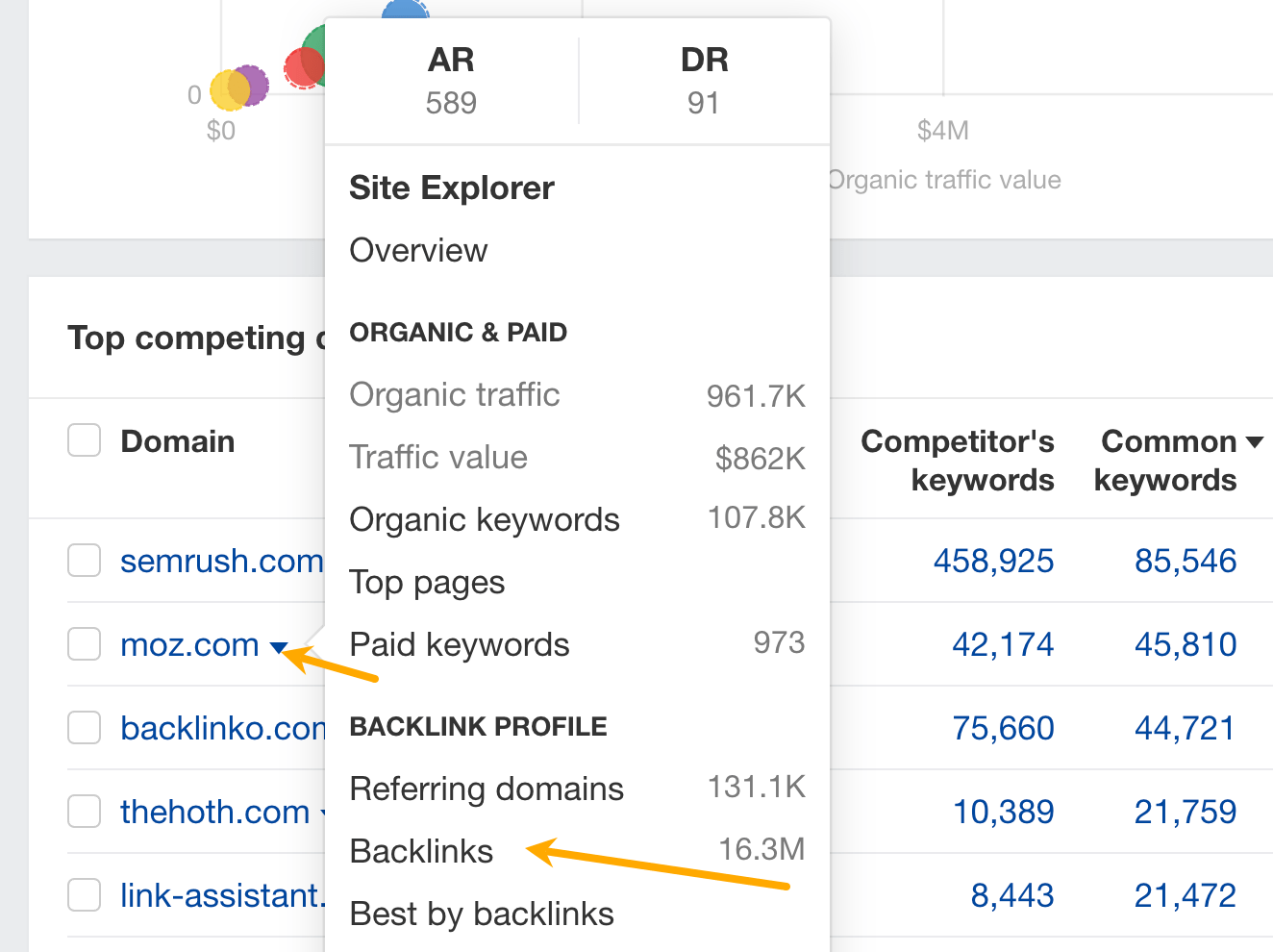
Next, turn on the Best links filter to show only links that likely have the biggest impact on your competitor’s performance.
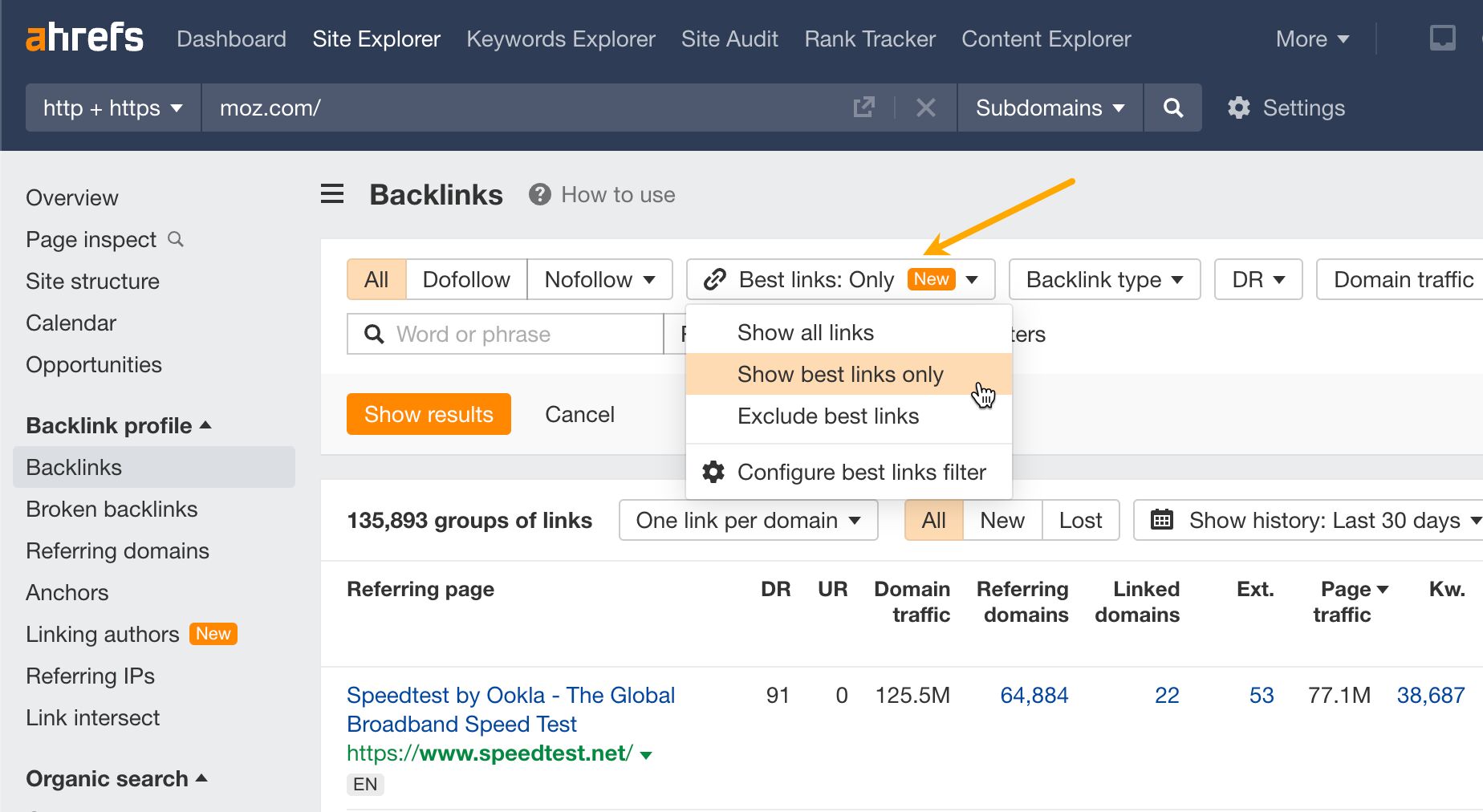
For example, a competitor earned a link from Microsoft via a page with original research. The page has 2016 data. If we published newer research on our site, we might win that link and others pointing to our competitor’s research.
There are a few other ways you can analyze backlinks.
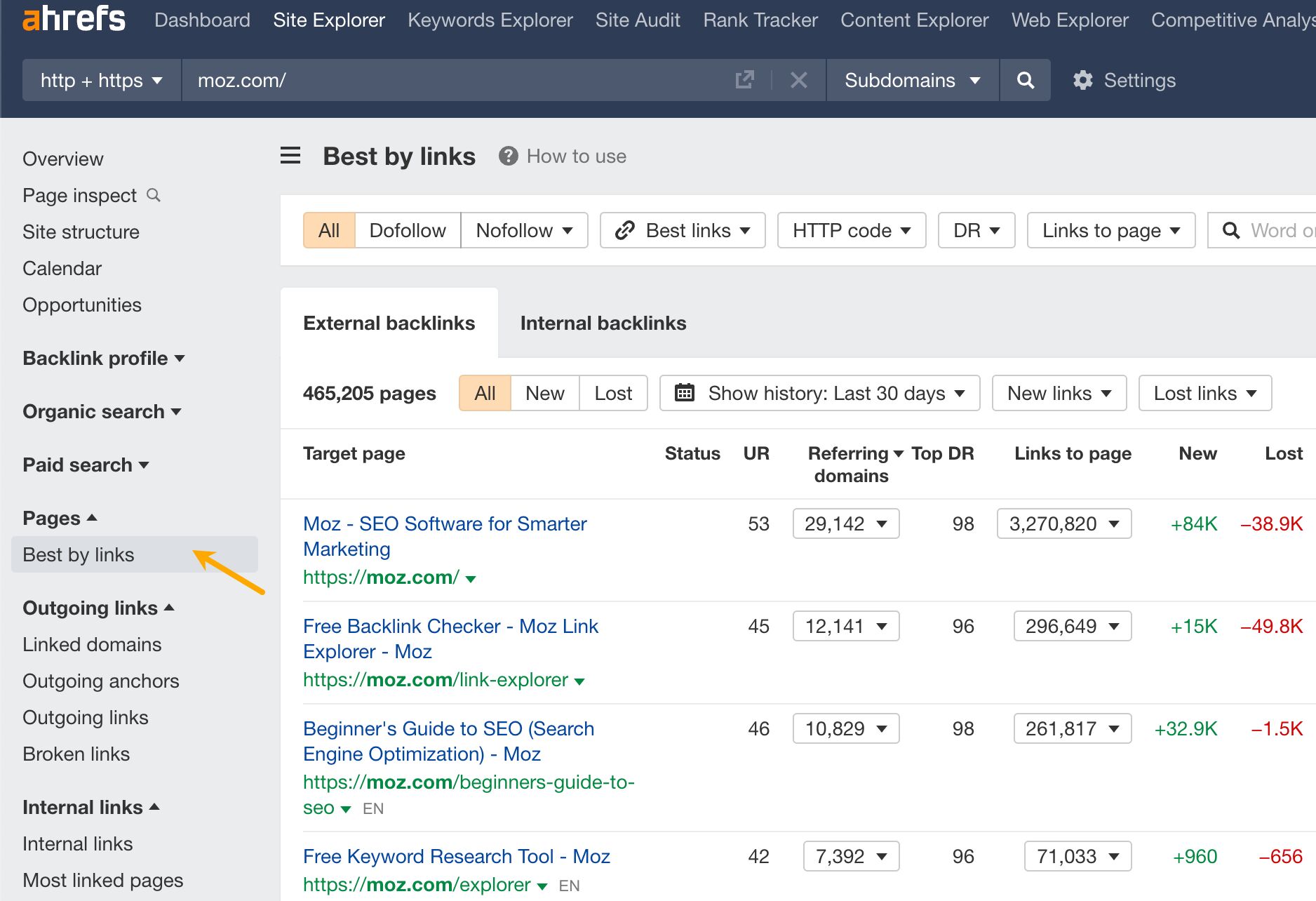
To discover the type of content that attracts the most links to your competitors, simply use the Best by links report.
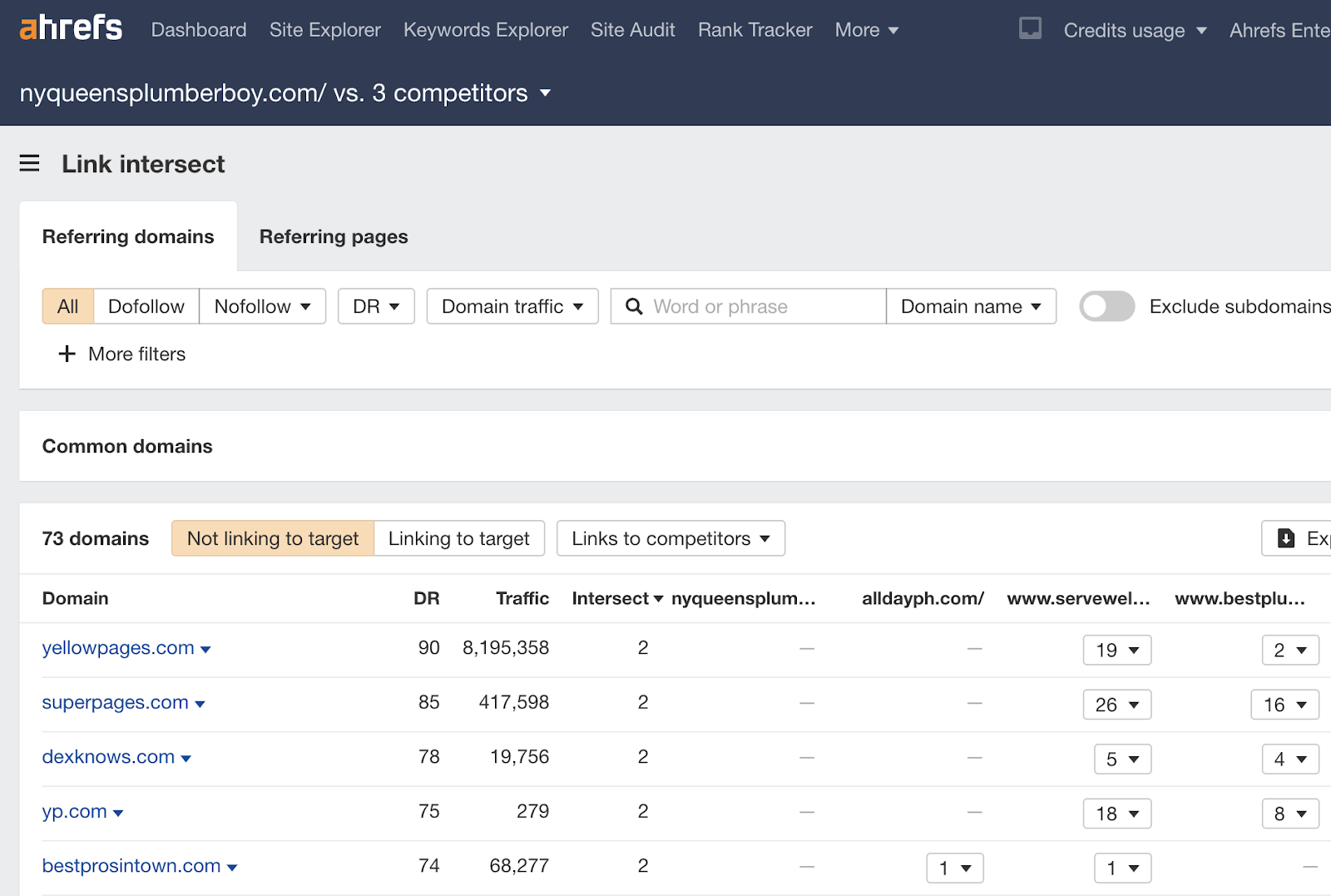
Another useful type of backlink analysis is the link intersect. This analysis checks backlinks to multiple domains at once. It shows shared backlinks, which is great for finding listicles to link from. It also shows domains that link to your competitors but not to you. Links from unlinked domains are likely to have a bigger impact.
To enter the report, select a few competitors from the Organic competitors report and click Open in Link intersect.
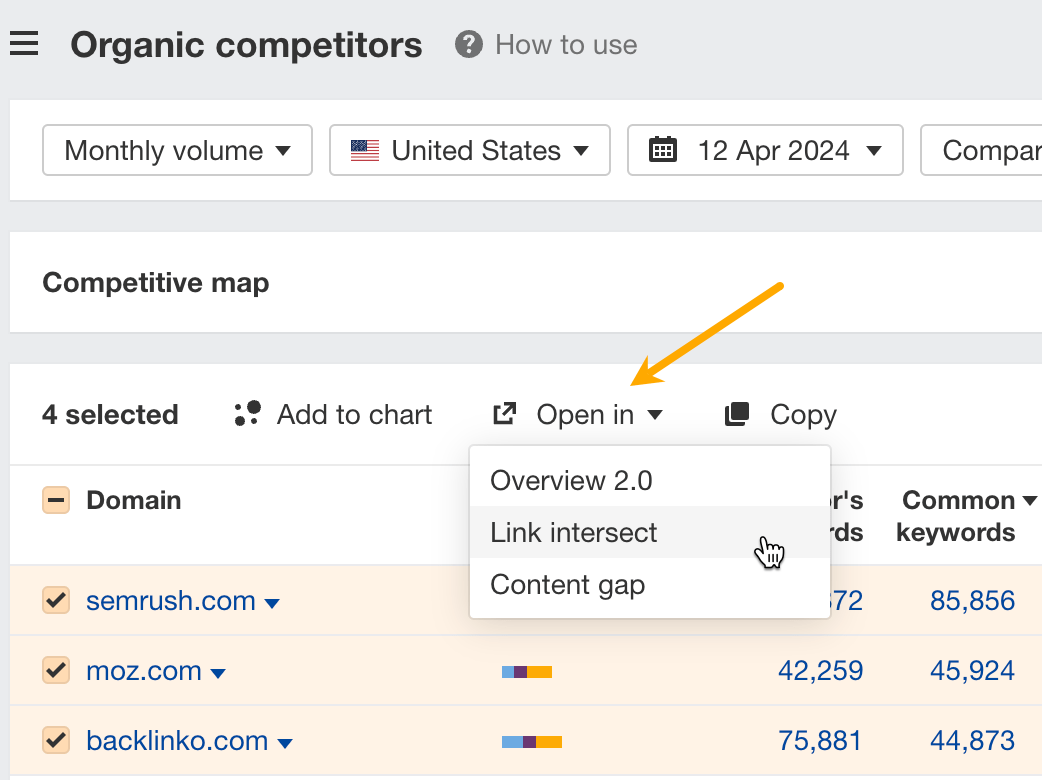
This will open the Competitive Analysis tool and show the gap in backlinks between you and your competitors.
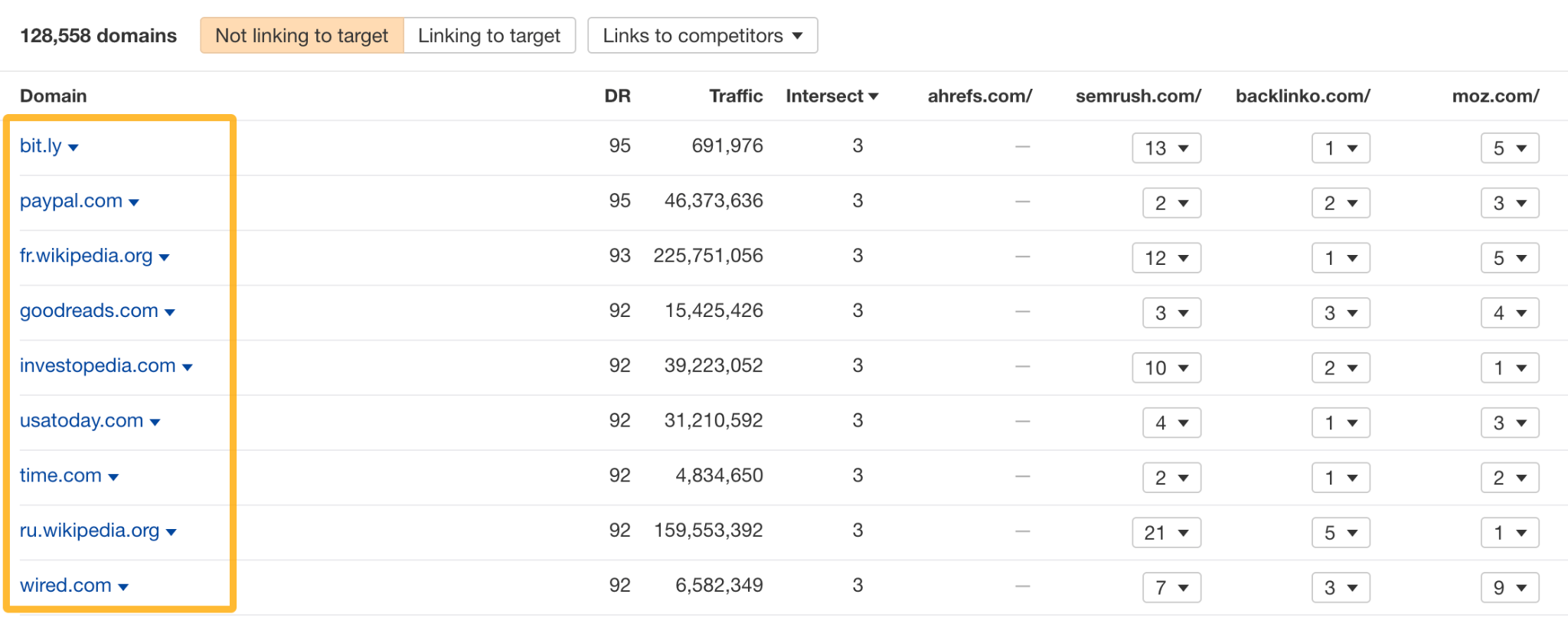
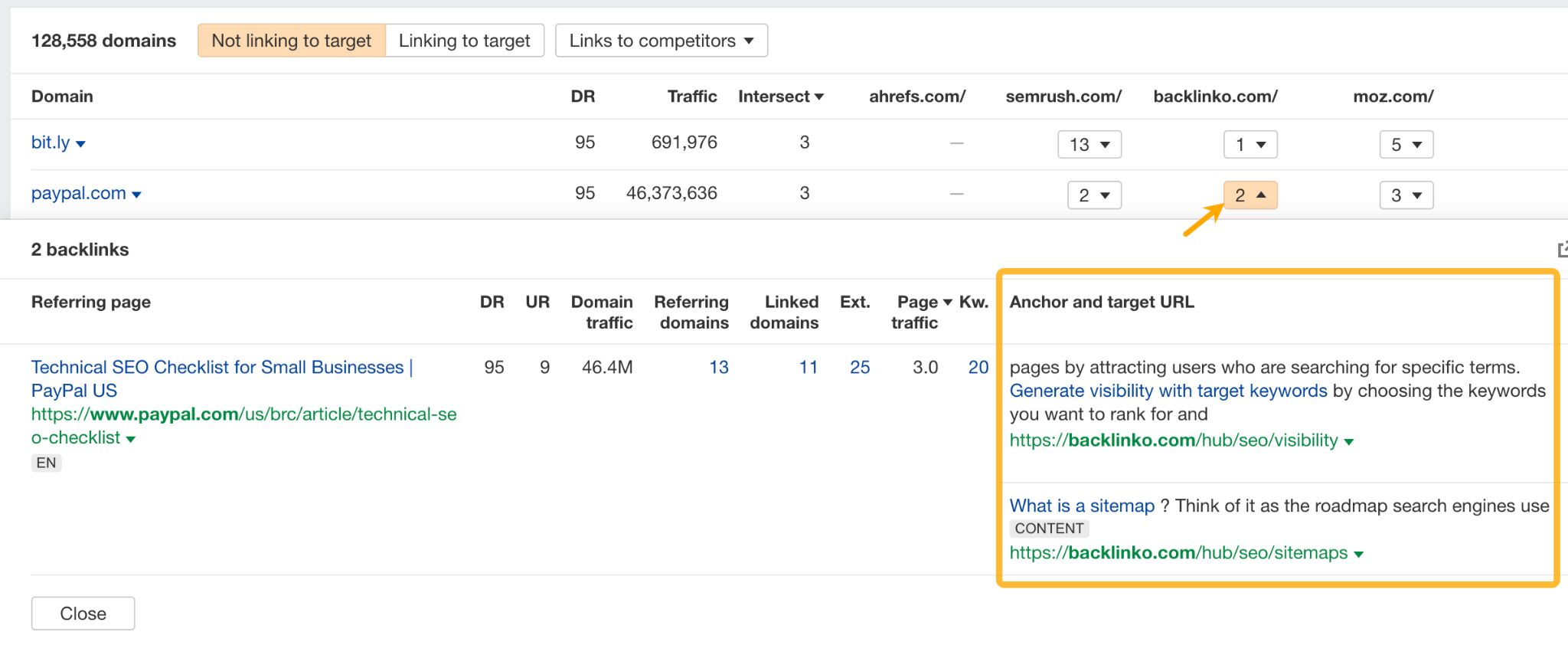
From there, you can click on the number of links to your competitors to see which pages earned the backlinks. This will show you what kind you need to get those missing links.
You can find more tips about competitive backlink analysis in these two guides:
- How to Perform a Competitor Link Analysis in 3 Steps
- How to Find Your Competitors’ Backlinks (And Get Them for Yourself)
Generally, there are four ways to build backlinks to your site:
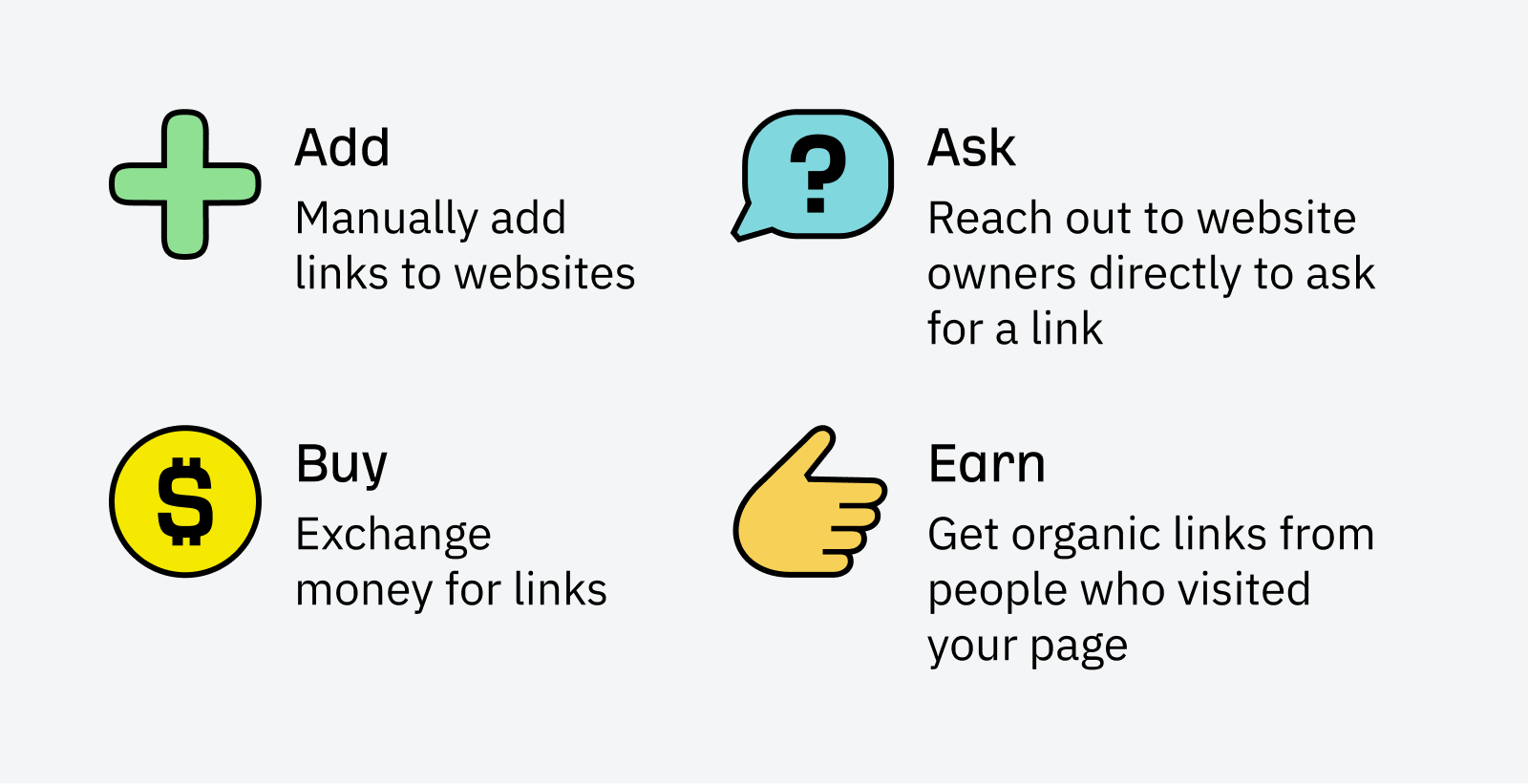
Adding backlinks
Some websites allow you to add a link either by manually submitting it or requesting to submit it. It’s easy to get a link this way, but it’s not always worth it. They can be low in value in the eyes of Google or even deemed spammy if you overdo it.
One of the most common (and legit) tactics here is to add your website to relevant local directories. These directories can help you rank for queries with local intent and get your business discovered directly through them, too.
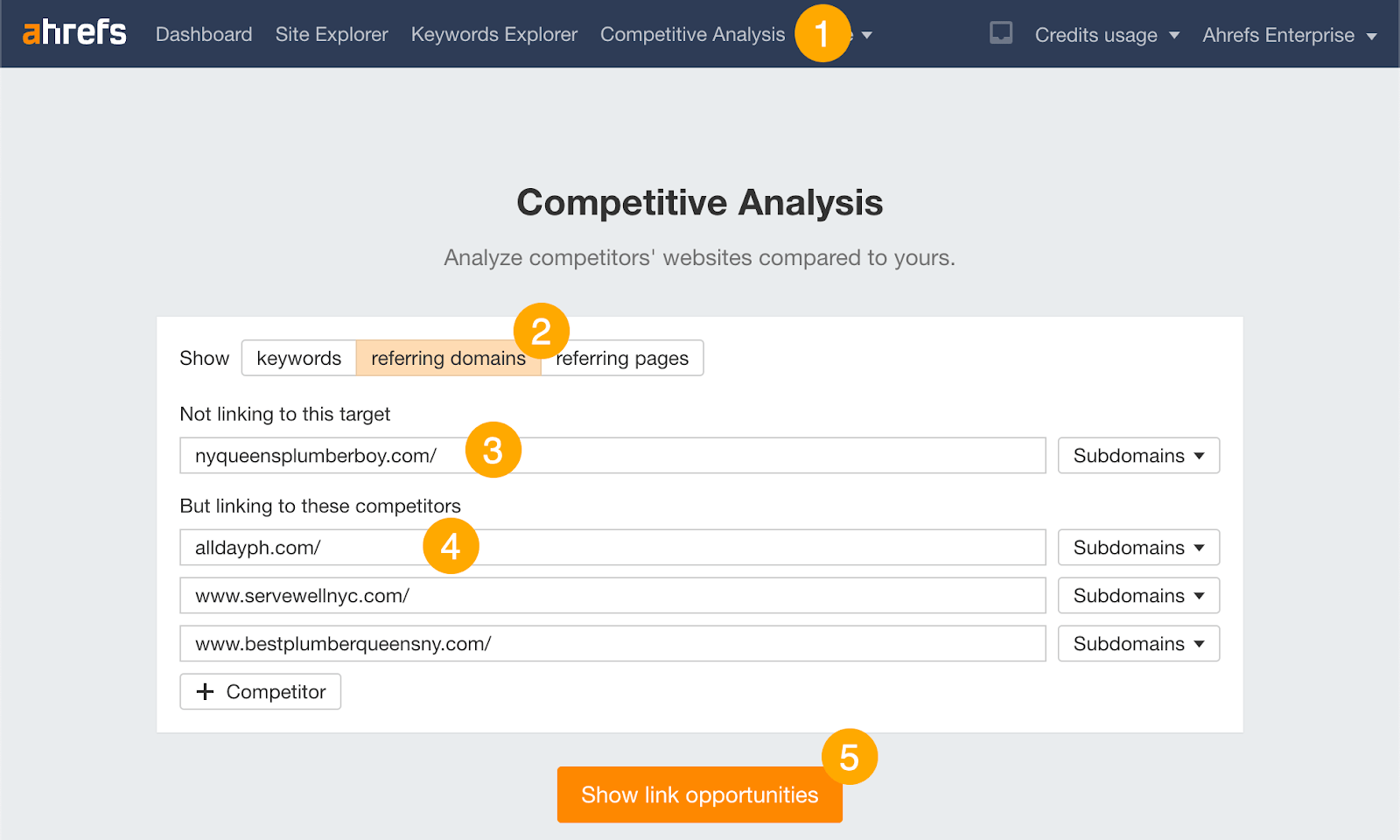
For example, you could do a link intersect analysis to find directories that rank to your competitors but not to you. Here’s how the process would look like in Ahrefs.
- Go to Ahrefs’ Competitive Analysis tool.
- Select the “referring domains” mode.
- Enter your site in the “Not linking to target” field.
- Enter the sites of a few competing businesses in the “But linking to these competitors” fields.
- Hit “Show link opportunities”.
The final step is to browse the results for relevant directories and add your site to them.
Asking for backlinks
This is when you reach out to other site owners, editors, or webmasters and ask them to link to your page. For this to work, you need to have a clear and compelling reason for them to link to you.
That’s where link building tactics come in. Here are a few tried and tested ones:
- Guest blogging. Offer to write a blog post for another website.
- Broken link building. Find relevant dead links on other sites, then reach out and suggest your working link as the replacement. (You can use our broken link checker).
- The skyscraper technique. Find relevant content with lots of links, make something better, then ask those linking to the original to link to you instead. Often used to pursue competitors’ backlinks.
- Unlinked mentions. Find unlinked mentions of your brand, then ask the author to make the mention clickable.
For example, here’s the process of finding guest blogging prospects in a nutshell.
- Go to Content Explorer.
- Enter a related topic and change the dropdown to In title.
- Filter for English results.
- Filter for results with 500+ words.
- Go to the Websites tab.
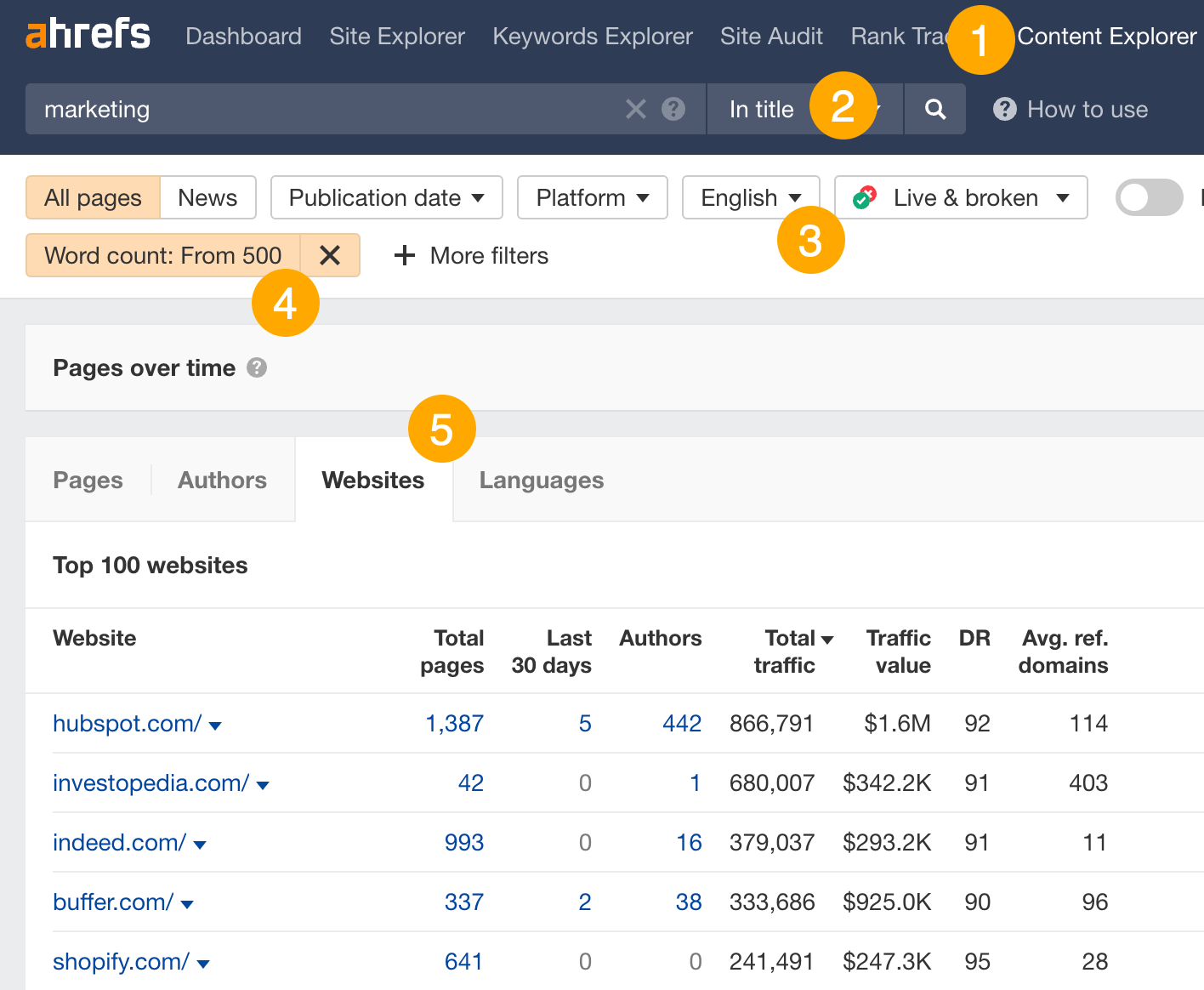
This shows you the websites getting the most search traffic to content about your target topic.
From here, look at the Authors tab and find sites with multiple authors, as this suggests that they may accept guest posts.
The final step is outreach — a message to the person in charge with a pitch of your article idea, typically sent via email or LinkedIn. The message can look something like this:
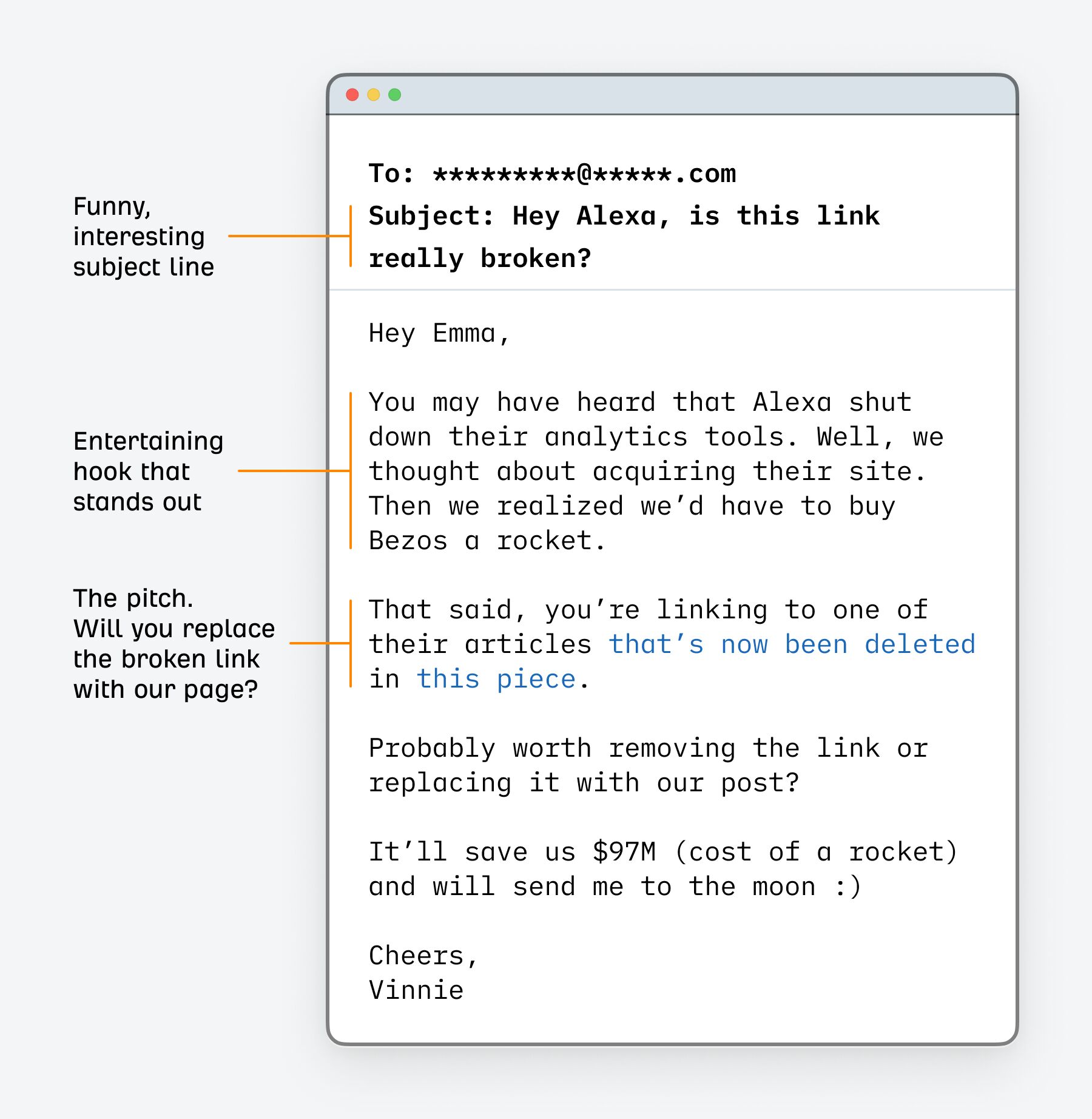
If you have only a few link prospects, invest some time to make a fully personalized message. If you have a large contact list, use a scalable method. Use a template with a few personal touches (the scoped shotgun approach).
Buying backlinks
Every now and then, you’ll come across an offer to buy links — don’t take it.
Buying backlinks is extremely risky. You can get your site penalized because Google is strongly against it.
This is not to be confused with paid link building services. Good link building agencies use legit, white-hat tactics that have nothing to do with spam or buying links for that matter.
Earning backlinks
Backlinks are earned organically when people find your content. They link to your page because they believe it has value for their audience.
You can increase your chances of earning backlinks by creating genuinely valuable content that people want to link to. “Link bait” is content made to attract backlinks. It’s so useful that bloggers and journalists want to link to it.
Links are more likely if you use: calculators, guides, and opinionated takes. Also, use emotional stories, appealing visuals, news articles, and engaging narratives.
But honestly, there is no one type of effective link bait — it all depends on your creativity. On the one side of the spectrum, you have meticulous data studies with high educational value like our study of pages that get no traffic from Google.
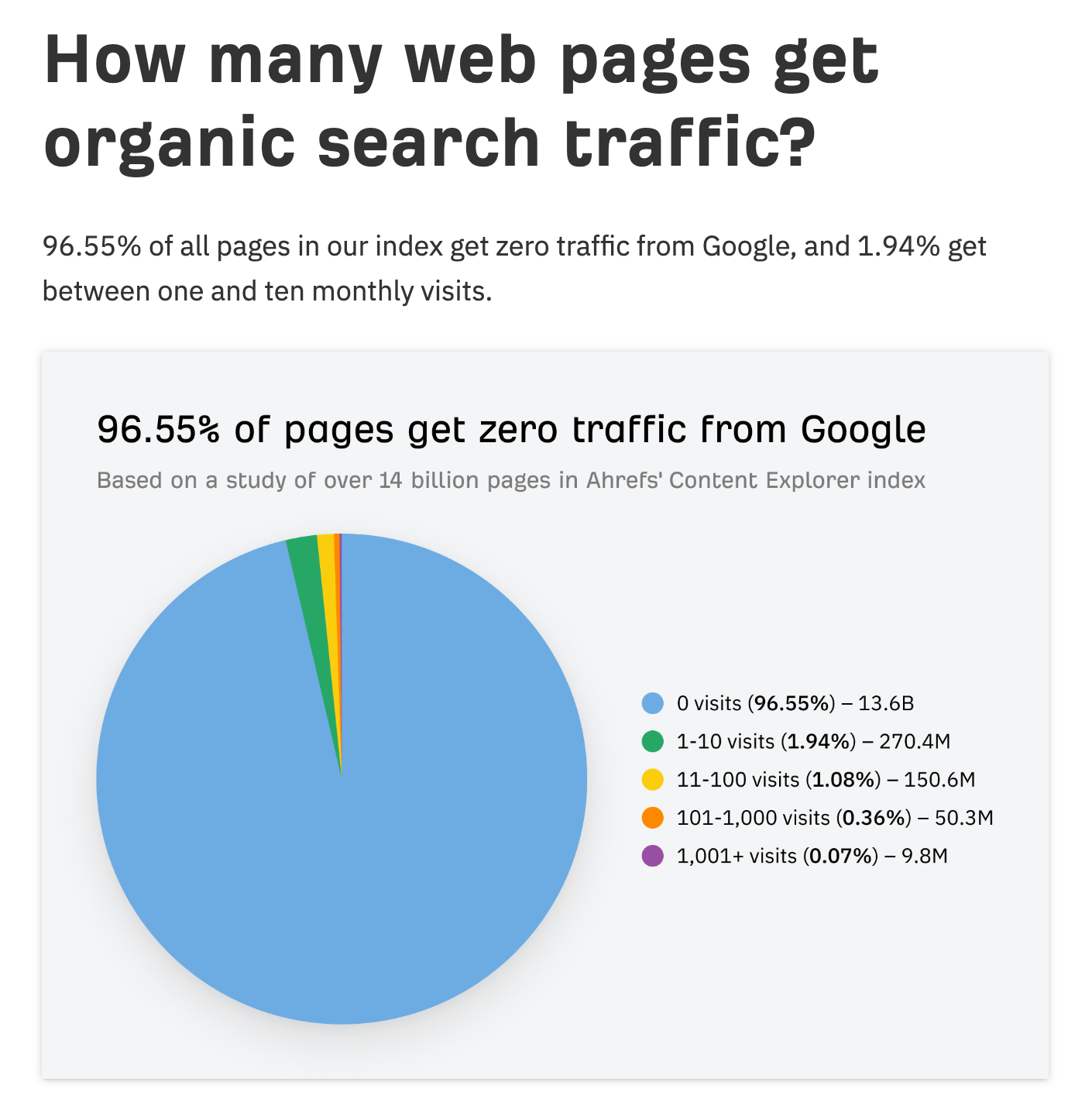
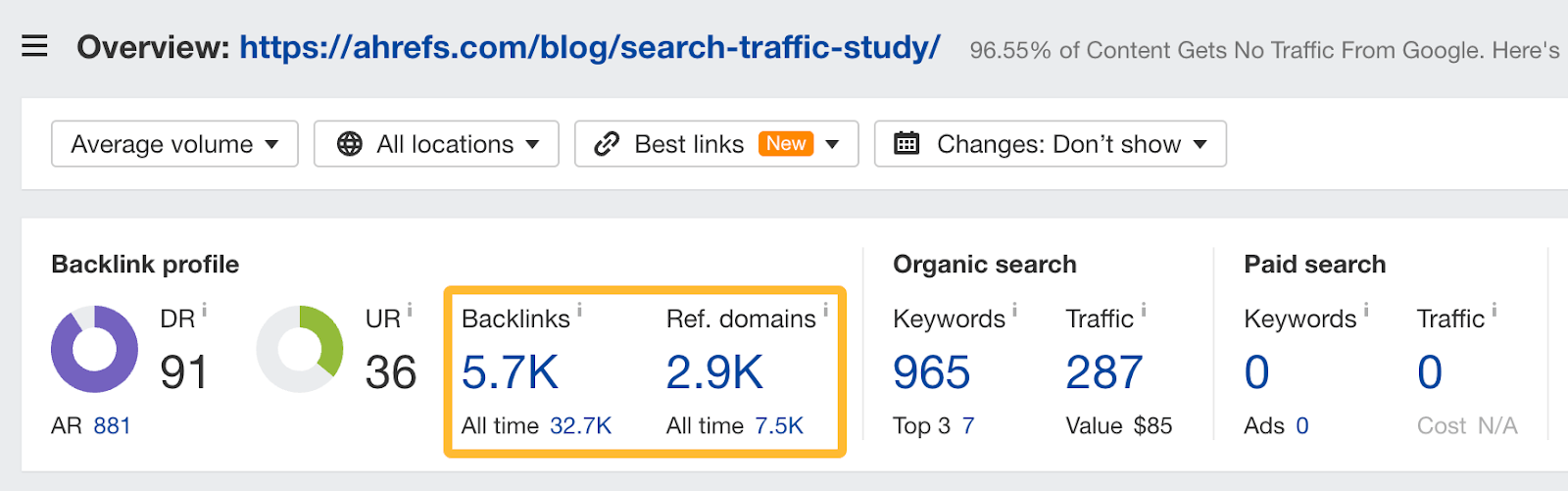
This study earned 5.7k backlinks from 2.9k unique referring domains.
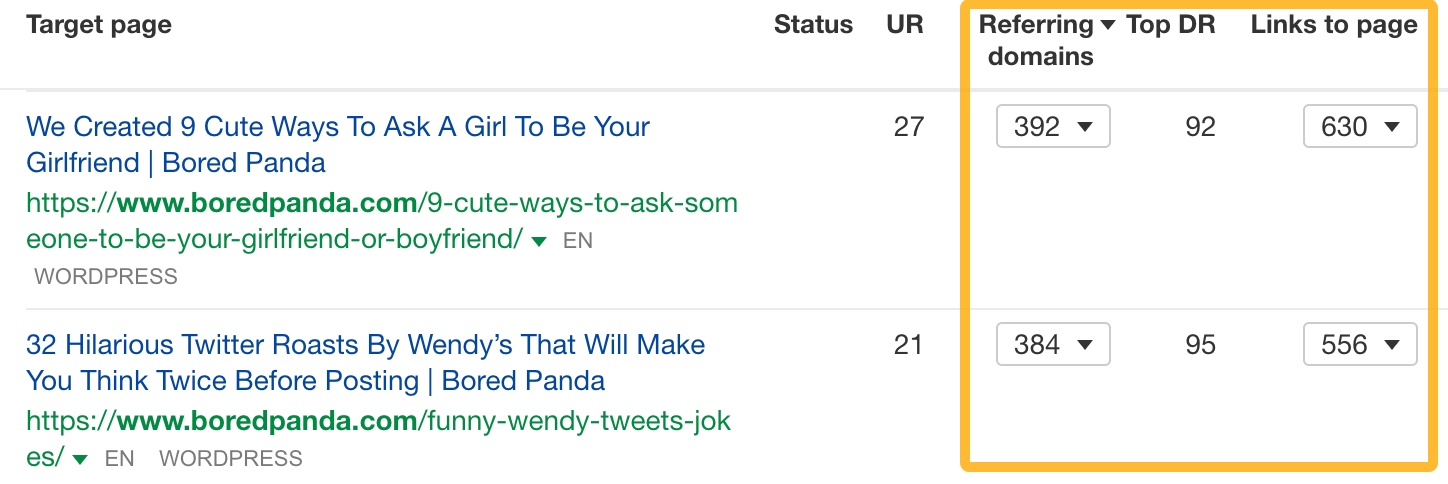
On the other hand, you have link bait created mostly for entertainment. Take a site like Bored Panda or Upworthy and run it through Ahrefs to see what topics earn hundreds of links.
Over the years, I’ve seen various forms of successful link bait content, and they were at least one of those things:
- Practical: provided immediate utility, like tools, guides, and templates.
- Opinionated: had a strong, unique viewpoint or a fresh take on a common issue.
- Emotional: used stories, humor, or controversy to spark feelings. This aimed to connect on a human level and encourage sharing.
- Visual: used eye-catching infographics or videos.
- Newsworthy: leveraged current events or trending topics by adding value to ongoing conversations.
- Storied: utilized storytelling to make abstract or dry topics more relatable and engaging.
Just as you will come across high-quality backlinks, you will definitely see some links that are best avoided.
At best, links like that won’t have any impact on your rankings. At worst, they may make your pages rank lower on Google or even not appear at all.

Here are some types of links you should definitely avoid:
- PBNs: multiple sites linking together in order to manipulate search engines.
- Paid links: exchanging money, goods, or services in return for links.
- Link exchanges: linking to a site in exchange for that site also linking to yours.
- Automated links: use of automated software or services to generate large volumes of links to a site.
- Forum and comment spam links: adding spam links in forums.
You should also avoid link building overoptimization. This is when your link profile (all backlinks to your site) has too many links with anchor text that matches your target keyword. Google might see this as a link manipulation attempt. A “natural” link profile has a mix of anchor texts.
For example, if 90% of the backlinks to this article had the anchor “what are backlinks,” it would likely raise a red flag for Google.
Let’s wrap this up with a quick cheat sheet of backlink types and their impact on SEO. Keep in mind, this is a generalization. Use it as a rule of thumb for spotting good and bad backlinks. But, always check each one against the six traits of a good backlink discussed earlier.
- Editorial backlinks: achieved by being cited as an authoritative source within content. High-authority sites’ links boost SEO and can drive referral traffic.
- Guest blogging backlinks: come from writing on sites you don’t own. They benefit both parties with quality backlinks and content.
- Relationship-based backlinks: come from nurturing ties with writers or site owners who’ve linked to you before. They’re built over time and can be highly rewarding.
- Backlinks in business profiles: Creating profiles on reputable business listing sites can establish your site as a credible entity in your field.
- Backlinks from public speaking: Speaking at events can earn backlinks from the websites of the event organizers. This shows your expertise and authority.
- Embedded asset links: these include tools, widgets, awards, and badges embedded on other sites, linking back to yours. It’s a creative way to gain continuous backlinks with minimal effort.
- Link schemes (avoid): any unnatural links designed to manipulate search rankings can lead to penalties. This includes buying links, excessive link exchanges, and using private blog networks (PBNs).
- Automated links (avoid): they’re generated by software and often part of black hat SEO. They can harm your site’s credibility.
- Low-quality or irrelevant directory links (avoid): search engines view mass business profile creation on low-quality directories as spammy.
- Low-quality forum backlinks (avoid): spamming forums for backlinks is ineffective. It can also harm your SEO.
Frequently asked questions about backlinks.
How many backlinks do you need to rank?
There is no set number of backlinks needed for ranking. There is no “sweet spot” for backlinks, either.
The number of backlinks needed to rank can vary. It depends on the competition and the quality of the backlinks.
Use tools like Ahrefs’ keyword difficulty to gauge the backlinks needed to rank in the top 10.
For instance, to rank in the top 10 for “tea,” you need about 756 unique backlinks.
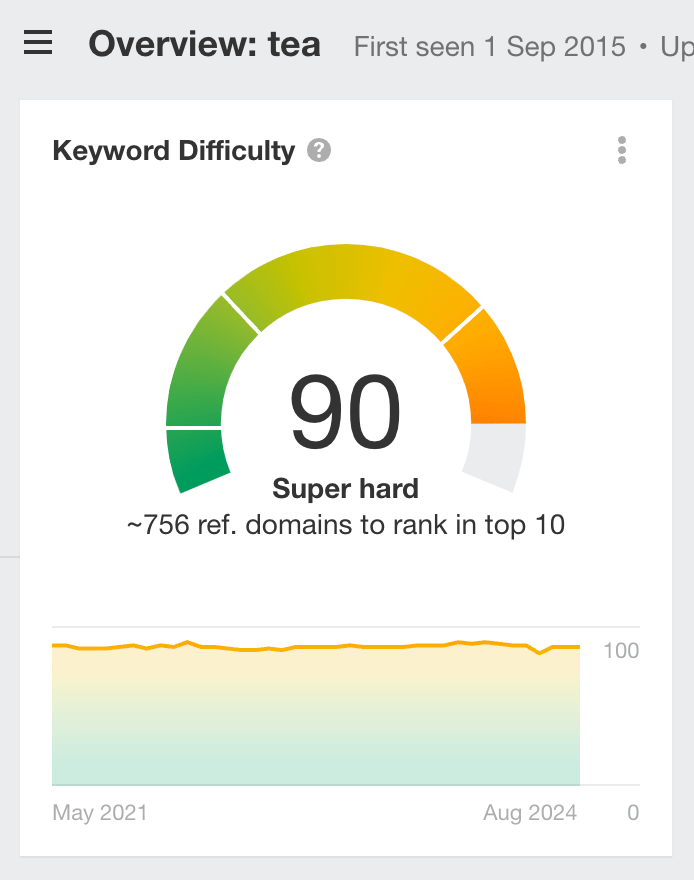
But you wouldn’t need many to rank for “best non caffeinated tea”.
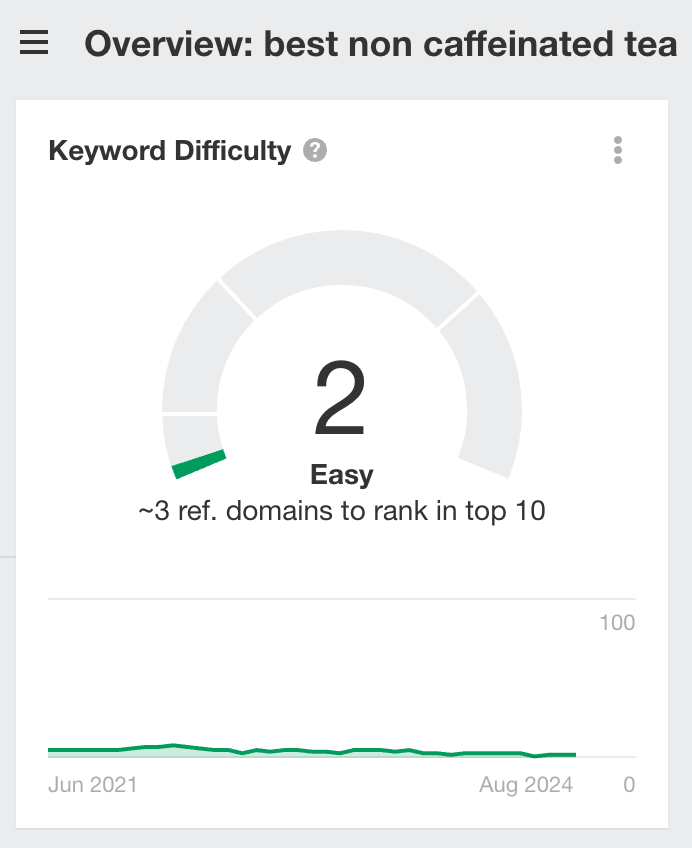
Keep in mind that in SEO, the quality of backlinks matters more than their quantity.
Can you rank without backlinks?
Yes, it is possible to rank without backlinks, especially for low-competition keywords.
For example, our data shows a page with no backlinks. It ranks for 84 keywords in the top 3 (749 total) and gets an estimated 2.5K organic visits.
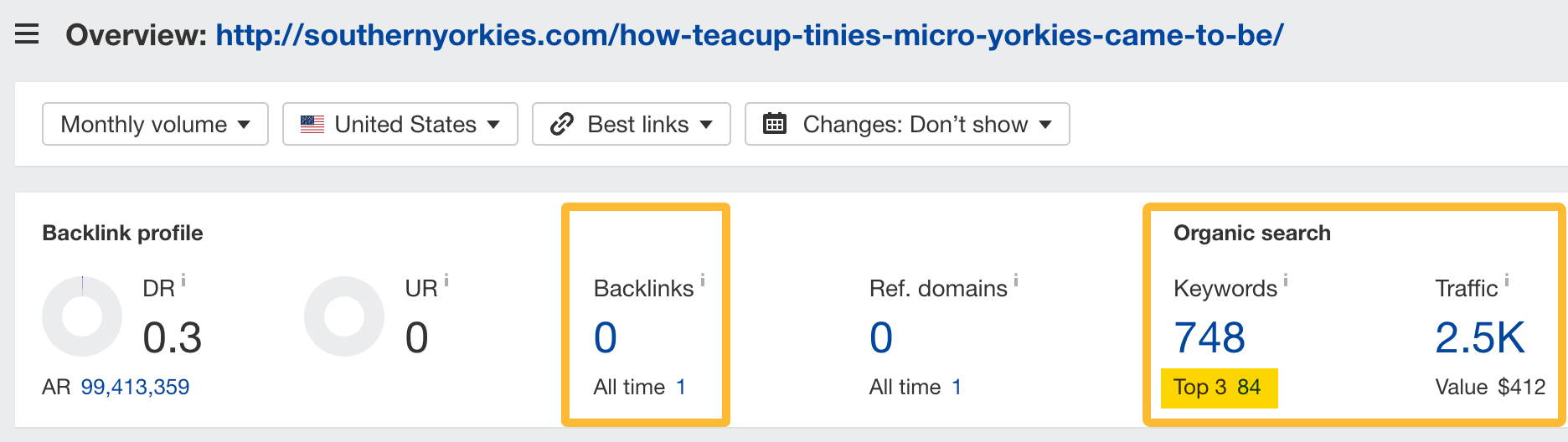
But, it is possible to rank without backlinks. However, high-quality backlinks can boost your rankings. They can help you keep a top position despite the competition.
What are toxic backlinks? Do you need to disavow them?
Toxic backlinks are an SEO term, not used by Google. They are links that can harm your site’s search performance or lead to a manual action. Toxic backlinks are typically some form of link spam, such as exchanging links for money.
Disavowing links means listing the backlinks you want to be ignored and submitting it to Google.
Google advises disavowing links if your site has a manual action, or if you suspect one might occur. For example, if a link-building agency you hired made spammy backlinks, disavowing them can help you avoid penalties.
We found that a single low-quality link probably won’t pose a threat to your site. Only a large number of spammy links can alert Google’s webspam team or lower your site’s rankings.
If you want to learn more about toxic backlinks, read our guide. We also tested disavowing toxic backlinks in an experiment. You can read the results here.
Should you worry about “low-quality” backlinks?
If you suspect some of your backlinks are part of a link exchange, you can disavow them. Other than that, low-authority or irrelevant sites link to you. It’s normal on the web. You don’t need to do anything about it.
Are backlinks becoming less important?
We confirmed that links have a high impact on rankings in two studies. One study showed that pages that don’t get traffic from Google, typically don’t have any backlinks. In another study we demonstrated how removing and adding backlinks affects organic traffic.
And we were not the only ones confirming that links still matter.
Google: Links are not a top 3 ranking factor.
— Gael Breton (@GaelBreton) October 3, 2023
We redirected 100+ links (from old posts we removed) to this page without updating ANYTHING.
Result: #11 > #1
Now, we need to update the page… We shouldn’t recommend Jasper. 😬
Food for thought for anything Google shares. pic.twitter.com/6QBBC2mhi5
But in April 2024, Google’s Gary Illyes said during a conference that links matter less than before:
I shouldn’t have said that… I definitely shouldn’t have said that
— Gary 鯨理/경리 Illyes (so official, trust me) (@methode) April 19, 2024
So we checked again in a study by Patrick Stox, which became one of the reasons I’m updating the article. Here are the key takeaways:
- Links still correlate with rankings, although the correlation is generally weak. This supports Google’s statement to some degree.
- Links correlate more strongly with higher search volume queries, likely because these are more competitive and links act as a differentiator.
- External links (backlinks) correlate much more strongly with rankings than internal links. This suggests Google weights external links more heavily.
- Comparing with a 2019 study, link correlation has decreased for low-volume, non-branded queries, aligning with Google’s statement and SEO perception. However, the author anticipates a potential resurgence of link importance due to the rise of AI content.
Final thoughts
Backlinks are crucial for ranking on Google, especially for competitive queries. But the easier it is to get a link, typically the less valuable it is.
Want to get started with link building? Read our beginner-friendly guide or watch our link building tutorials on YouTube.
Got questions? Let me know on LinkedIn.




