For example, if you’re a plumber in London, you might want to show up when people search for “plumber near me” or “london plumber.” Most people click the first result, so appearing at the top usually means more traffic, leads, and customers.
But how exactly do you appear here above the competition?
Just follow this flowchart:
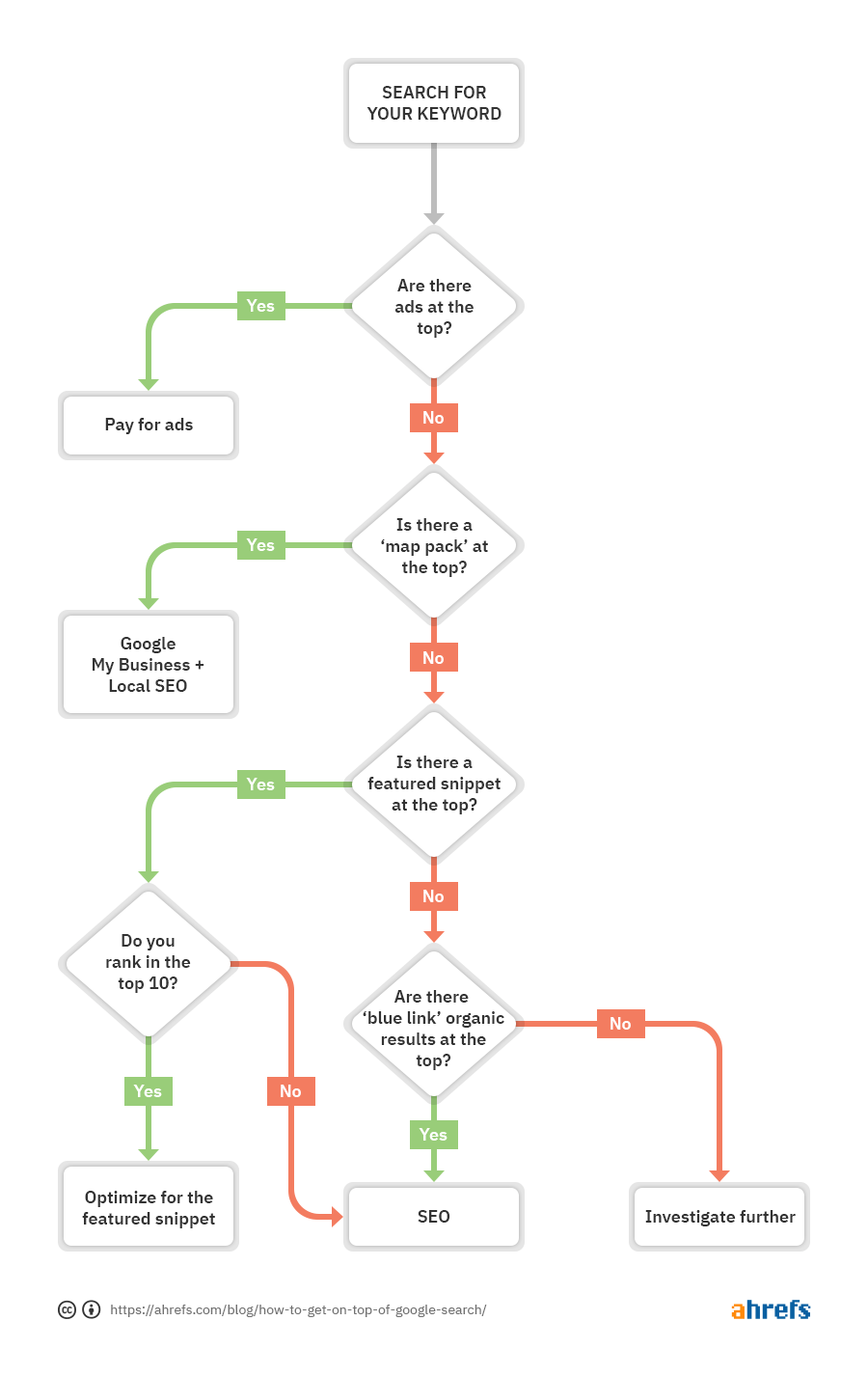
Not sure what each of those four possibilities look like?
Here’s a quick cheat sheet:
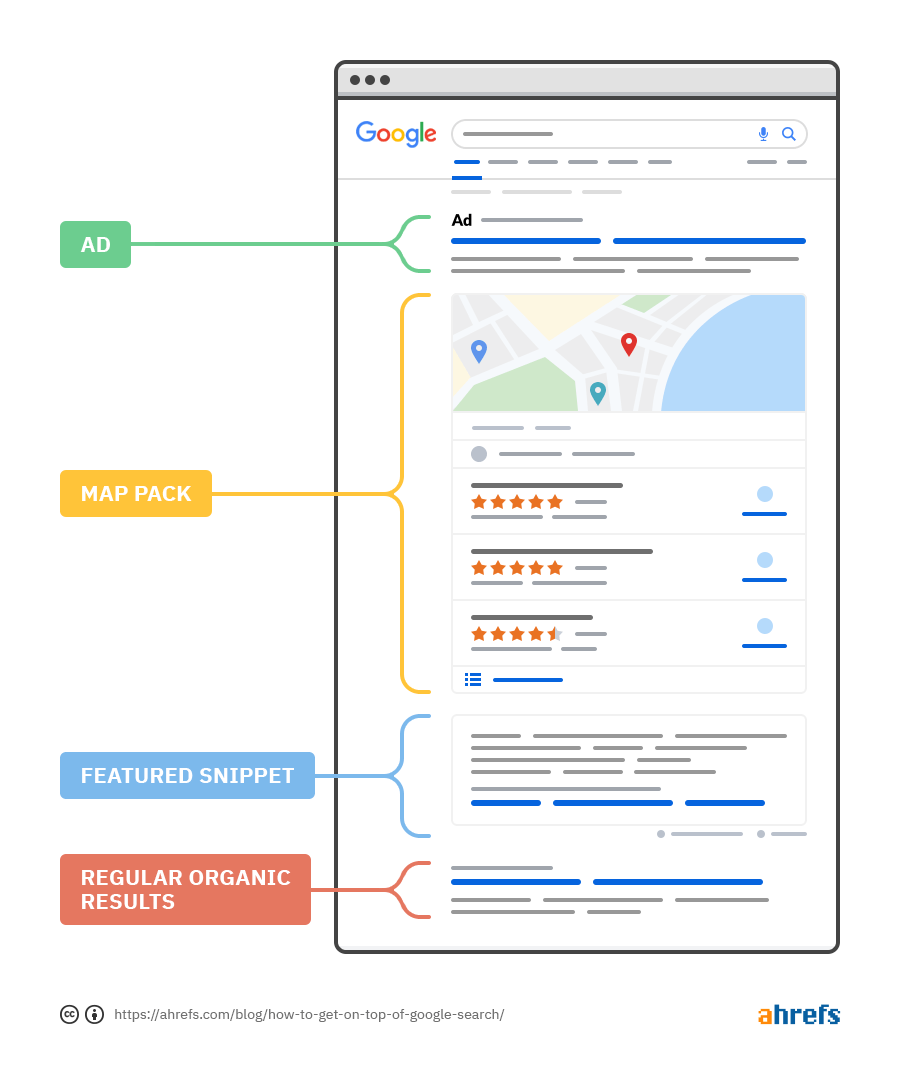
If you’ve hit the end of the flow chart, check our list of SERP features. There might still be a way to appear right at the top.
Otherwise, hit one of the options below to jump straight to the instructions:
- How to get to the top of Google with ads
- How to get to the top of Google with local SEO
- How to get to the top of Google by winning the featured snippet
- How to get to the top of Google with SEO
If ads are what you see at the top of the results for your target keyword, then the only way to appear right at the top of Google is to pay for ads.
How? Just sign up for Google ads and run a search campaign.
Google search ads work on a pay per click (PPC) basis. That means you bid on the keywords that you want to show up for in Google. If you’re a plumber in London, you can bid on keywords like “plumber in london” and “plumber near me.”
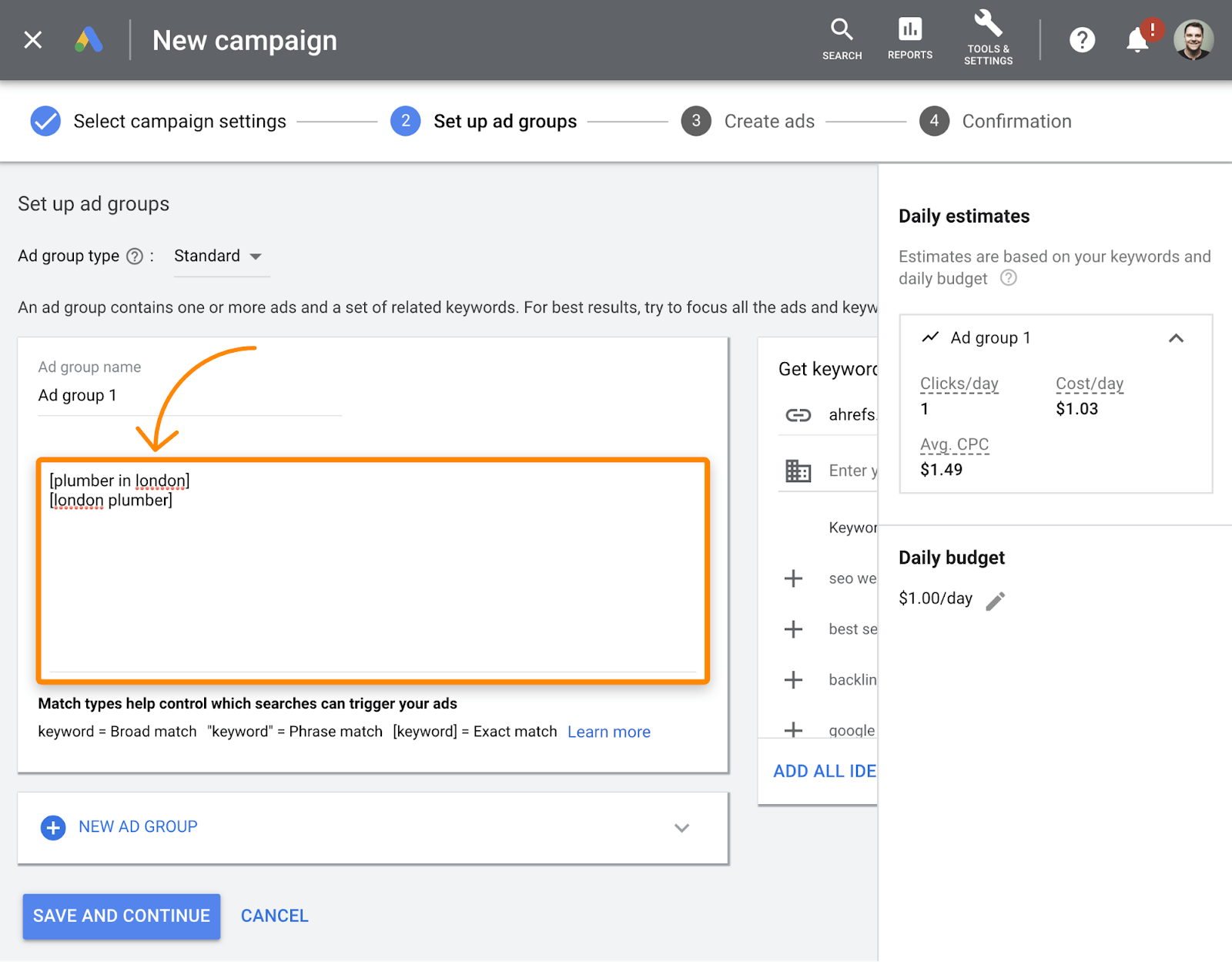
You can add geographic targeting, too, so you won’t be advertising to folks that live where your business doesn’t operate.
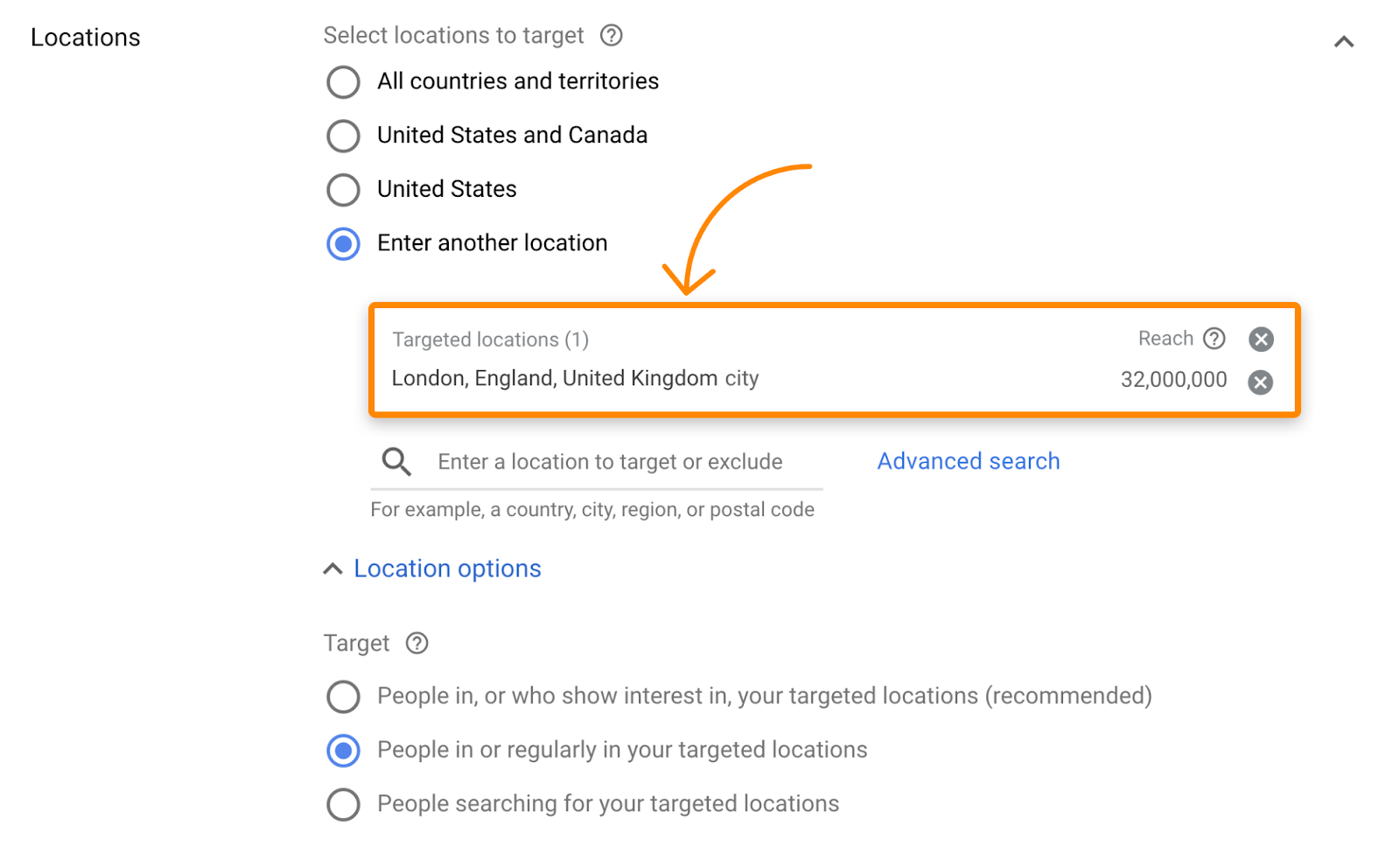
Just know that bidding on a keyword doesn’t mean that you’ll always show up at the top of the ads block. If other people are willing to pay more for a click, there’s a chance you’ll appear lower down or not at all.
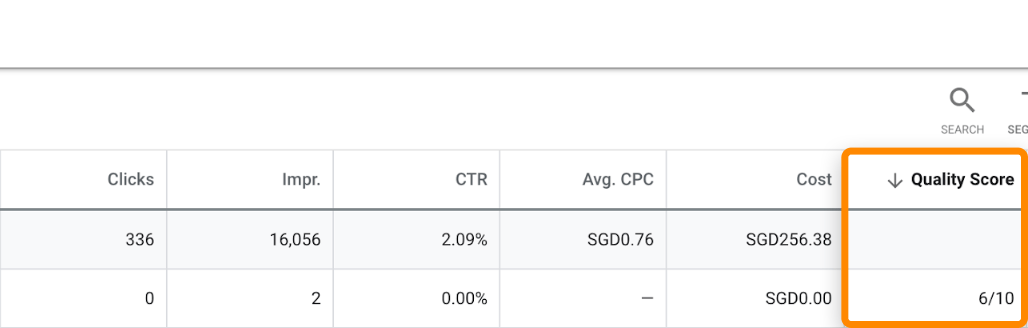
It’s also crucial that your landing page and ad copy align with the keyword you’re targeting. Google’s Quality Score gives you some insight into this. In Google’s words, “Higher Quality Scores typically lead to lower costs and better ad positions.”
That said, while ads are a fantastic way to appear at the top of Google fast, it’s 100% pay to play. The second you stop pumping money into your campaigns, the second you stop showing up at the top of Google.
It’s also true that organic results may get more clicks than ads, so being in position one with an ad doesn’t always equate to more clicks. That’s because most people prefer to click organic results.
For example, if we search for “best VPN,” we see four ads at the top of the results:
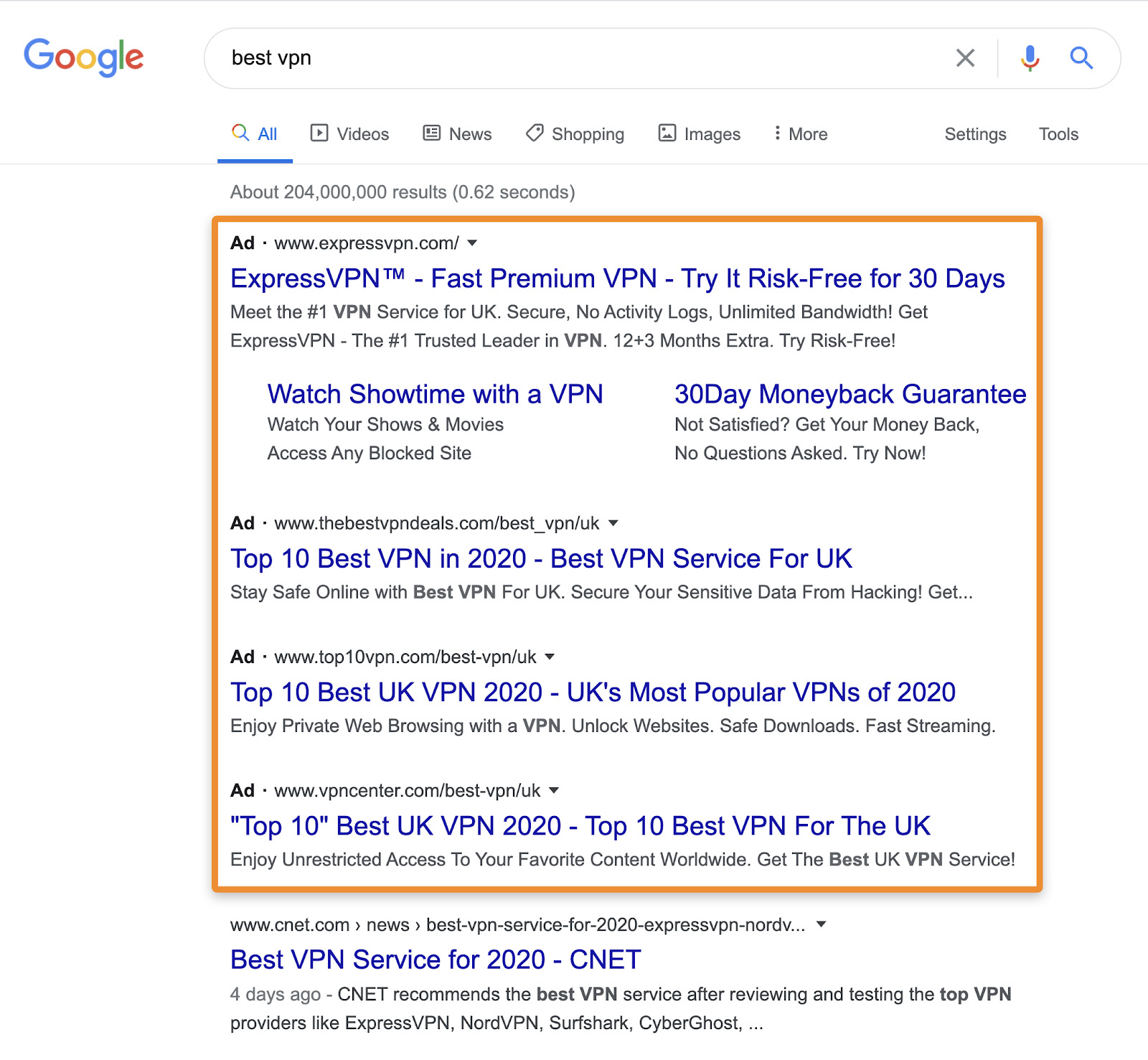
But if we check this keyword in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer, only 19% of clicks go to the paid results. Most of the clicks are on the organic (non-paid) search results further down the page.
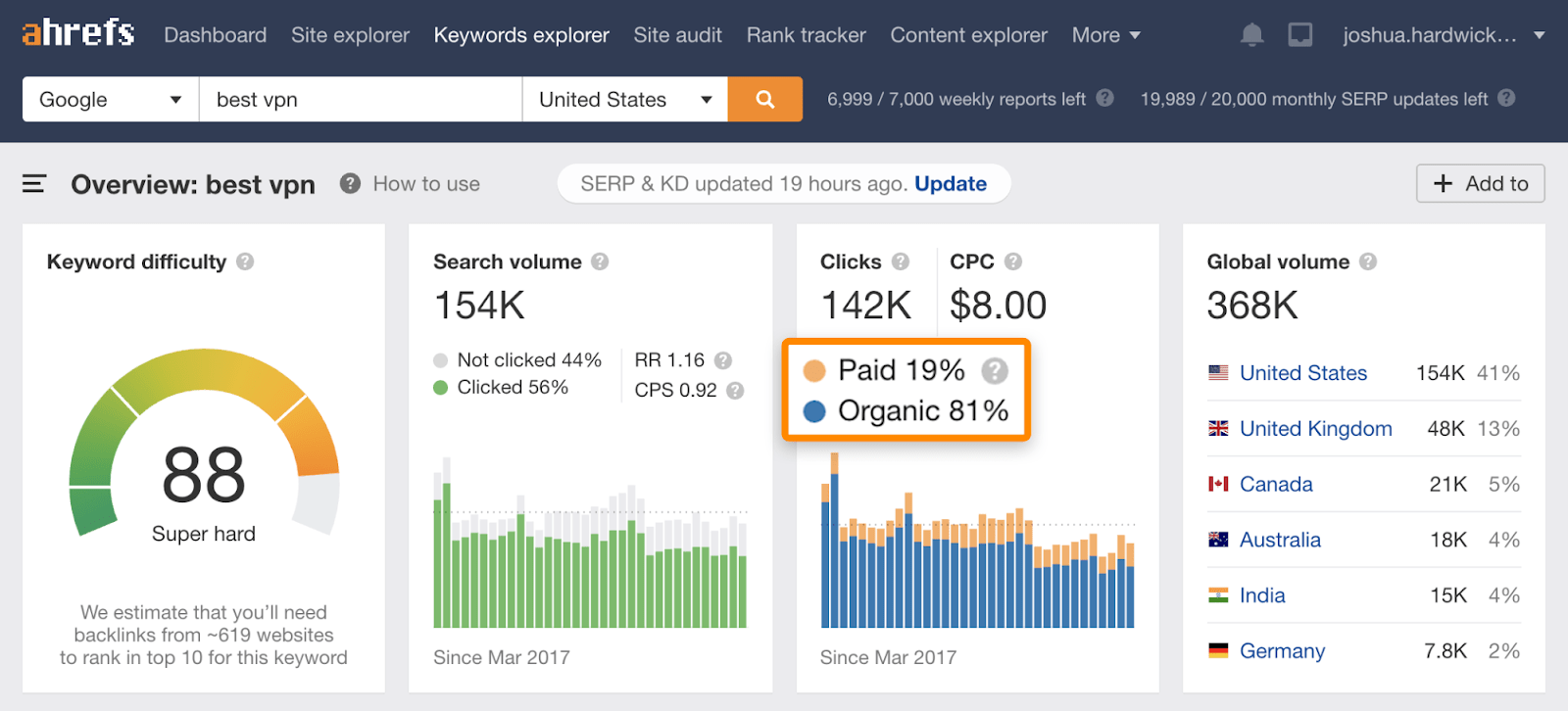
If this is the case for the keyword you want to get search traffic from, it might be worth investing in SEO instead of, or alongside PPC.
If people search for your keyword when looking for local businesses, you’ll often see a ‘map pack’ at the top of the results.
Unlike most search results, map pack listings take you to the business’s Google My Business listing, not their website.
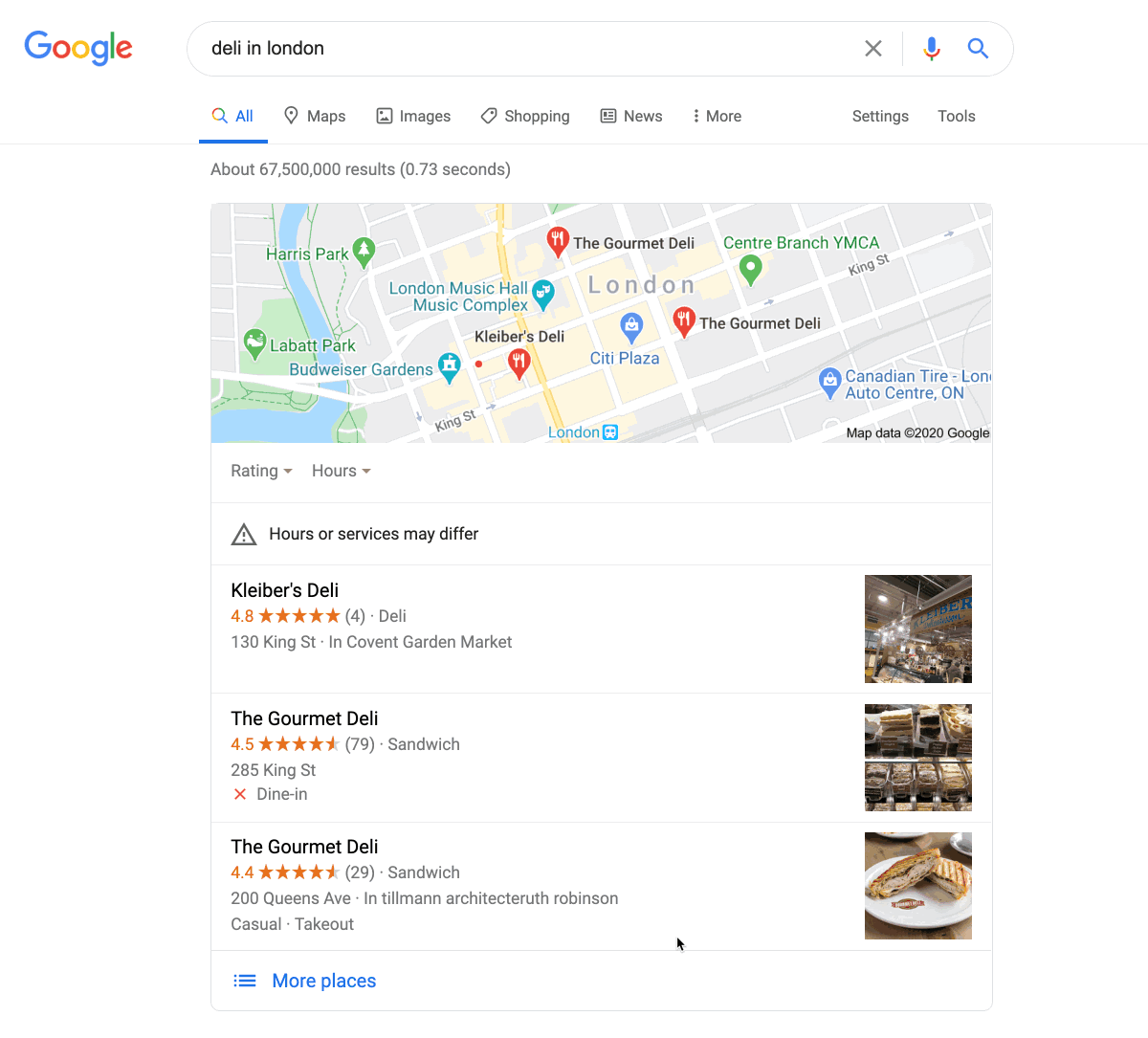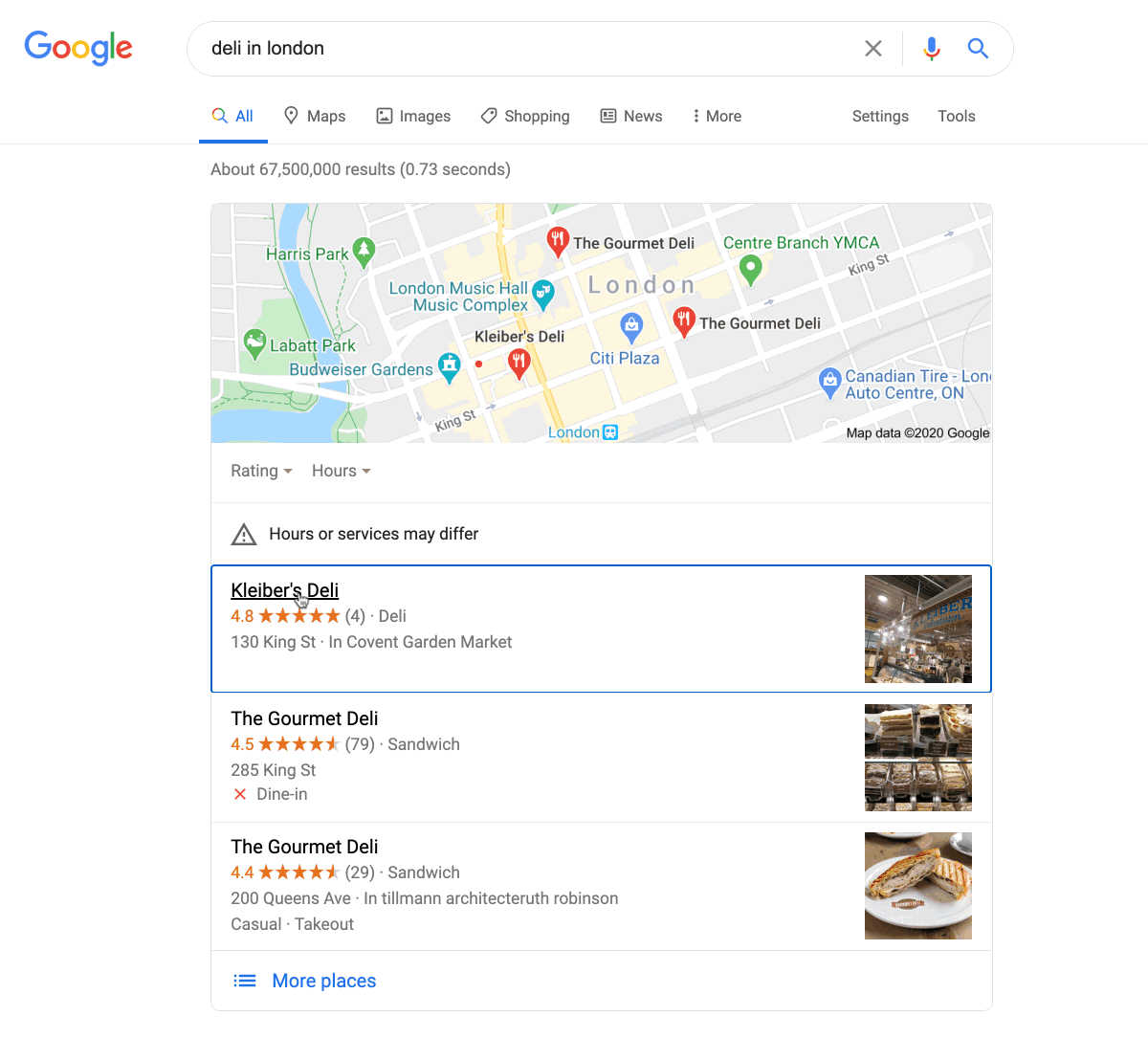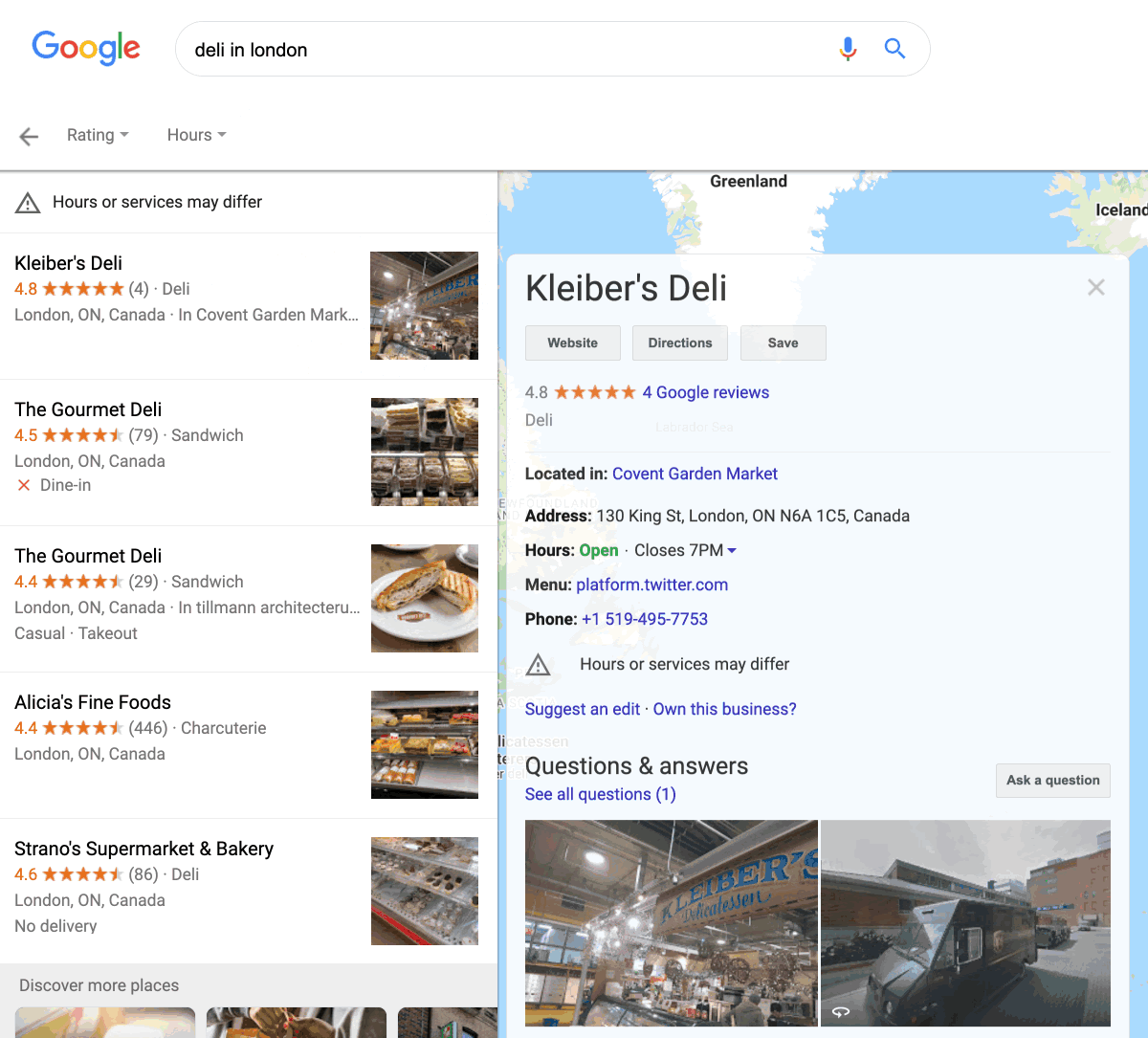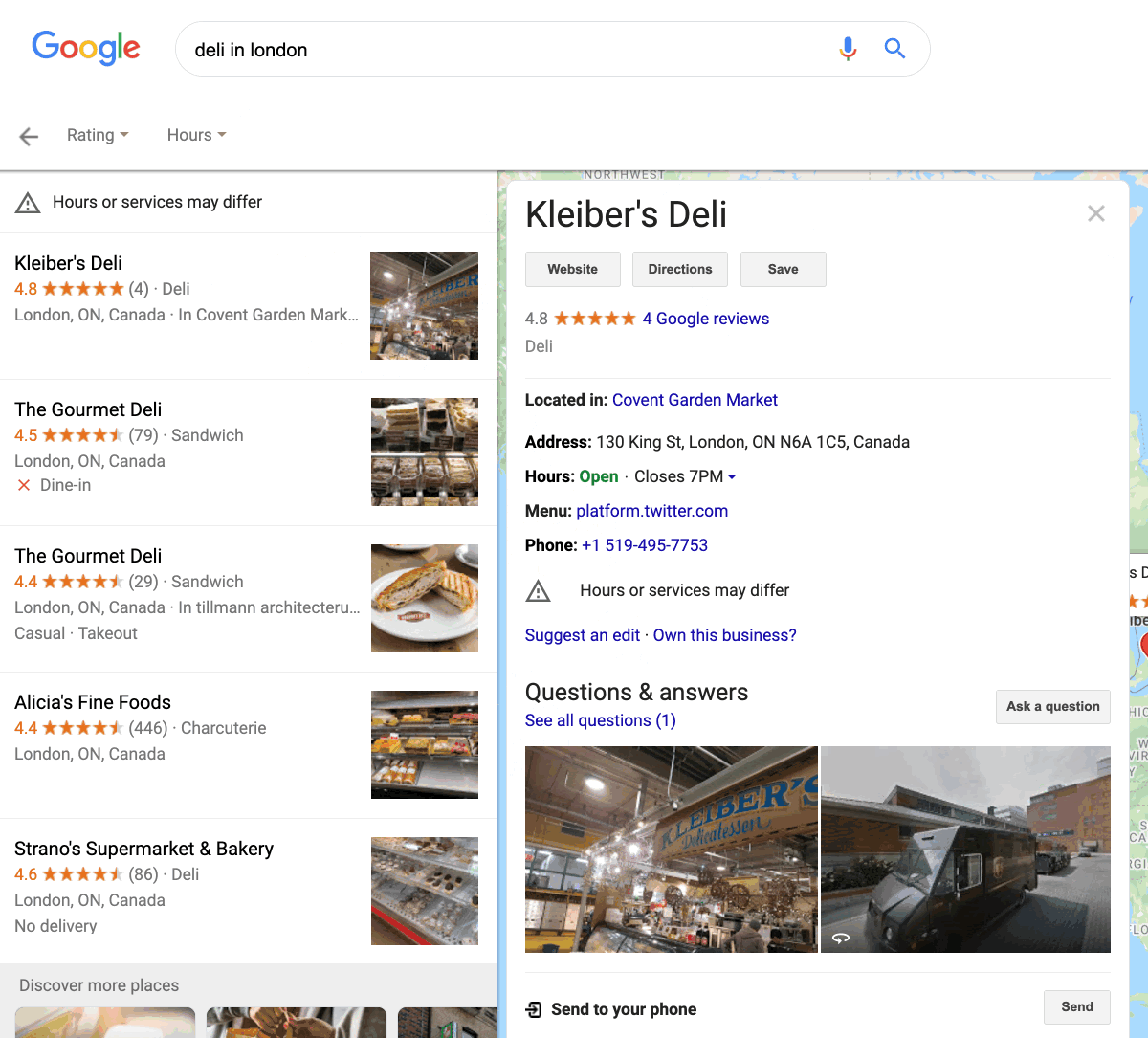
Google My Business is a free business listing from Google. It’s a place where you can list all the essential details about your business: opening times, address, phone number, website, and more. It’s also somewhere that customers can leave reviews.
If you want to appear in Google’s map pack results and don’t have a Google My Business listing, that’s your first port of call.
However, most businesses won’t be able to rank here just by signing up for Google My Business. Google’s aim is to rank the “best,” most trustworthy local businesses in the ‘map pack,’ so you need to use local SEO tactics to stand the best chance of showing up.
You can learn more in our complete guide to local SEO, but the basics are:
- Optimize your Google My Business listing.
- Build high-quality local citations.
- Get more reviews from customers.
- Build links to the pages that matter.
Featured snippets are boxes that appear at the top search results for some keywords. They show a short, relevant snippet from one of the top-ranking pages.
If you already rank on the first page for a query with a featured snippet at the top, it may be possible to win that position with a bit of on-page SEO.
You can check your current ranking position in Google or with Ahrefs’ free rank checker. Just plug in your keyword, country, and domain.
![]()
From there, assuming you rank in the top 10, it’s a case of making sure your page is optimized for the snippet.
We explain this process in more detail here, but the basics are quite simple.
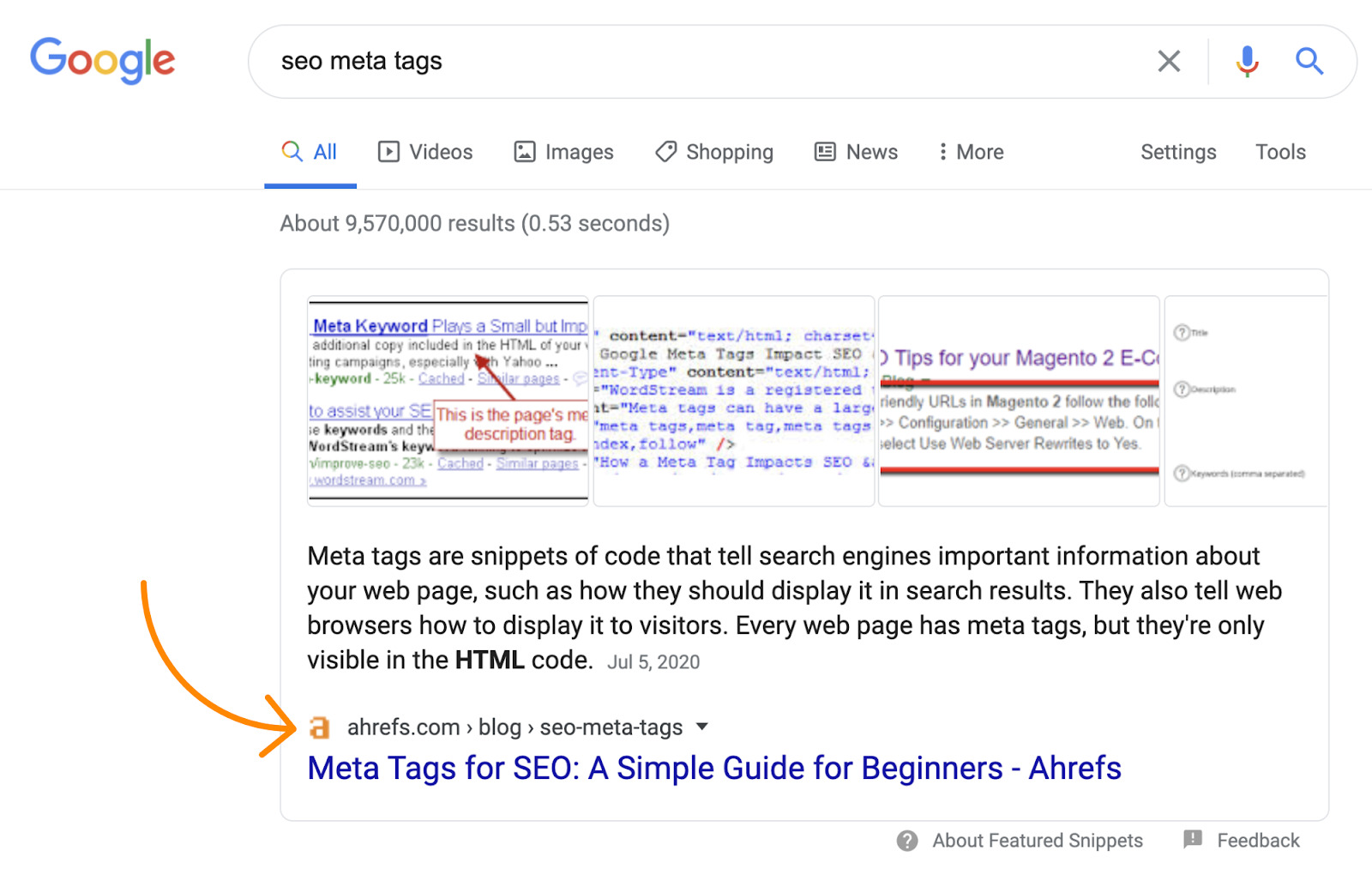
First, make sure that your page actually provides the information that Google wants to show in the snippet. For example, if we look at the featured snippet for the keyword “guest blogging,” we see that it’s a definition.
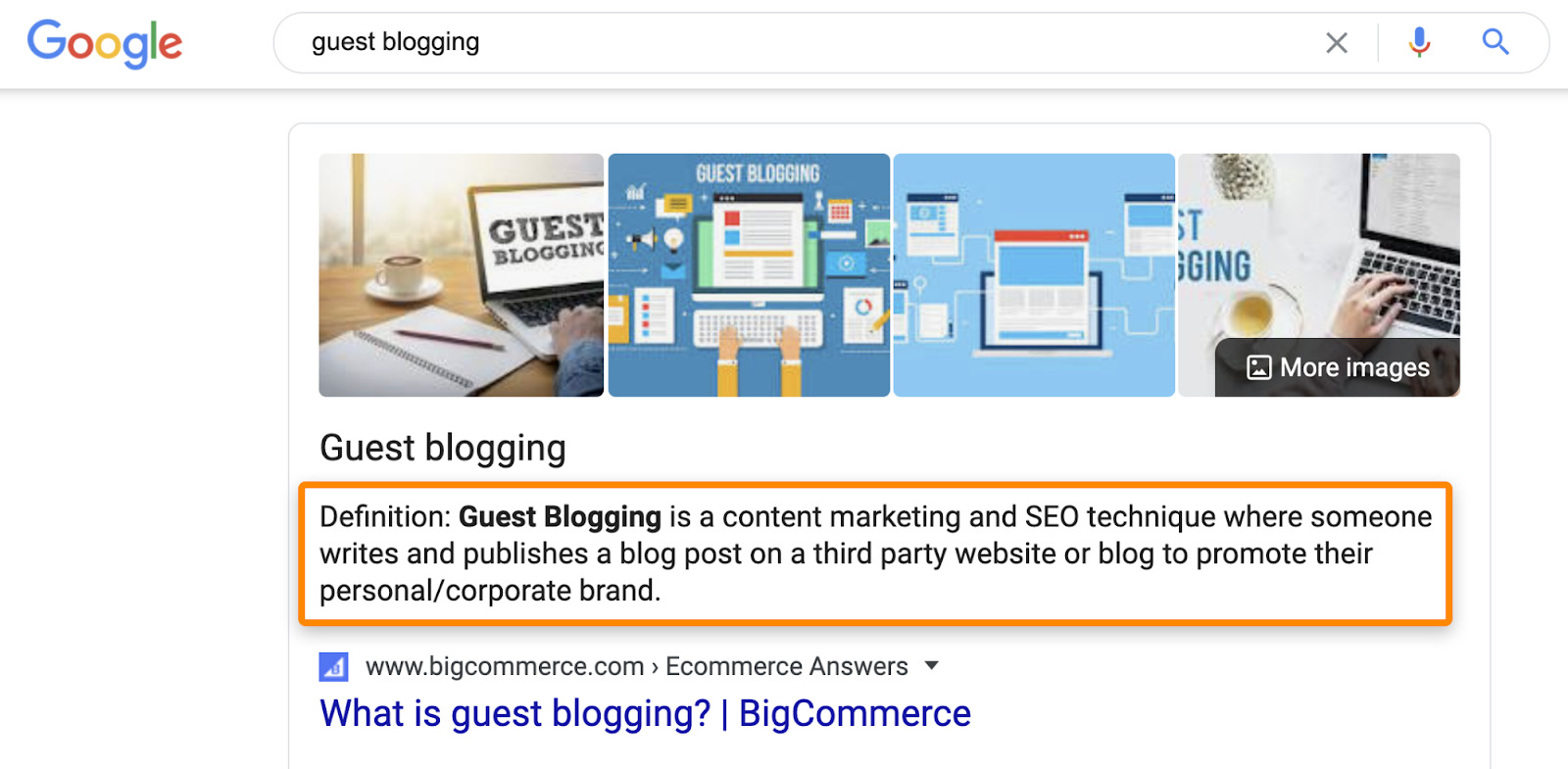
Our guide to guest blogging ranks in position 7, but as we didn’t define the term on the page, it would probably be impossible for us to win the snippet. We’d need to write and add a definition to the page to be eligible.
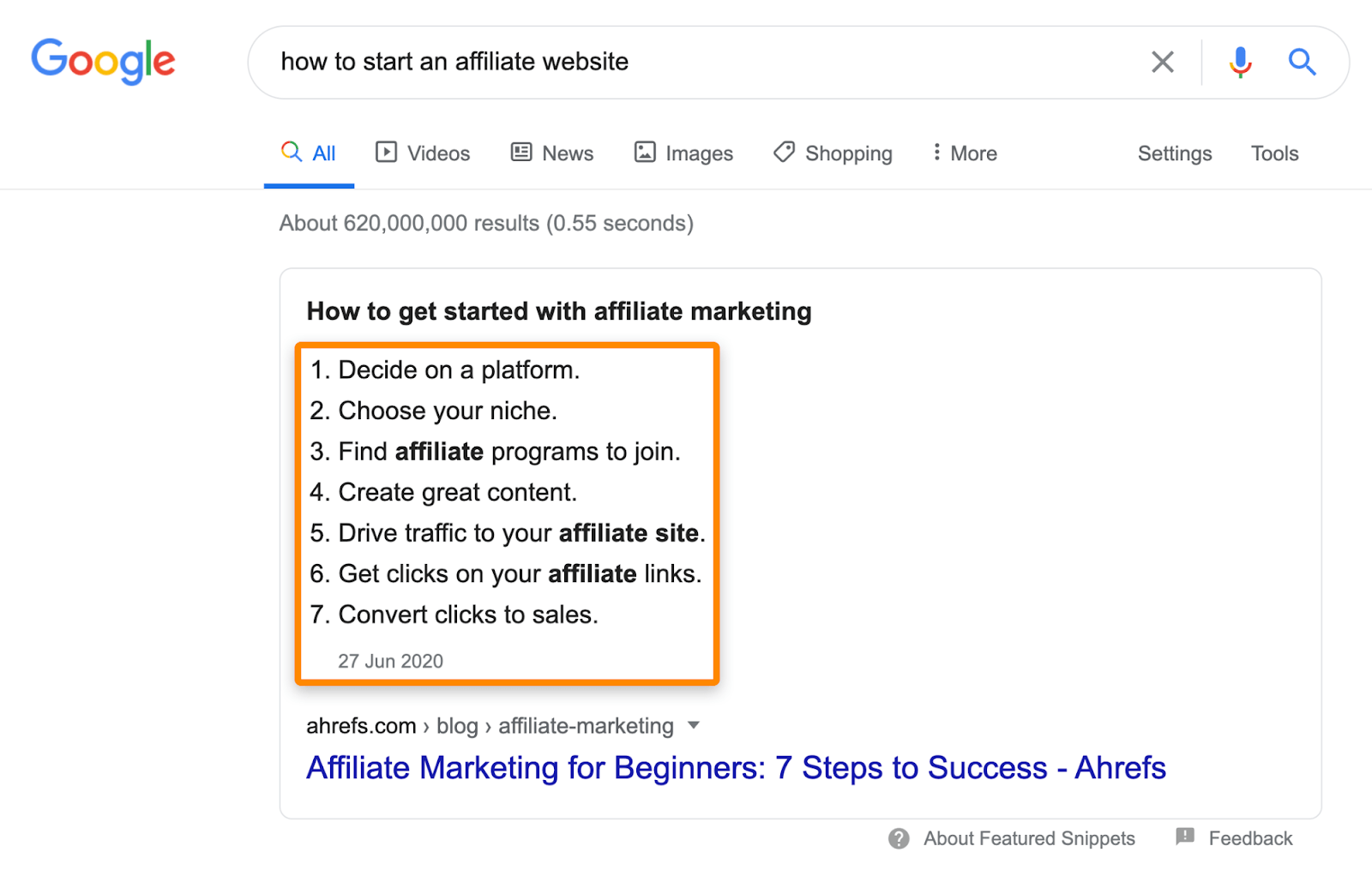
Second, make sure the information is in the format Google prefers. This varies depending on the keyword. For “guest blogging,” the snippet is a short paragraph. For “how to do affiliate marketing,” it’s a numbered list.
Recommended reading: How to Optimize for Google’s Featured Snippets
Paste your domain into Ahrefs’ Site Explorer, go to the Organic keywords report, then filter for keywords with featured snippets in the results where you currently rank in positions 2-10.
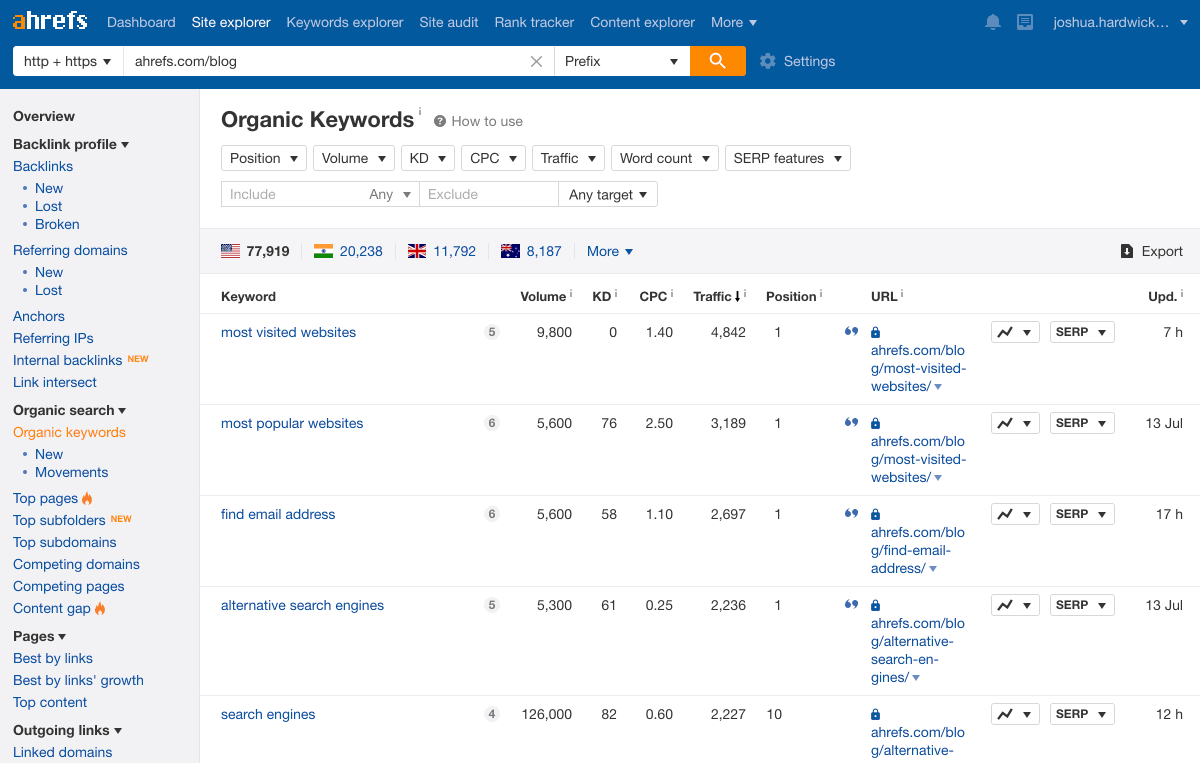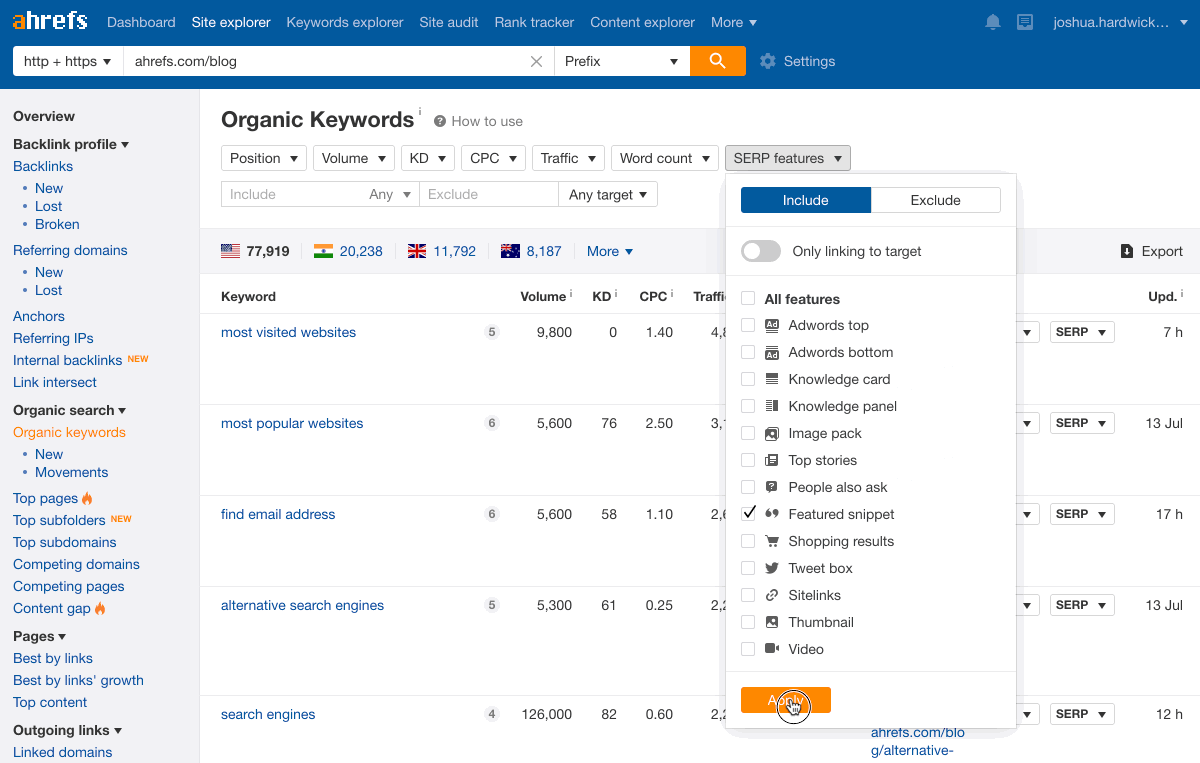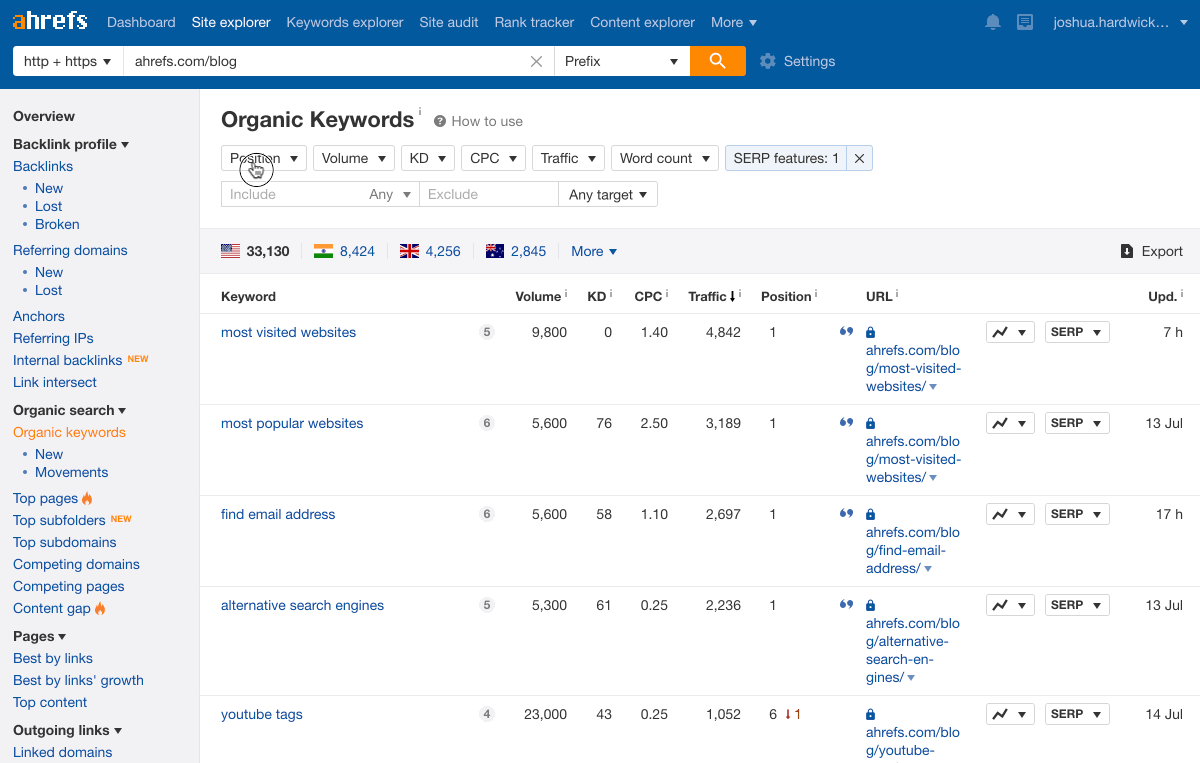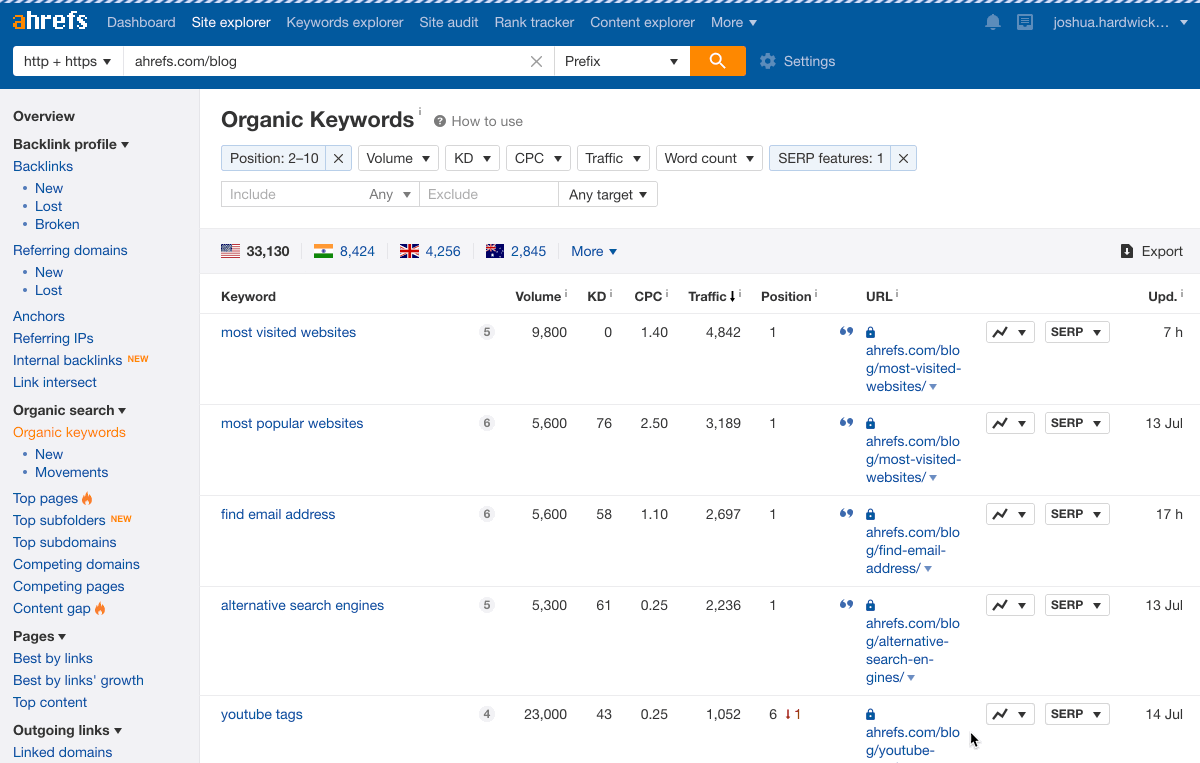
For example, we rank second for “google search operators” but don’t own the snippet.
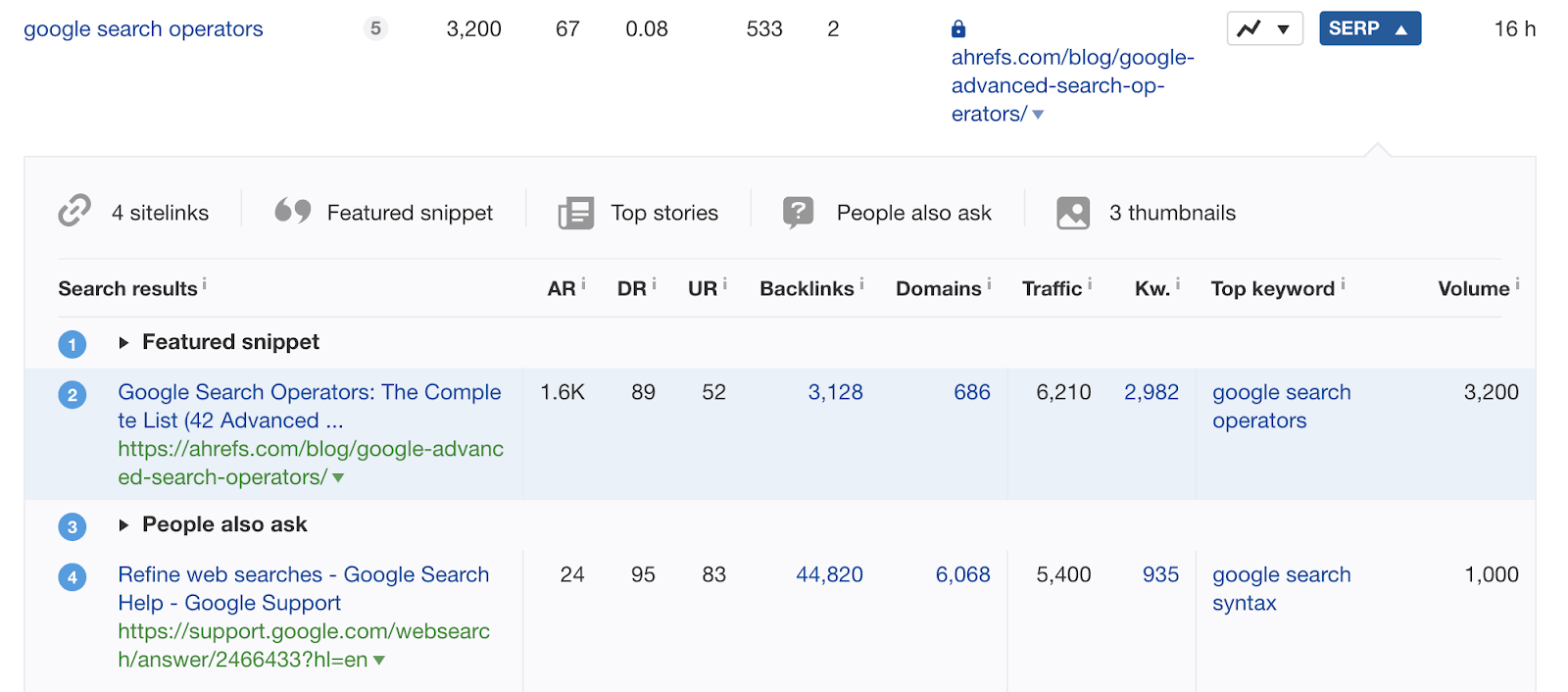
With a bit of on-page optimization, we could probably change that.
If you see regular ‘blue link’ organic results on top of Google, you’ll need to invest in SEO.
As a starting point, that means paying attention to SEO best practices and having a site that’s:
- Mobile-friendly
- Fast loading
- Easy to use (clear navigation, good UX, etc.)
- Secure (i.e., HTTPS not HTTP)
- Well-structured
- Free of other technical SEO issues.
However, best practices and optimizations will rarely be enough to rank in the top spot. If you’ve got the basics covered and are still nowhere to be seen, run through this flowchart:
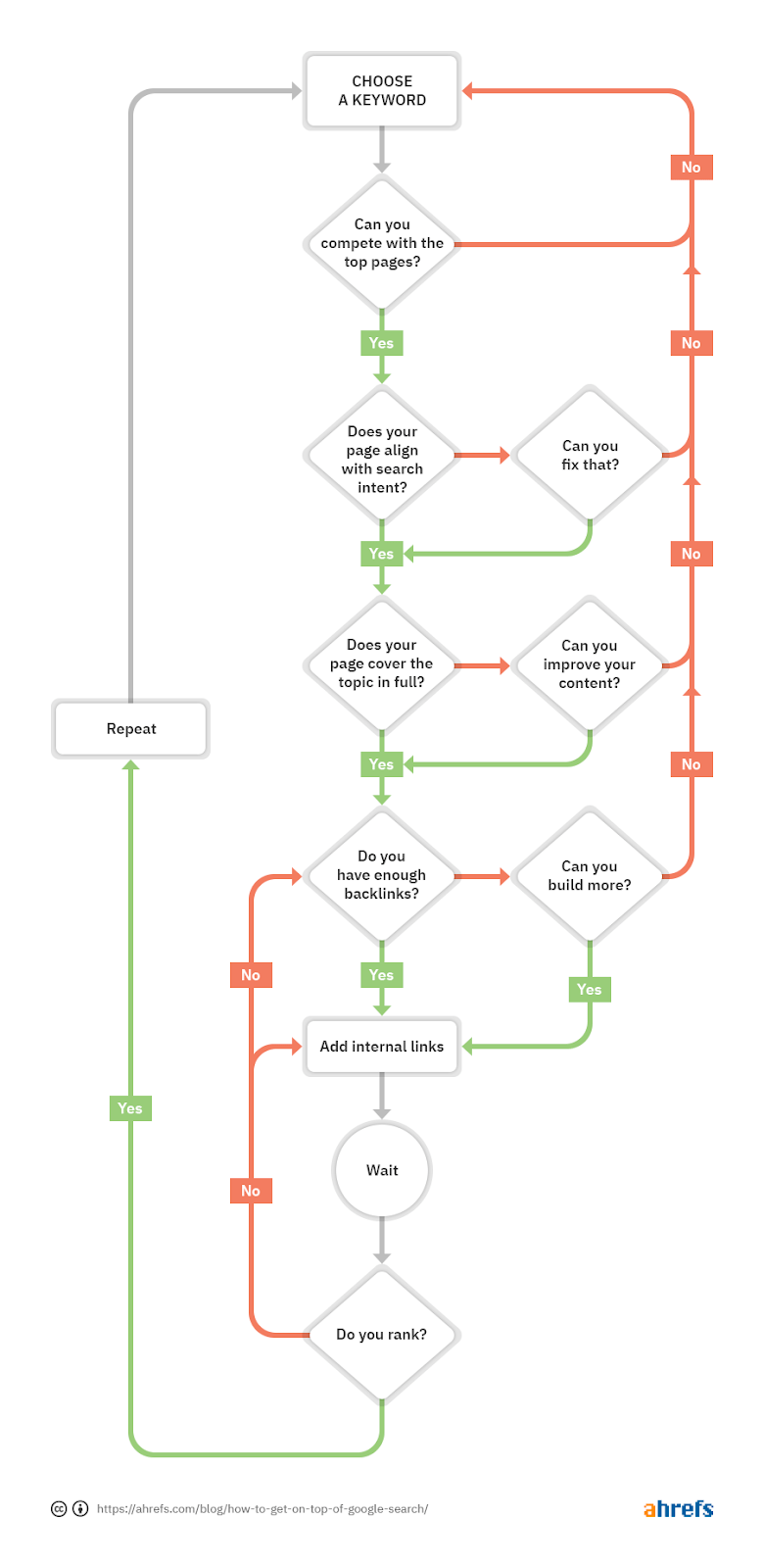
We explain how to execute this process from start-to-finish in our guide to ranking on Google’s first page, but here’s a simplified version to get you started:
- Check the competition
- Align your page with search intent
- Cover the topic in full
- Build high-quality backlinks
- Add internal links
Step 1. Check the competition
Ranking on Google is not a single-player game. Every site ranking on the first page is your competitor. You’ll have to surpass them to get to the number one spot. So the first thing you need to do is check the strength of the competition relative to your website.
To do that, search for your keyword and eyeball the caliber of sites on the first page.
If we do this for the keyword “womens pajamas,” the top results are dominated by huge brands like Kohls, Target, and Amazon.
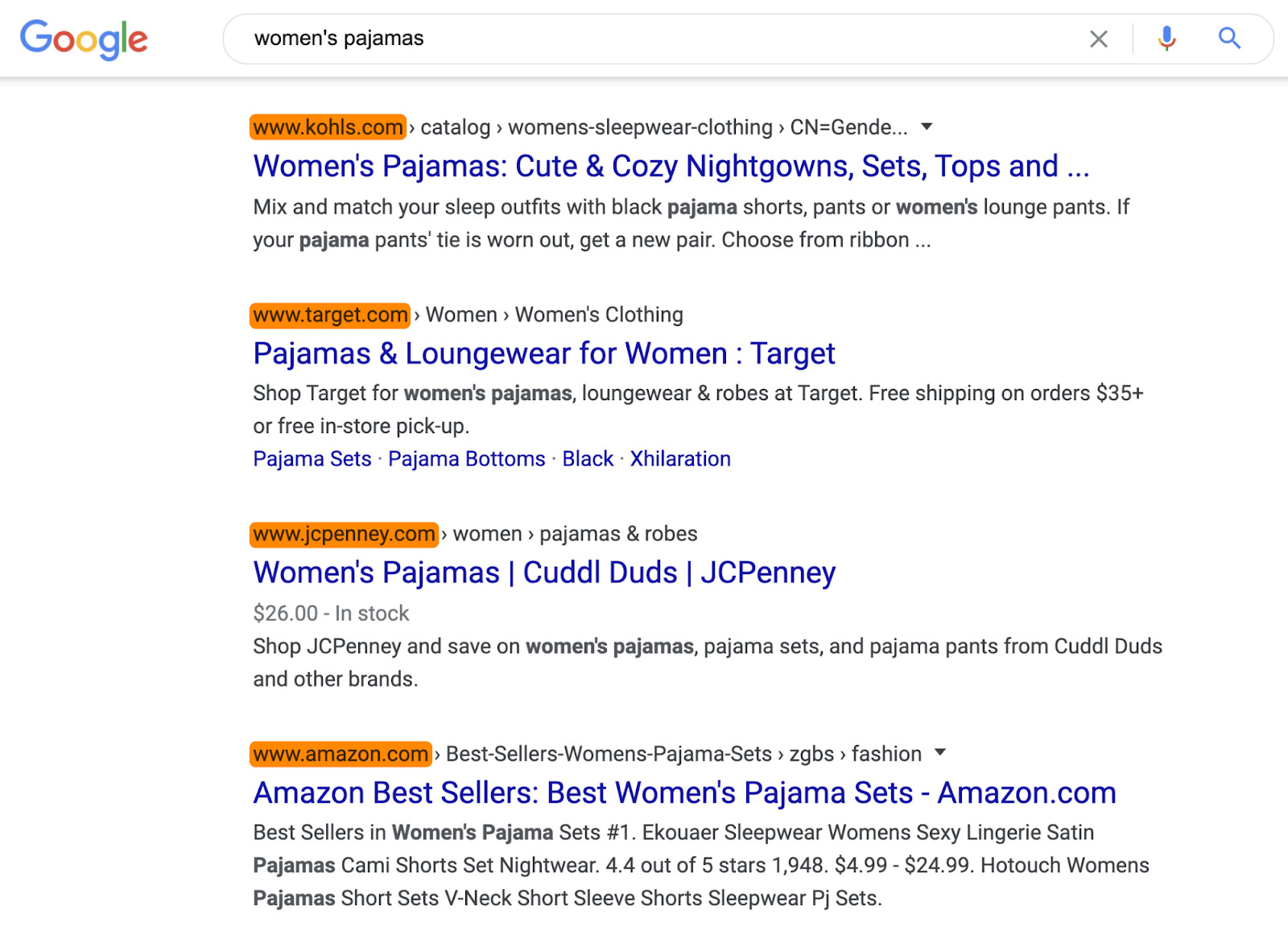
Unless you’re also a big brand, it’d probably be pretty challenging to outrank these sites.
For a keyword like “tall womens pajamas,” things look a bit more promising. There are a few lesser-known brands on the first page there’s even a small brand ranking #1.
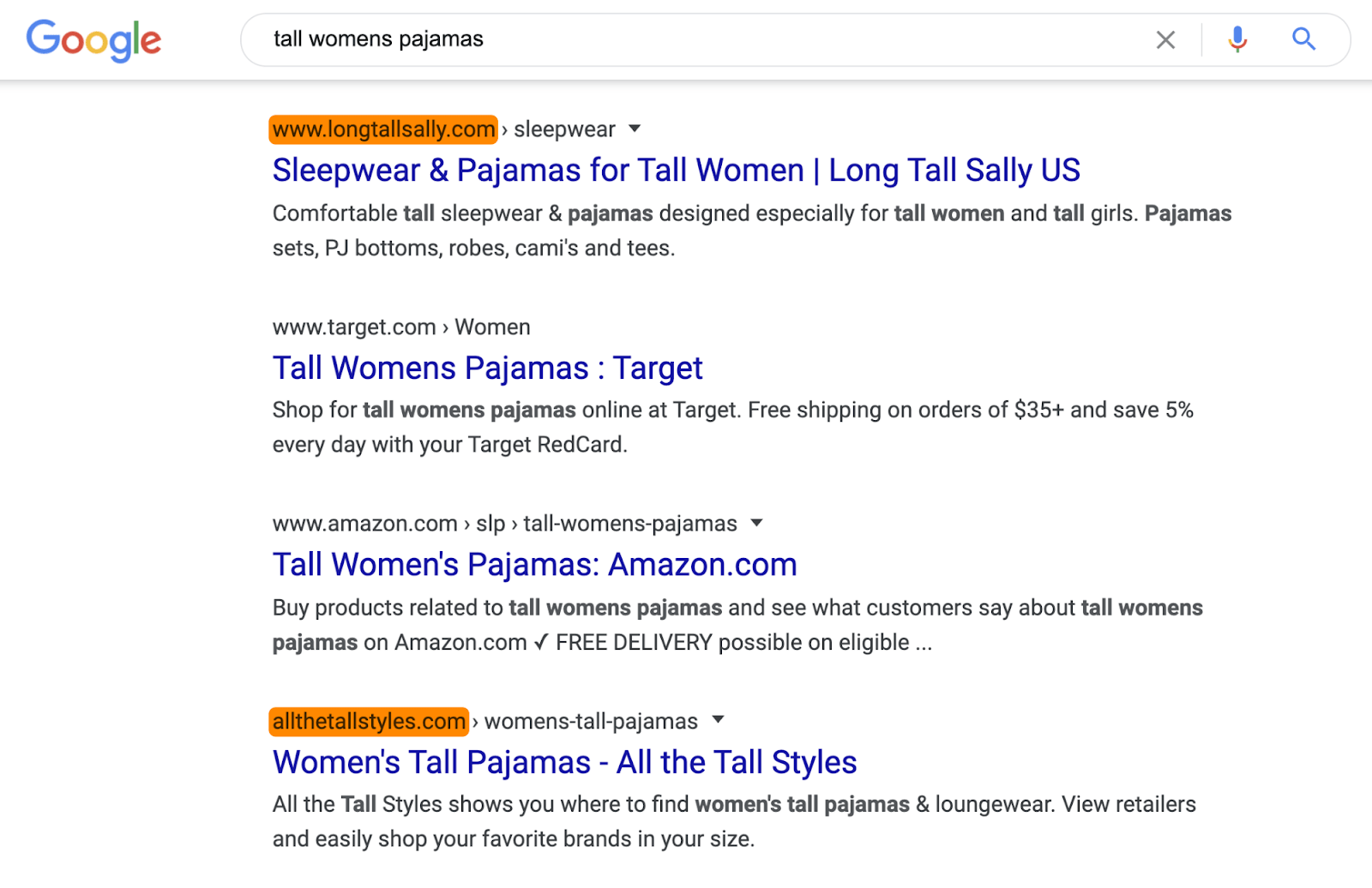
If things look difficult at this stage, it’s probably best to pursue a different keyword—at least if you want a chance of ranking in the short-to-medium term.
Recommended reading: Keyword Difficulty: How to Determine Your Chances of Ranking in Google
Step 2. Align your page with search intent
Search intent is the reason behind a searcher’s query. For example, if you search for “blogging tips,” you’ll notice that all of the top-ranking pages are unordered lists of tips.
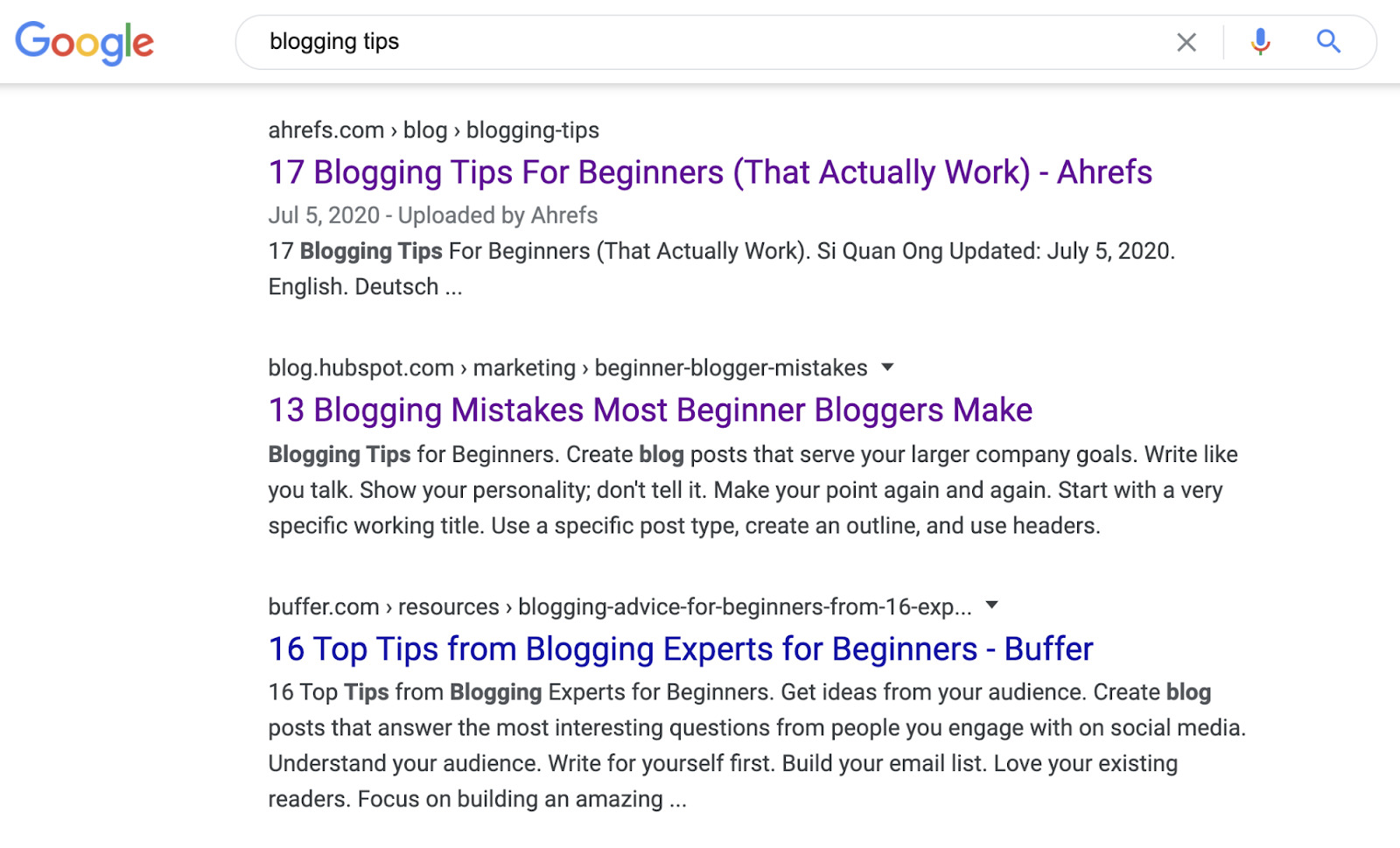
If you search for “how to write a blog post,” they’re all how-to guides with step-by-step instructions.
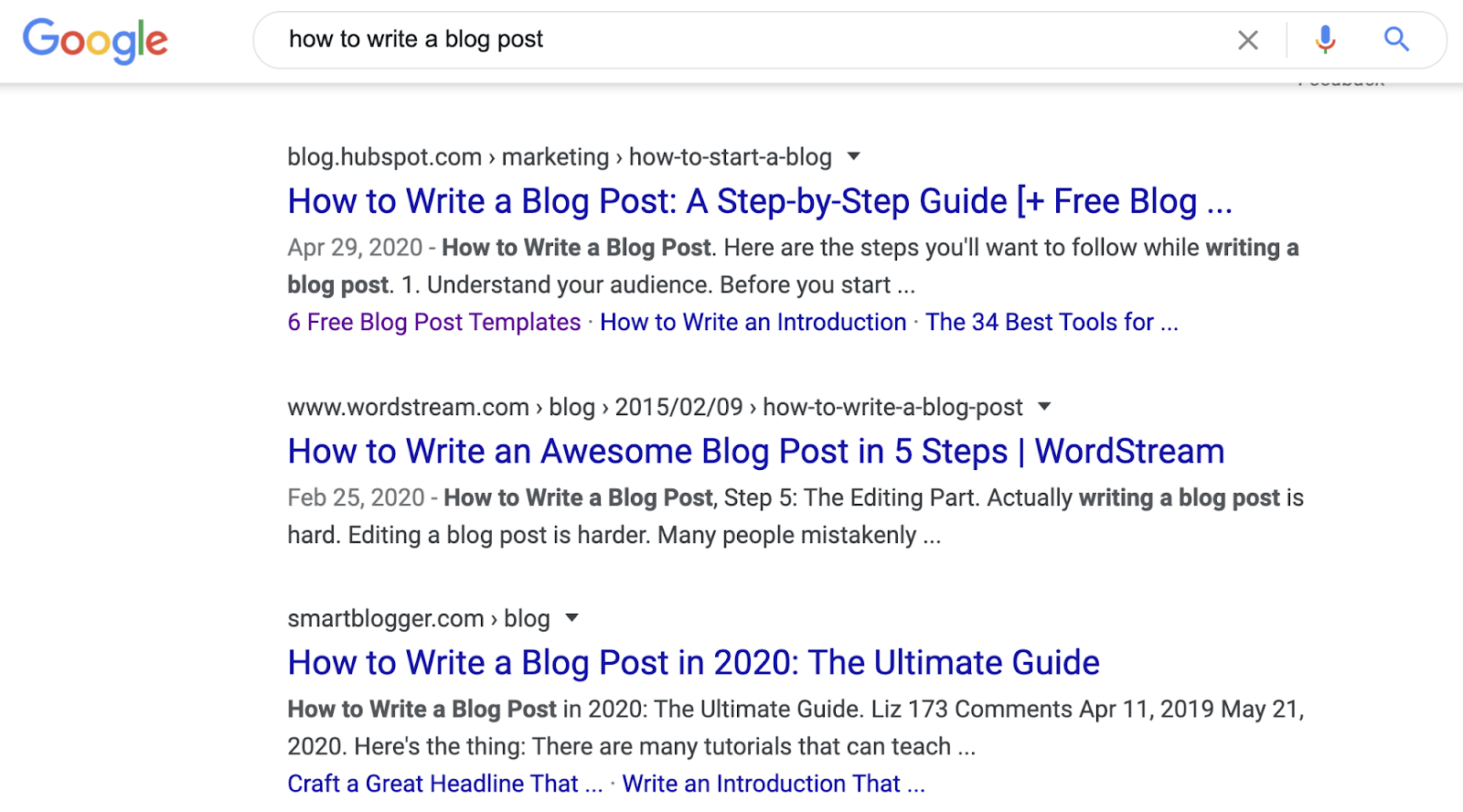
To stand the best chance of ranking at the top of Google, you should create the type of content that people are looking for. You can do this by searching for your target keyword and identifying the three C’s of search intent:
- Content type: Are the top-ranking pages mostly blog posts, product pages, product category pages, or landing pages?
- Content format: Are the top-ranking pages mostly how-to guides, step-by-step tutorials, list posts, opinion pieces, reviews, comparisons, or something else?
- Content angle: Is there a dominant unique selling proposition used by the top-ranking pages? (e.g., for beginners, in 2020, etc.)
Recommended reading: Searcher Intent: The Overlooked ‘Ranking Factor’ You Should Be Optimizing For
Step 3. Cover the topic in full
Google wants to rank pages that cover the things searchers want to know. But how do you know what questions and subtopics Google deems important for this keyword?
The best starting point is to eyeball top-ranking pages for commonalities. For example, the three top-ranking pages for “paleo diet” all talk about foods to eat. That tells us this is probably something most people searching for this keyword want to know about.
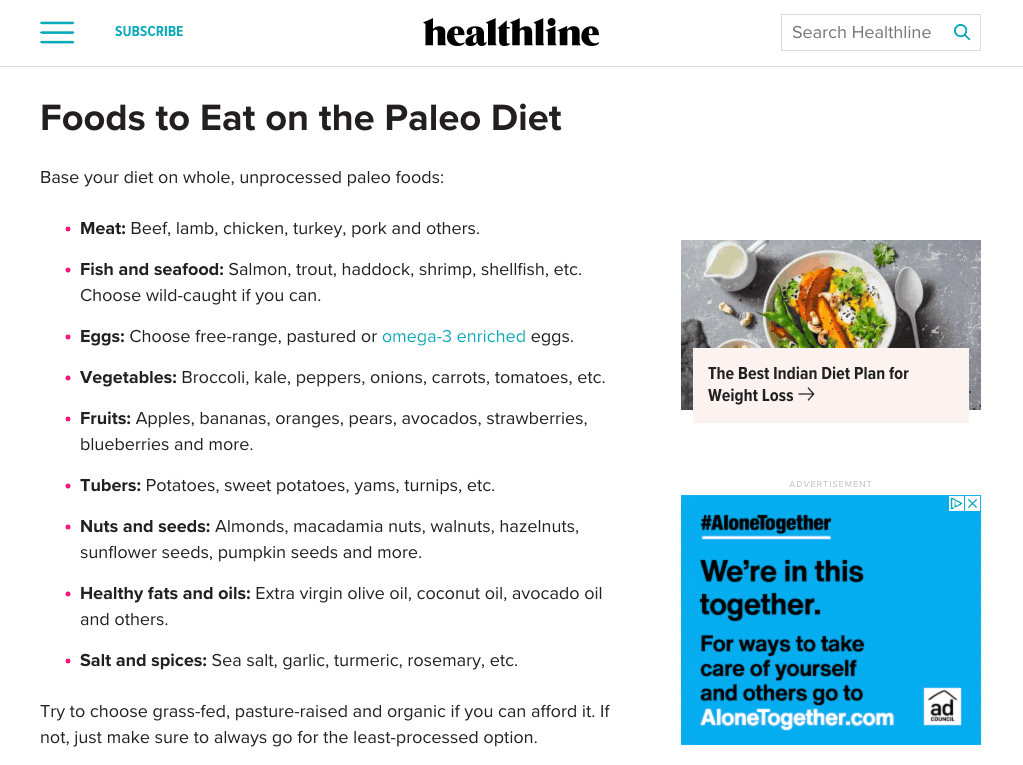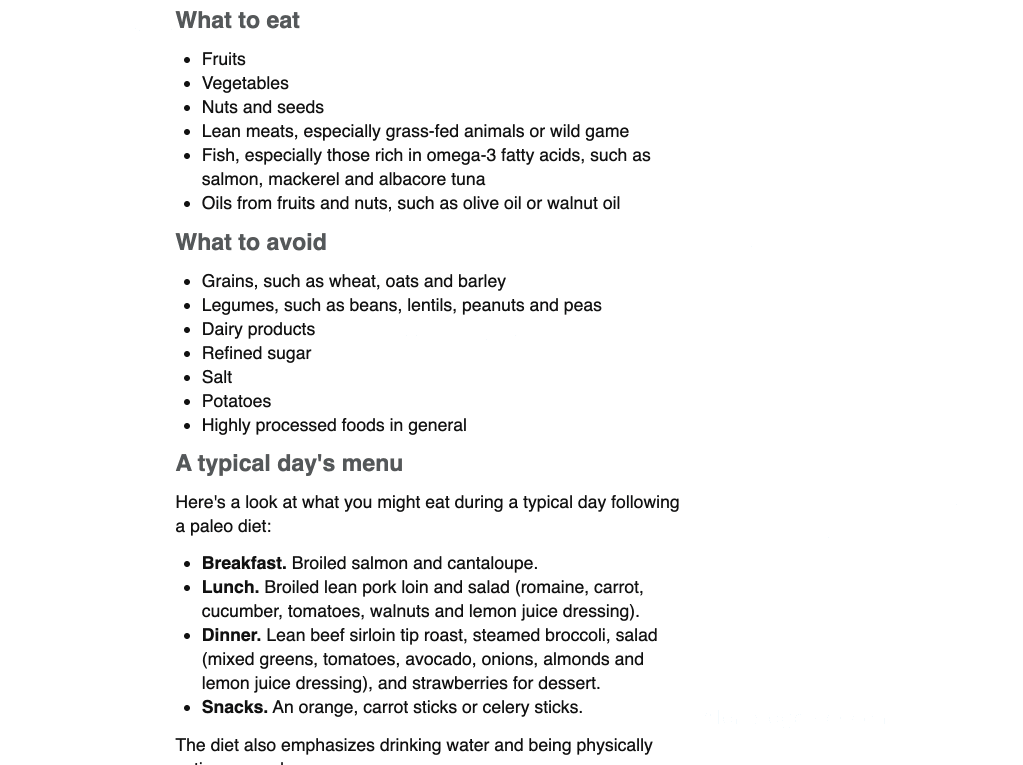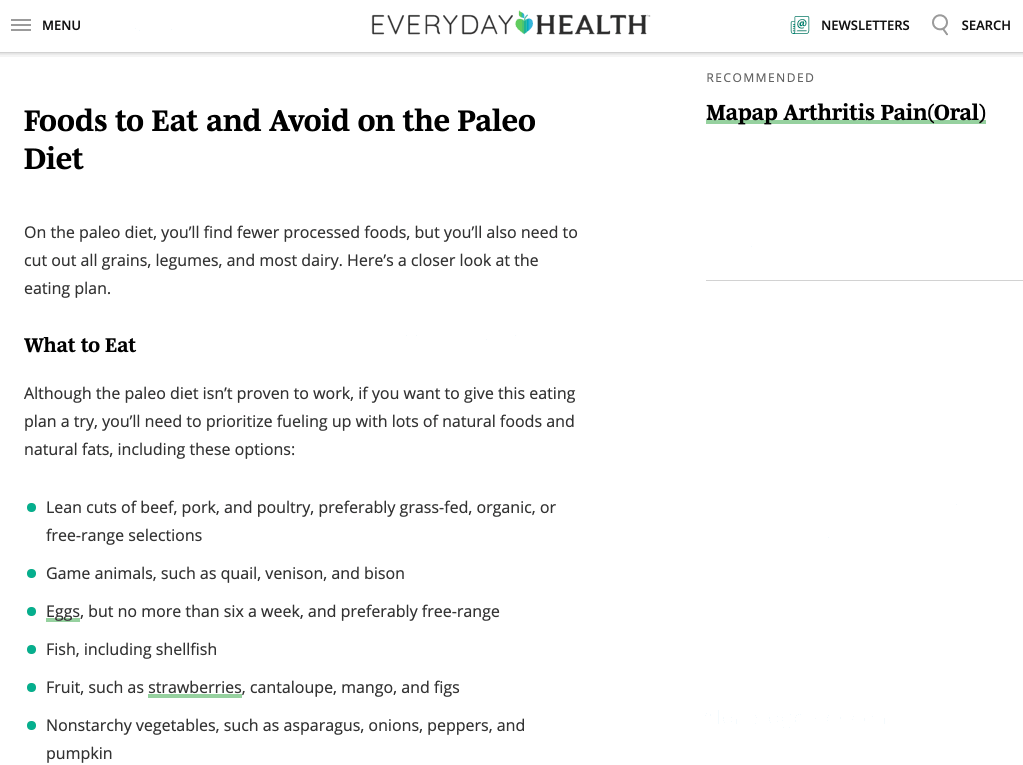
You can also plug a few top-ranking pages into Ahrefs’ Content Gap tool to find common keywords. Just paste in the page URLs and leave the bottom field blank.
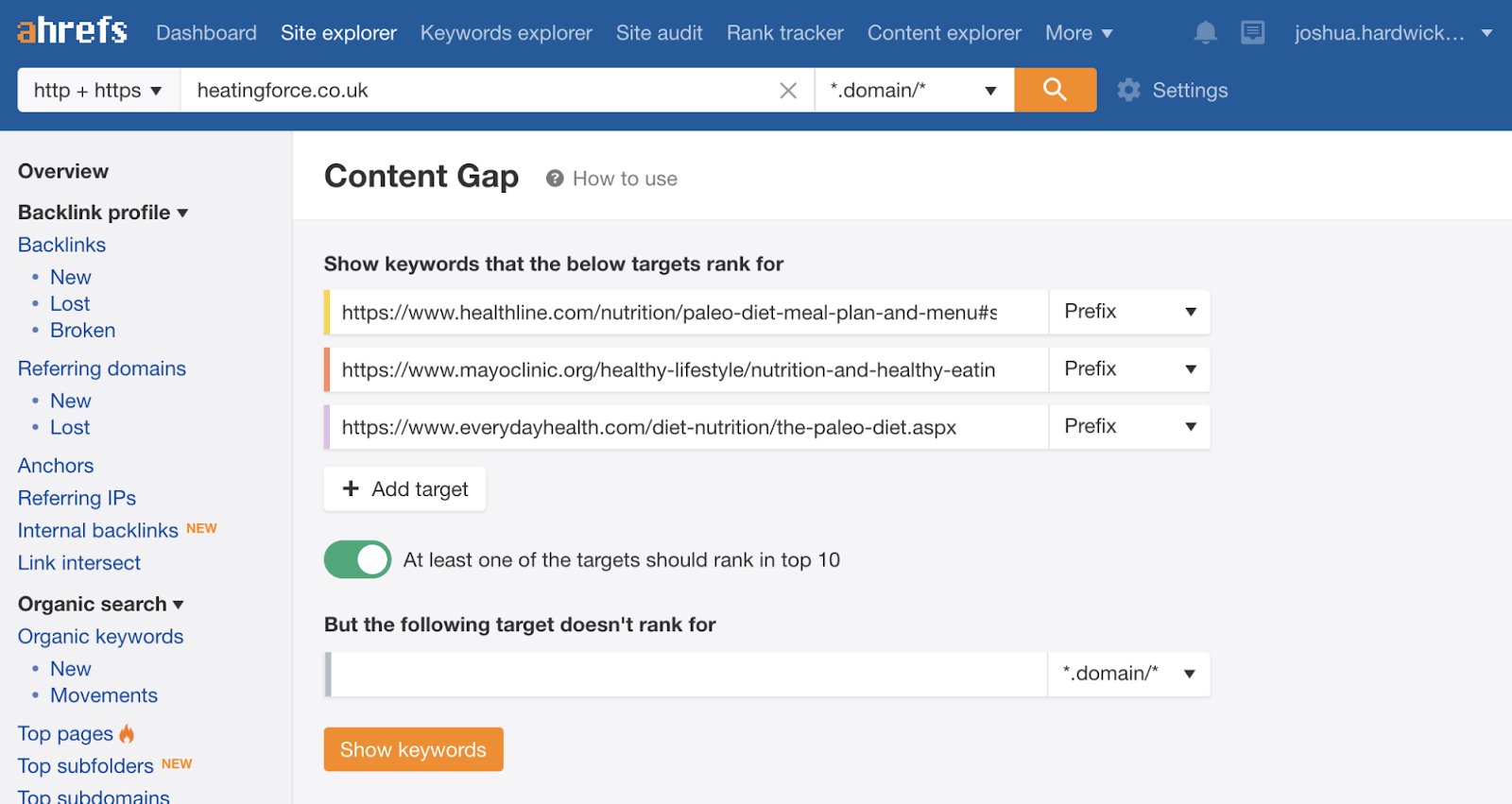
If we do this for the three top-ranking pages for “paleo diet,” there are hundreds of common keywords. While many are just different ways of searching for the same thing like “paleo diet” and “paleolithic diet,” there are a few keywords that represent subtopics like “what is the paleo diet,” “paleo diet foods,” and “why paleo is bad for you.”
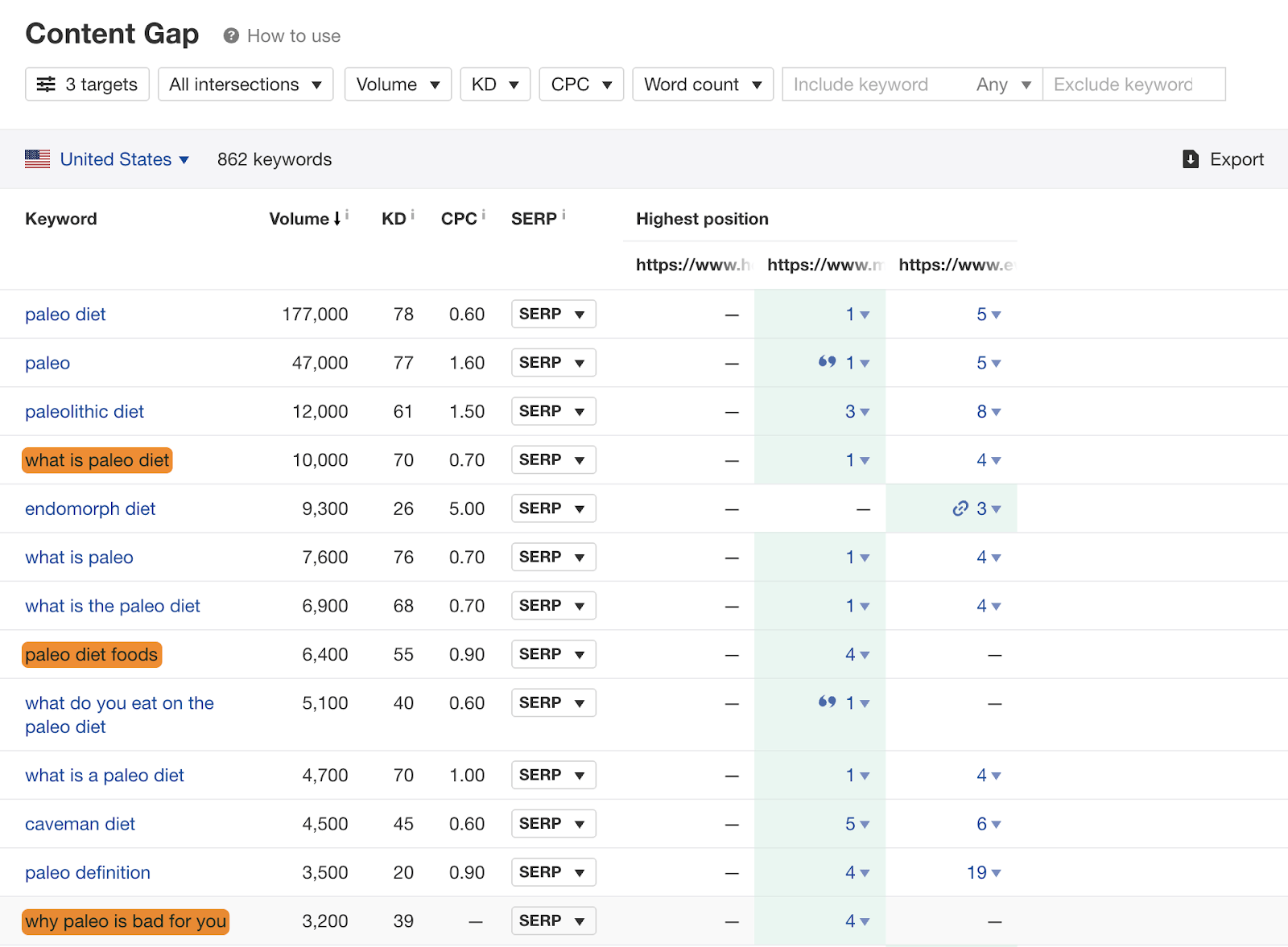
It would probably be worth talking about these things if you wanted to rank for “paleo diet.”
Step 4. Build high-quality backlinks
Backlinks are an important ranking factor. Google talks about them here, and we also found a clear positive correlation between backlinks and organic traffic in our study of over one billion pages.
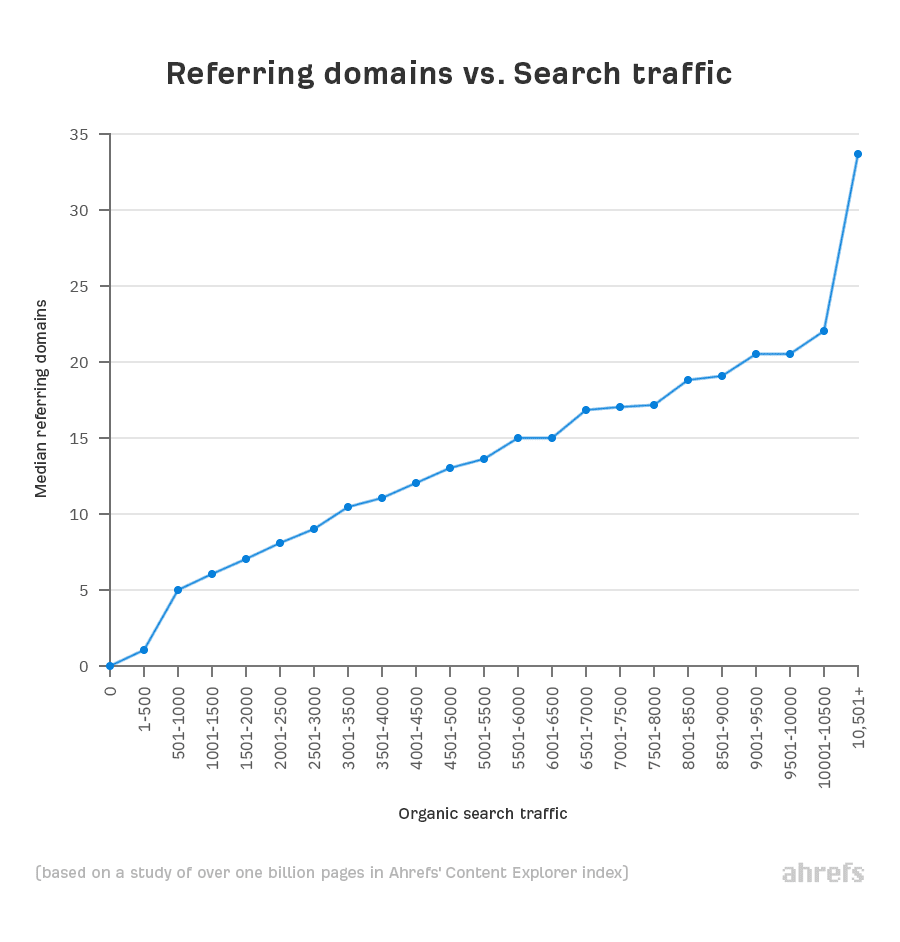
But how do you know how many backlinks you need to rank on top of Google?
Plug your keyword into Ahrefs’ free SERP checker and see how many domains link to the top-ranking page.
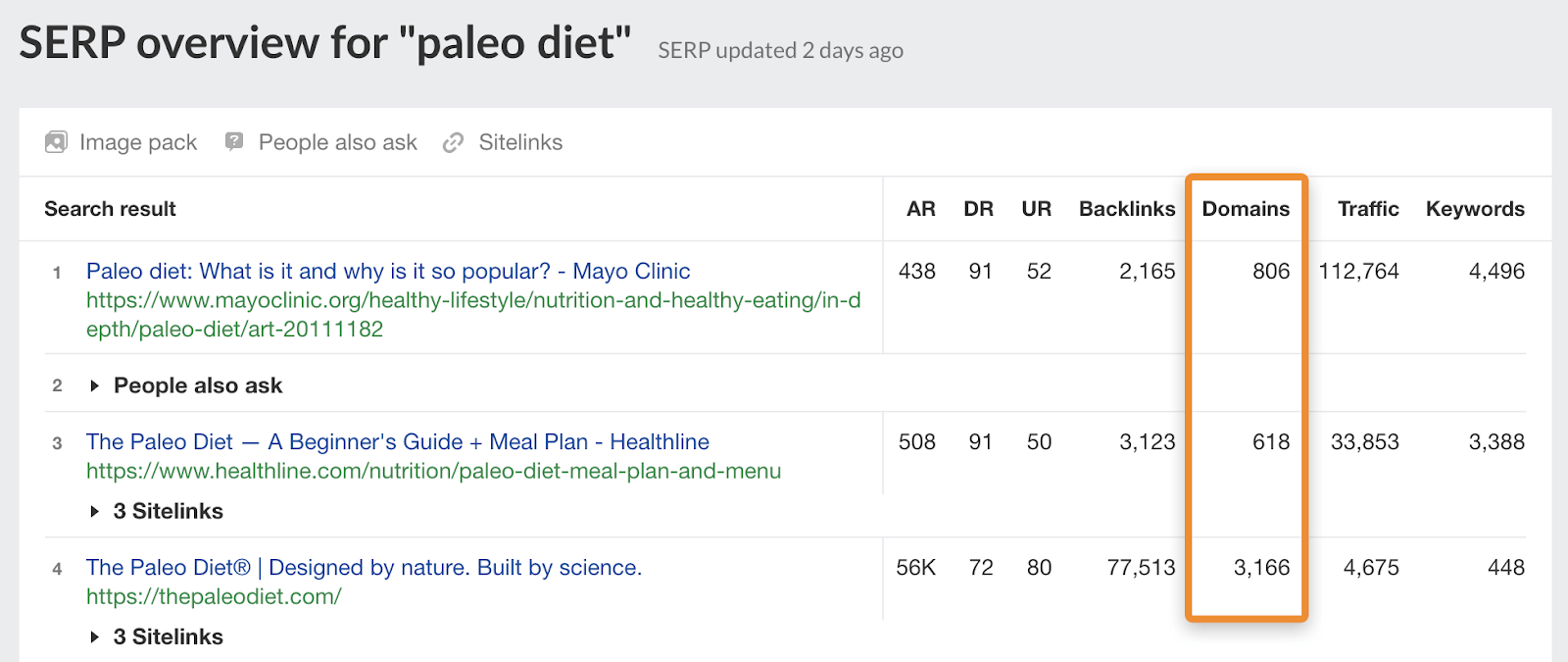
Just know that it’s not all about quantity. You might be able to outrank a page with lots of mediocre links with only a few high-quality links. Learn more in this video.
Recommended reading: The Noob Friendly Guide to Link Building
Step 5. Add internal links
Backlinks aren’t the only way to boost the ‘authority’ of a web page. Relevant internal links from other pages on your site also help. If you think you’ve built enough high-quality backlinks and still haven’t quite hit the number one spot, it might be worth adding a few internal links.
How can you find relevant internal linking opportunities? Just Google site:yourwebsite.com "keyword" to find pages on your site that mention the keyword or phrase.
For example, if we wanted to add relevant internal links to our SEO checklist, we’d search site:ahrefs.com "seo checklist".
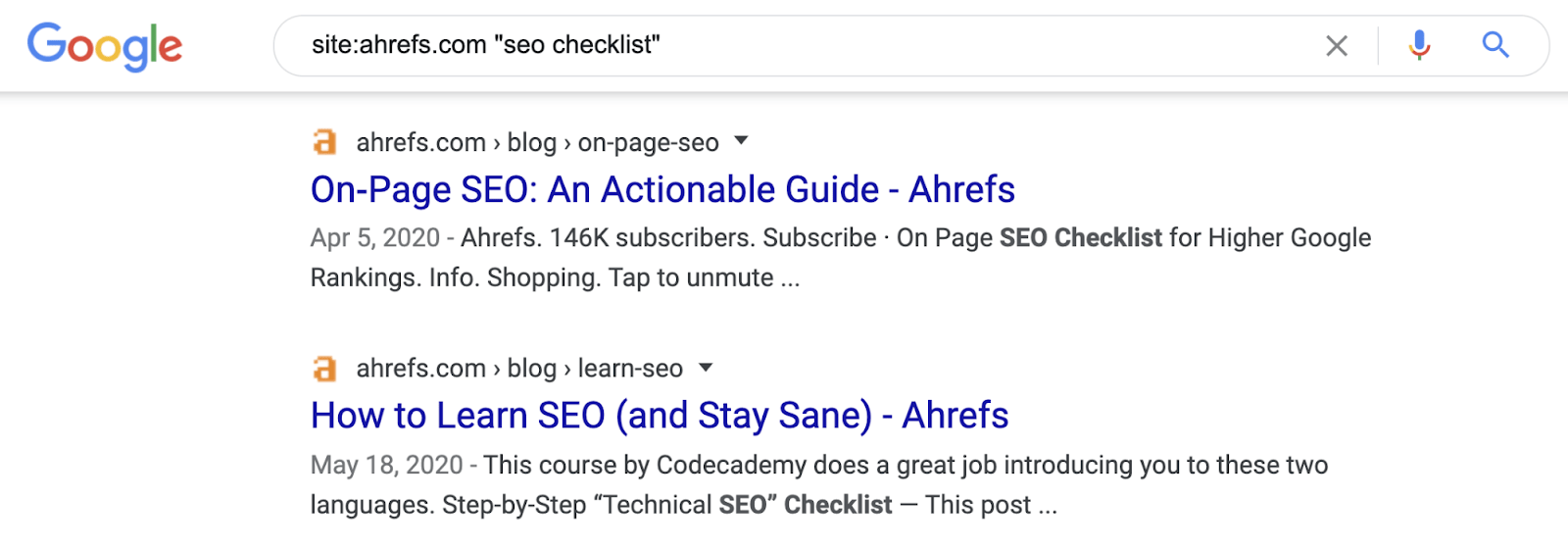
Here’s one example we found from our search:

You can see that the post includes the phrase “SEO checklist” but it doesn’t link anywhere. This is a great opportunity to add an internal link to our blog post.
Final thoughts
Getting on top of Google search is rarely an easy task, but it’s not rocket science either. You just need to figure out what type of results show up first and make an effort to get your website to show up there.
Looking to learn more about SEO? Read this or watch the video below.
Got questions? Ping me on Twitter.
![How to Get to the Top of Google’s Search Results [Interactive Guide]](https://ahrefs.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/blog-how-to-get-to-the-top-of-google-400x200.png)