Here are the top 15 mistakes organized from most to least major:
If Google can’t crawl your content, it can’t see what’s on the page. And if it can’t see what’s on the page, it’s unlikely it’ll rank for any relevant keywords.
How to ensure Google can crawl your site
Make sure you’re not blocking Googlebot.
Do this check by going to your robots.txt (yourdomain.com/robots.txt) and looking for these two snippets of code:
User-agent: Googlebot Disallow: /
User-agent: * Disallow: /
Both lines of code tell Googlebot it’s not allowed to crawl any pages on your site. To fix the issue, remove them.
If you’ve accidentally blocked Google from indexing your site or its pages, it’s impossible to rank. For example, that can happen if you accidentally added a noindex tag on any of your pages.
How to ensure Google can index your content
Sign up for a free Ahrefs Webmaster Tools account, then run a crawl on your site using Site Audit. If you have pages that are noindexed, that will pop up as an issue:
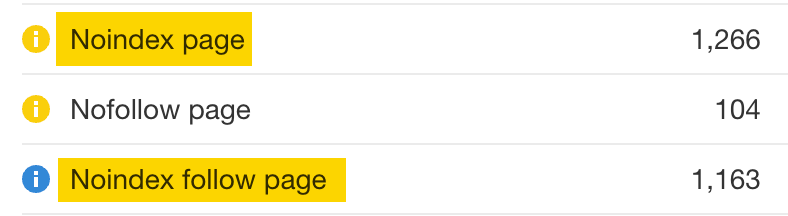
Fix the issue by removing the noindex tag.
Many people randomly create content and expect to get search traffic. But if no one’s searching for those topics, then no one’s clicking through to any pages.
That’s likely one of the reasons why 96.55% of pages get no traffic from Google, according to our study.
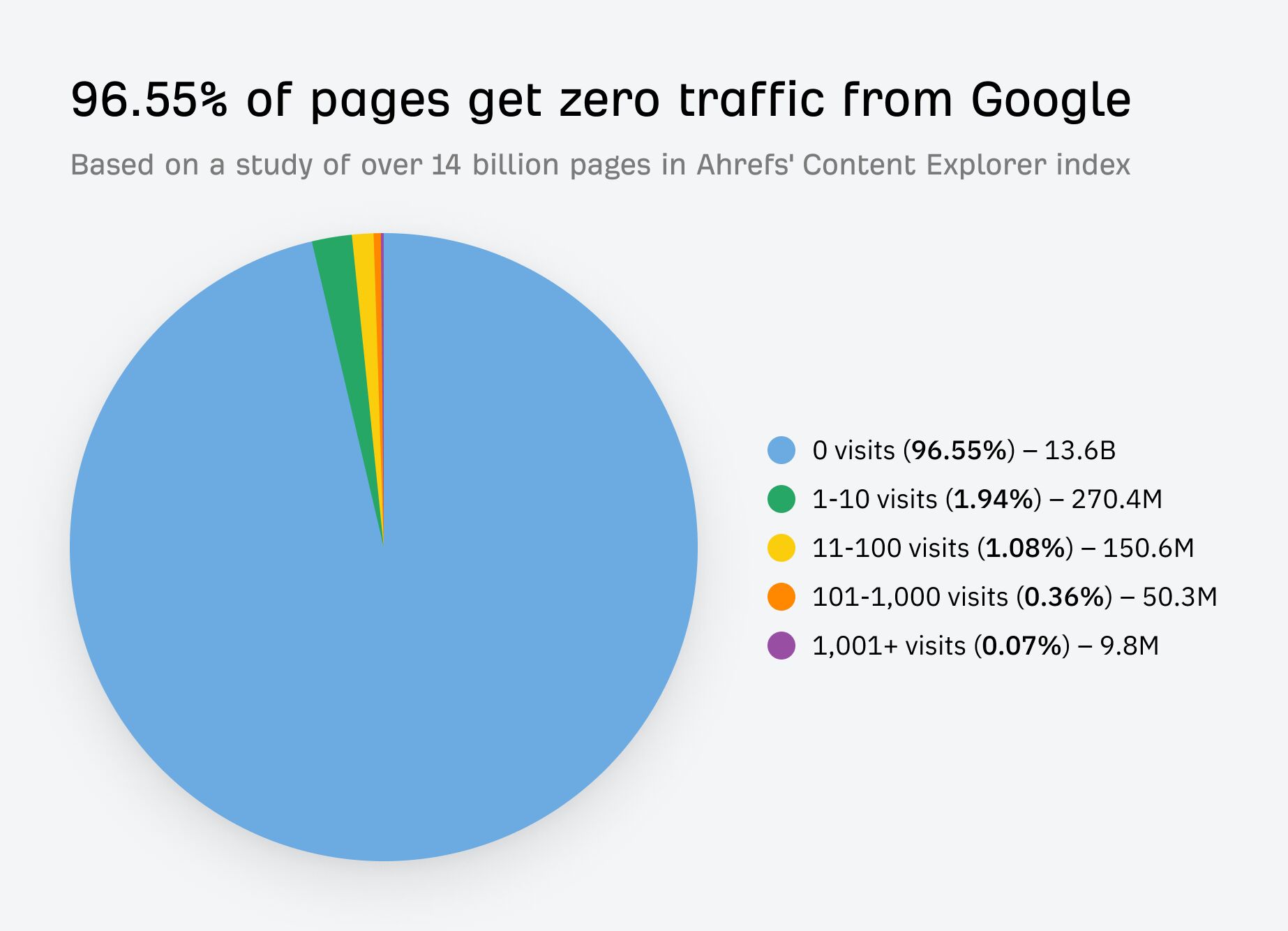
If you want search traffic, you need to target topics people are searching for.
How to do keyword research
- Go to Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Enter one or a few relevant keywords related to your website or niche
- Go to the Matching terms report
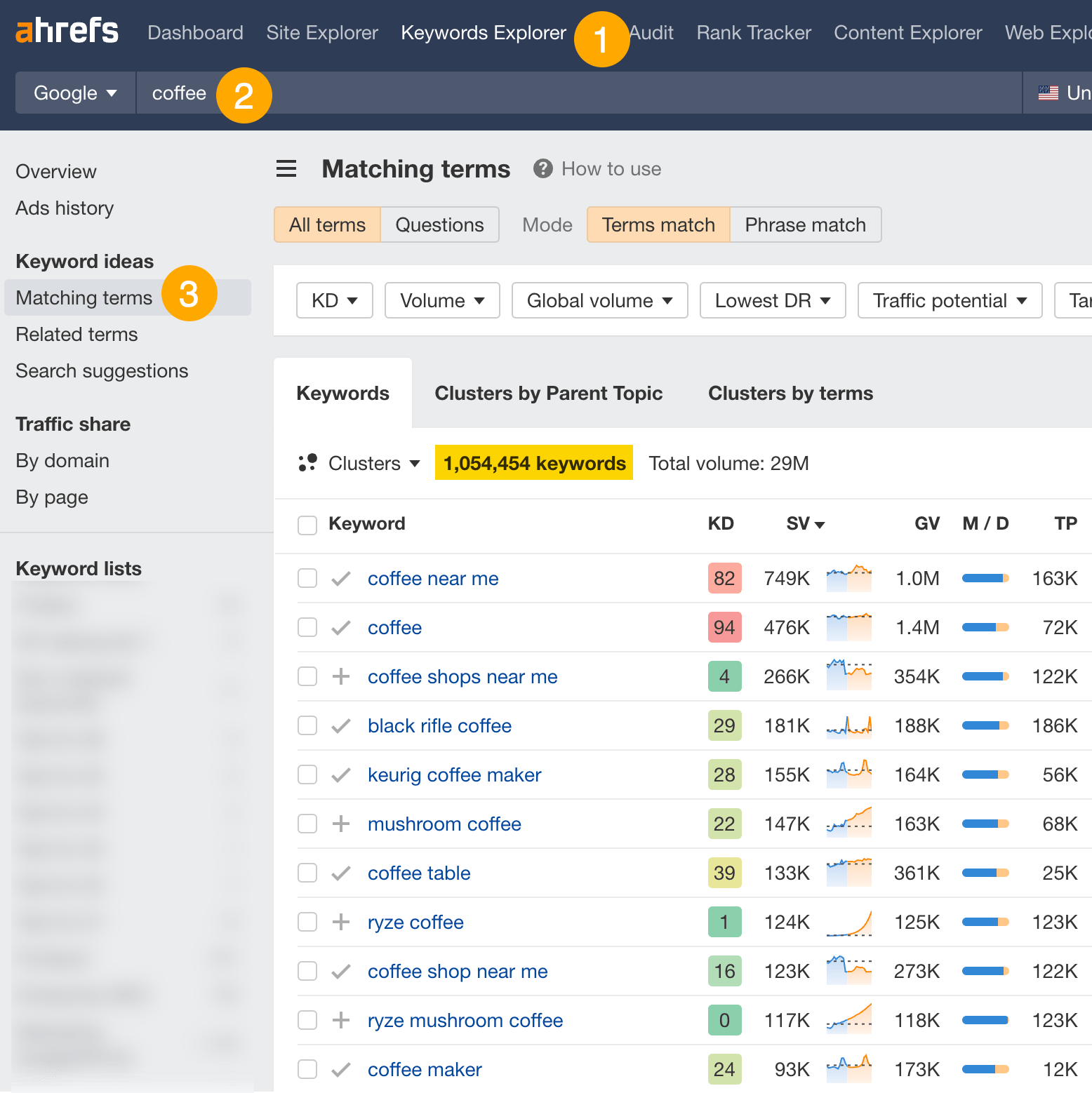
For example, if you sell coffee equipment, you’ll see >1 million potential keywords you can target. Look through the list and pick out keywords that are relevant and have traffic potential (look at the TP column.)
Google’s goal is to provide users with the most relevant result for every query.
So, if you want to rank high on Google, you need to be the most relevant result. This means matching search intent, the why behind a query.
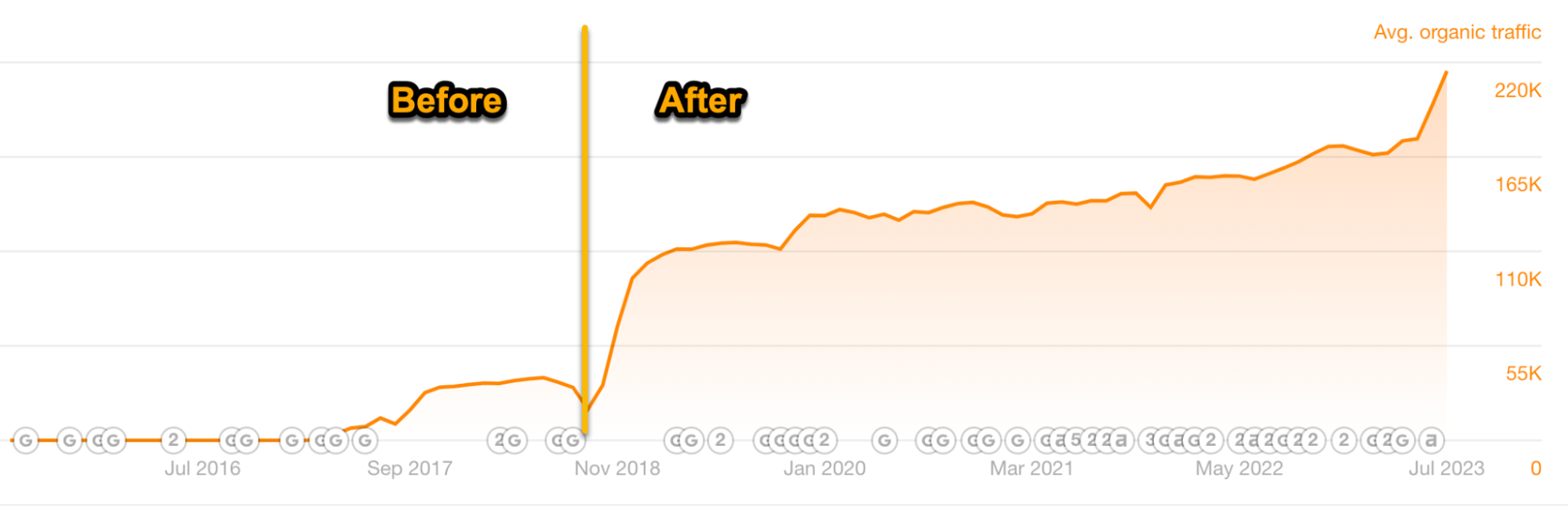
For example, we previously created a landing page to target the keyword “backlink checker.” But it didn’t rank well because searchers wanted a free tool. So, we added it.
The result: 516% more traffic in less than six months.
How to match search intent
Links are an important Google ranking factor.
So, if your pages are not ranking well, a key reason might be you don’t have enough links.
For example, we would like to rank for the keyword “seo.” But if you look at the top-ranking pages for that keyword, they have tons of backlinks.
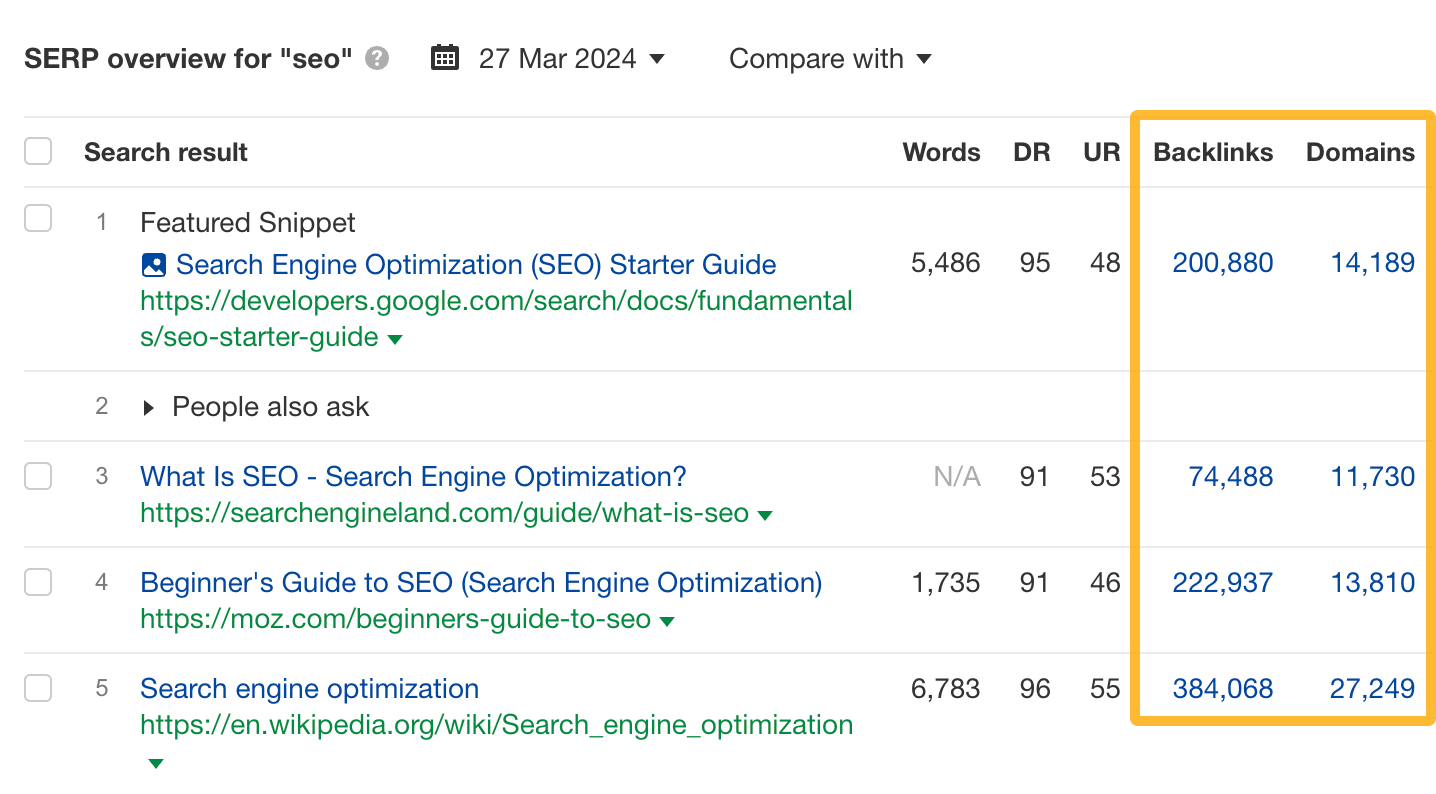
As of right now, our page simply doesn’t have enough:
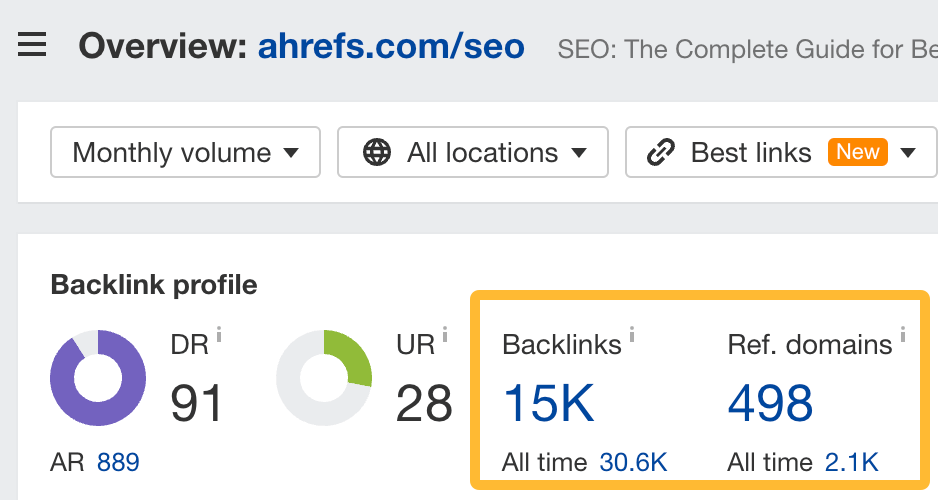
How to build more links
There are many ways to build links, but one good way to start is to see how your competitors have gotten their links. From there, you can attempt to “replicate” their links.
Bear in mind that it’s impossible to replicate all their backlinks, and replicate them like-for-like. But there are a few ways you can attempt to reproduce similar links.
For example, if you’re in an industry with many interviews and podcasts, you can find out where they’ve appeared and see if you can pitch to be on the same podcasts.
Here’s how to find their podcast appearances:
- Go to Site Explorer
- Enter the Twitter profile URL of your competitor’s CEO, CMO, or whoever the most prolific marketer is within the company
- Go to the Backlinks report
- Filter for results where the referring page URL contains “podcast,” “episode,” or “interview”
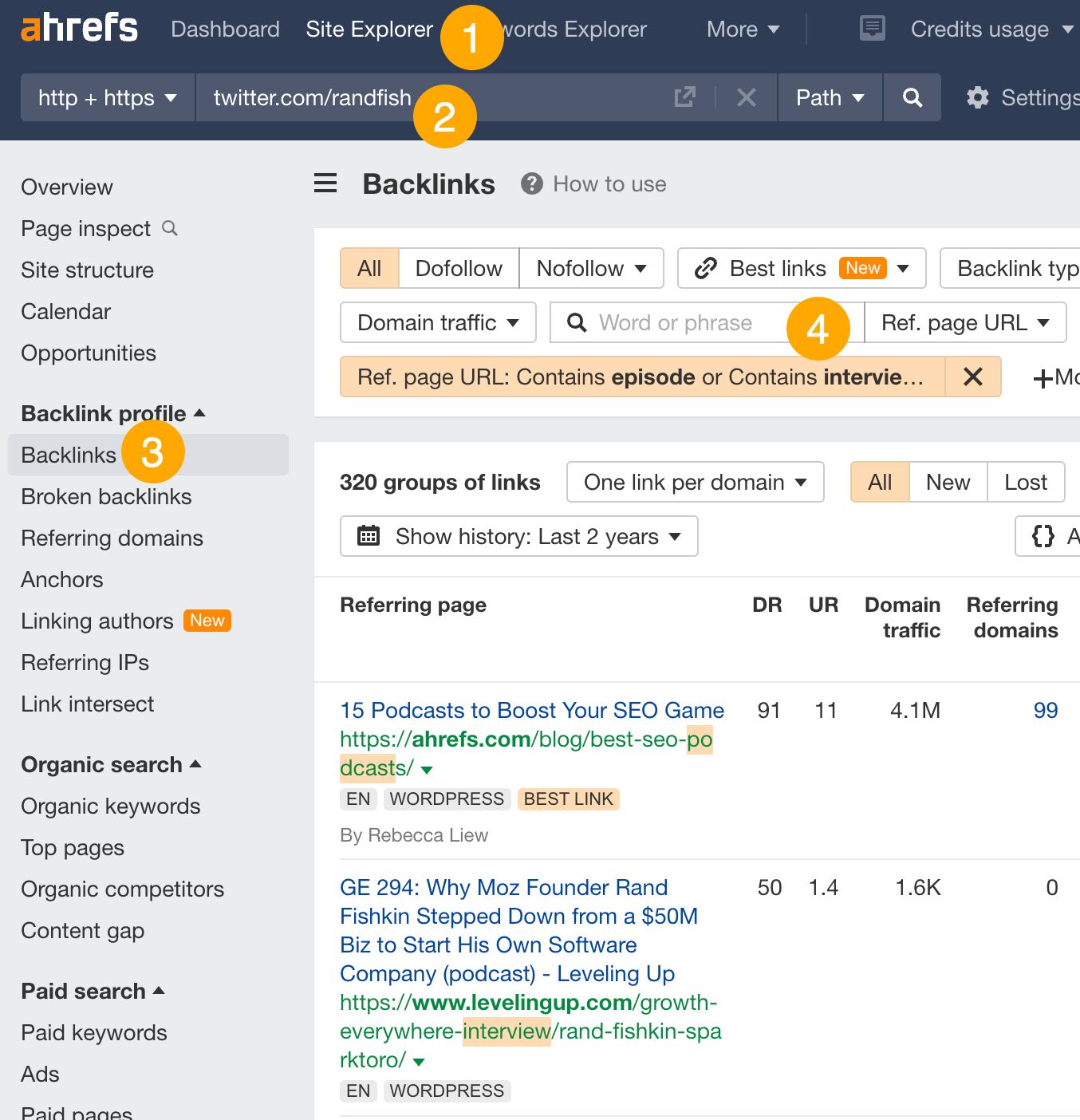
You just need to pitch the same interviews and podcasts.
Buying backlinks is against Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. If they suspect you of doing this, they might slap you with an unnatural links manual action and demote or remove your site from their search results.
https://twitter.com/NicheDown/status/1587168448697737217
Even if you don’t get a manual action, you might get demoted algorithmically.
Here’s what Google’s John Mueller says:
“If our systems recognize that they can’t isolate and ignore these links across a website, if we see a very strong pattern there, then it can happen that our algorithms say well we really have kind of lost trust with this website and at the moment based on the bigger picture on the web, we kind of need to be more on almost a conservative side when it comes to understanding this website’s content and ranking it in the search results and then you can see kind of a drop in the visibility there.”
How to avoid this SEO mistake
Don’t buy links.
SEO is not simply a matter of fixing all of these mistakes and calling it a day.
Even if you’re ranking in pole position today, there is no guarantee you’ll be number one tomorrow. Ranking high on search engines is a competition. Your competitors will invest plenty of resources to knock you off the perch.
How to avoid this SEO mistake
The recommendations in this post aren’t just for fixing a one-time mistake. They’re strategies you should be consistently doing to rank high on Google:
- Doing keyword research
- Creating content that aligns with search intent
- Trying to build and earn more backlinks
- Ensuring your site is technically sound
- Updating content when it’s outdated
Case studies like this are seductive:
We pulled off an SEO heist that stole 3.6M total traffic from a competitor.
— Jake Ward (@jakezward) November 24, 2023
We got 489,509 traffic in October alone.
Here’s how we did it: pic.twitter.com/sTJ7xbRjrT
How to use AI in content creation
Google is not fundamentally opposed to AI content. It doesn’t care how you create it; it just cares about helpfulness for users.
The problem, however, is that AI cannot create valuable content that users want to see. It cannot conduct research, share personal experiences, defend an opinion, or provide nuanced discussions.
So, while you may use AI to help with your content creation, don’t generate content and publish it as-is. Make sure you’re adding value where AI cannot.
My colleague Ryan Law has identified three areas where humans can generate unique value:
- Experimentation — Go into the real world, test ideas, and collect new information that has never existed before. For example, conducting industry surveys or running tests.
- Experience — Prove to the reader you have experienced the thing you’re writing about. For example, only writing about topics you have experience with or interviewing people on topics you don’t.
- Effort — Expend energy and create content that’s more than just words on a page. For example, webcomics, video series, books, and more.
Internal links are important:
- Google uses them to discover new content.
- They aid the flow of PageRank around your site. Generally speaking, the more internal links a page has, the higher its PageRank.
- Google looks at the anchor texts of internal links to better understand the context.
Yet, internal links are usually not prioritized. Big mistake.
How to find internal link opportunities
Run a crawl using Ahrefs’ Site Audit (via AWT). Once the crawl is complete, go to the Internal link opportunities report.
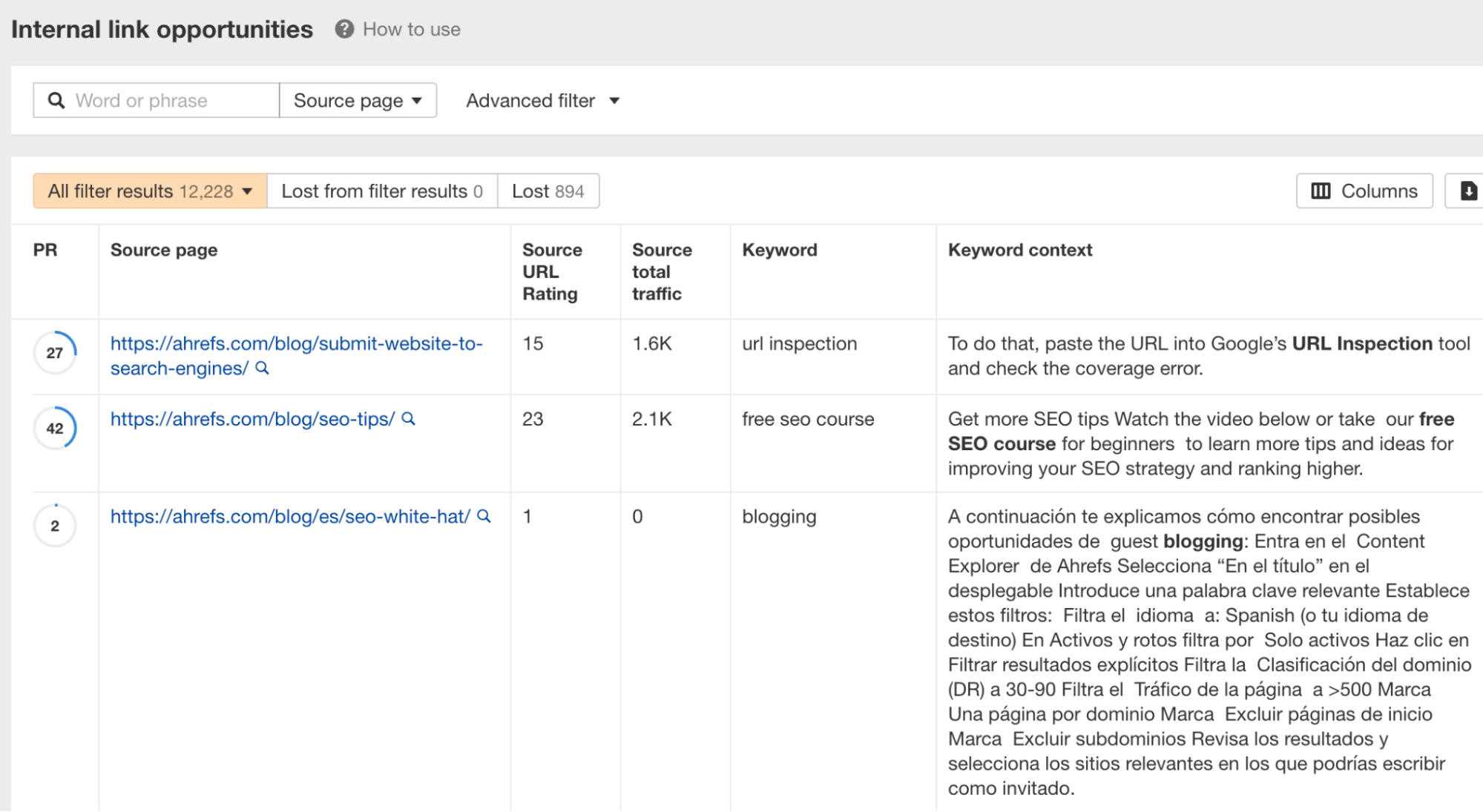
This report will show you relevant internal link opportunities. Go through the list and add internal links where relevant.
Core Web Vitals are metrics that are part of Google’s Page Experience signals used to measure user experience. They’re also a Google ranking factor.
Not only will a slow site affect your Google rankings, but it will also impact your sales. According to Unbounce, nearly 70% of consumers admit that page speed impacts their willingness to buy from an online retailer.
How to fix slow pages
Run a website crawl using Site Audit and you’ll be able to see your Core Web Vitals performance:
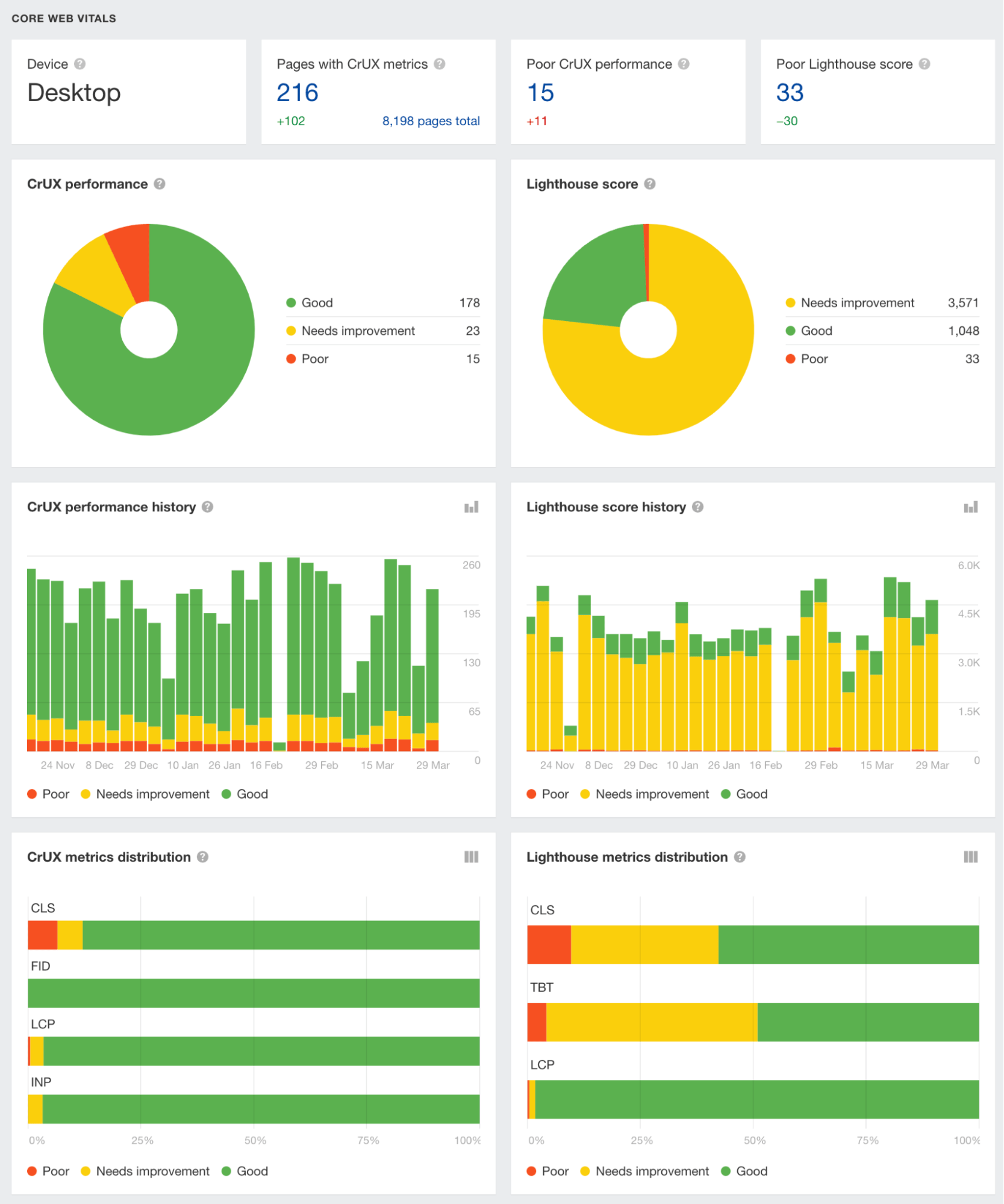
Some ways to improve your Core Web Vitals:
- Use caching — If you’re using WordPress, you can install a plugin like W3 Total Cache or WPRocket
- Make files smaller, e.g. images — Plugins like Shortpixel help to compress and optimize your images
- Serve files closer to users — For example, you can use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Optimize fonts — WPRocket helps with this
- Reduce the amount of JavaScript — Similarly, WPRocket helps with this. You can also use Autoptimize
Schema markup is code that helps search engines understand the information on a page. Google can use it to show rich results (also known as rich snippets), which can earn a page more clicks.

Unfortunately, some SEOs have taken it to mean that they can add all sorts of irrelevant schema to their pages, in hopes of ranking higher.
It can’t be further from the truth: Not only can schema markup spam lead to a Google penalty, it rarely works because Google can spot it.
How to avoid this SEO mistake
Here are instructions directly from Google’s structured data guidelines:
- Follow the spam policies for Google web search.
- Provide up-to-date information.
- Provide original content that you or your users have generated.
- Don’t mark up content that is not visible to readers of the page.
- Don’t mark up irrelevant or misleading content, such as fake reviews or content unrelated to a page’s focus.
- Don’t use structured data to deceive or mislead users. Don’t impersonate any person or organization, or misrepresent your ownership, affiliation, or primary purpose.
- Content in structured data must also follow the additional content guidelines or policies, as documented in the specific feature guide.
Keyword stuffing is the process of cramming a page full of keywords, in an attempt to rank higher for those keywords.
Here’s an example of keyword stuffing:
Finding the top mirrorless camera can be a daunting task. Yet, with our comprehensive best mirrorless camera guide, we simplify the process by ranking the best mirrorless camera models and the most reliable mirrorless camera brands.
Not only does keyword stuffing make your content look unnatural, it is also against Google’s spam policies.
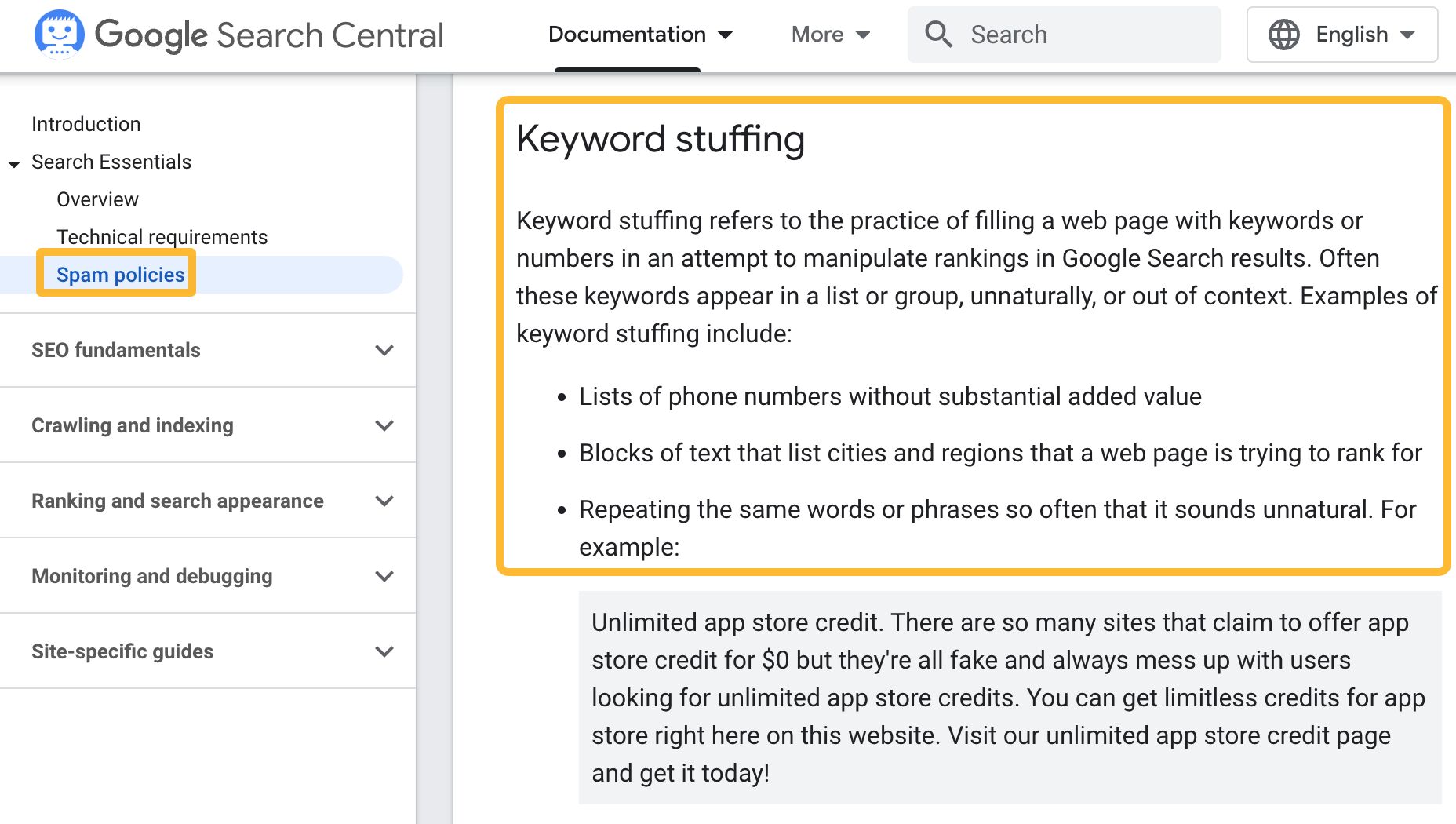
How to avoid keyword stuffing
Instead of trying to shoehorn related keywords into your content, focus on creating content that’s comprehensive instead. In fact, Google encourages this in their Helpful Content guidelines:

To create comprehensive content, you need to cover important subtopics searchers expect to see. Here’s how to find these subtopics:
- Go to Keywords Explorer
- Enter your target keyword
- Scroll down to SERP Overview
- Check three relevant top-ranking pages
- Click Open in and choose Content gap
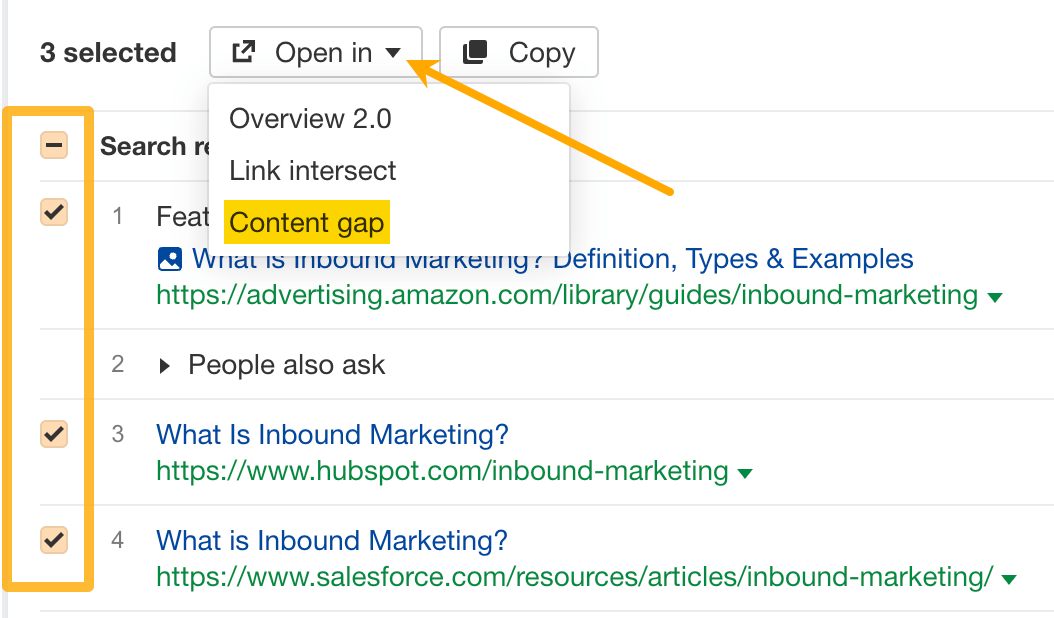
This will open the Content gap report, which shows you the common keywords these three pages are ranking for. Many of them will be important subtopics you should cover.

For example, if we were targeting the keyword “inbound marketing”, these would make great H2s:
- What is inbound marketing
- Inbound marketing strategy
- Inbound marketing examples
- Inbound marketing tools
There is a myth in SEO that longer content performs better. This ends up in an arms race: SEOs fighting to make their blog posts as long as possible.
But nobody is clamoring to read longer posts. When Medium studied the correlation between post length and average reading time, they noticed that engagement started to drop for posts with a reading time longer than seven minutes.
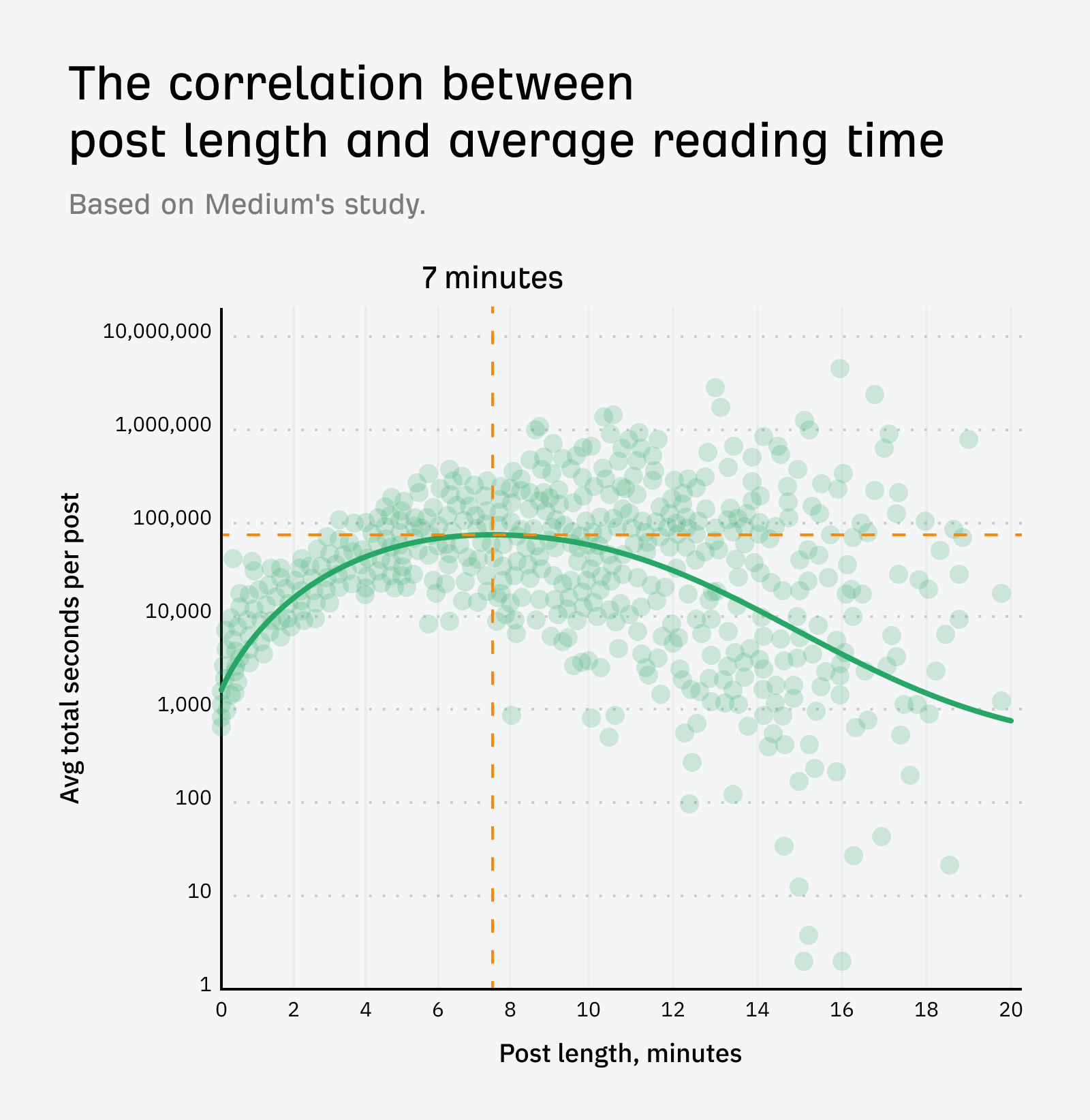
Our own study has also found that there was only a moderate correlation between content length and organic traffic up to 2,000 words. For posts longer than 2,000 words, there is a moderate negative correlation between word count and organic traffic.
How to avoid this SEO mistake
If your article is long because the topic you’re tackling is deep, so be it. If your article is short because the topic is simple, then let it be. Don’t make it longer than necessary.
In short: Focus on being comprehensive, not being lengthy. Nobody wants to read Dostoyevsky just to cook a simple fried rice.
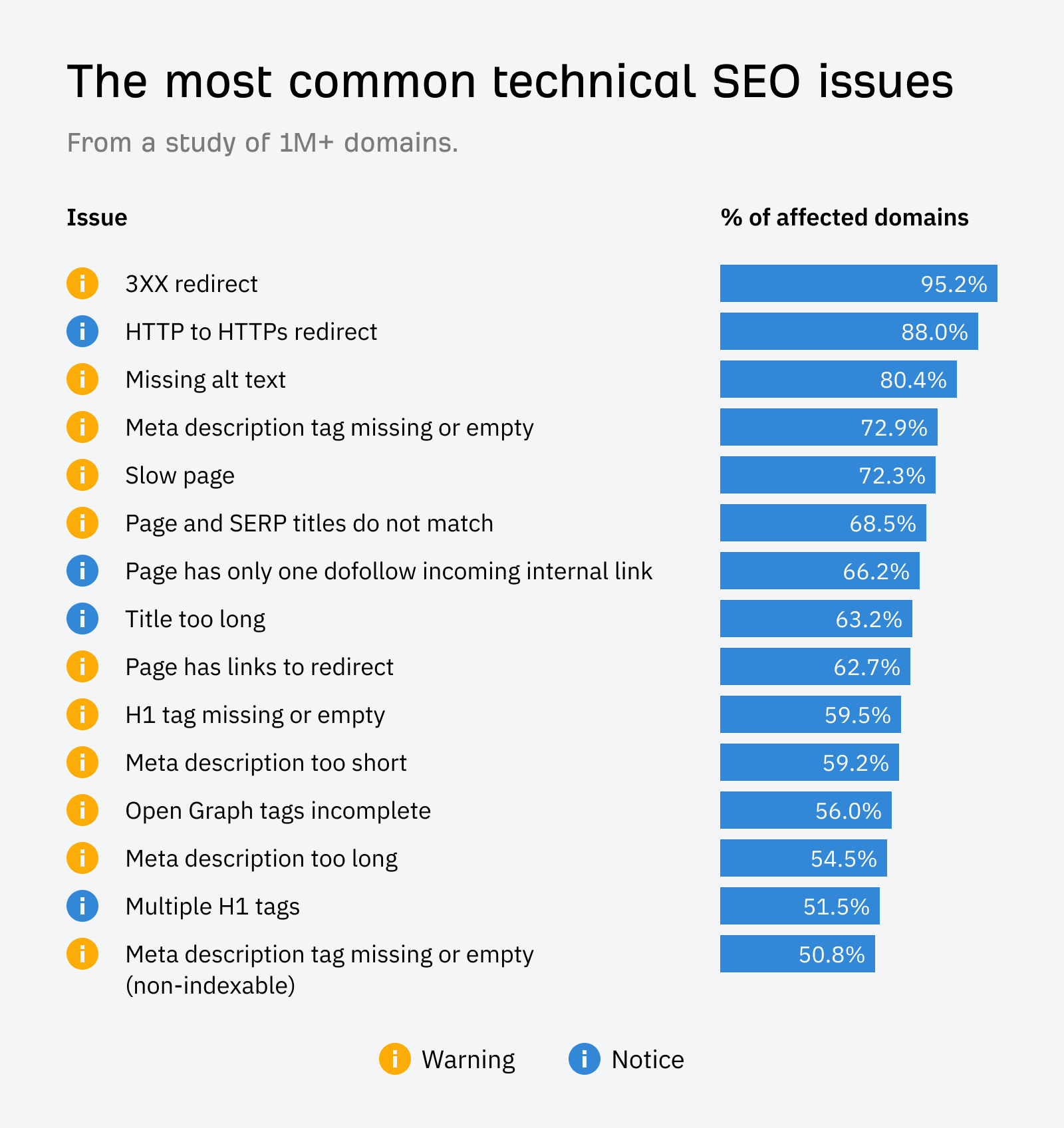
Title tags and meta descriptions are the first things a searcher sees when they enter a query. It can be the difference behind whether a searcher clicks through.

However, many websites neglect these two tags. When we looked at >1 million domains to find the most common technical SEO issues, meta tag issues like:
- Meta description tag missing or empty
- Page and SERP titles do not match
- Title too long
- Meta description too short
- Meta description too long
Were in the top 15 most common.
How to fix under-optimized meta titles and descriptions
Run a crawl with Site Audit (free with AWT). You’ll see all the meta tag issues, along with the affected URLs.
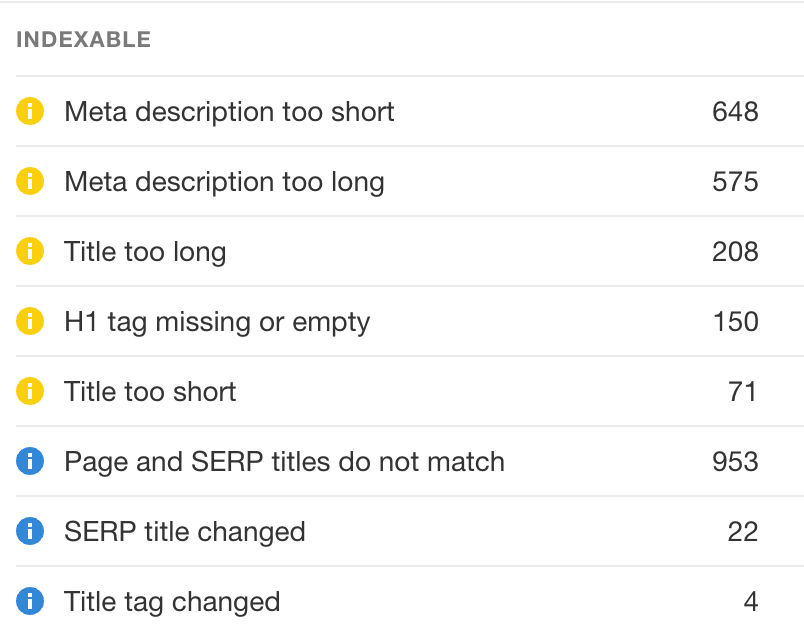
Fix them.
If you’re stuck, you can ask ChatGPT to brainstorm title tag ideas for you and get inspiration.

Alt text describes an image on a web page.
Not only can it help improve topical relevance on a page, it can also help you rank in Google images. And while you may not think it, Google Images is the second largest search engine in the world.
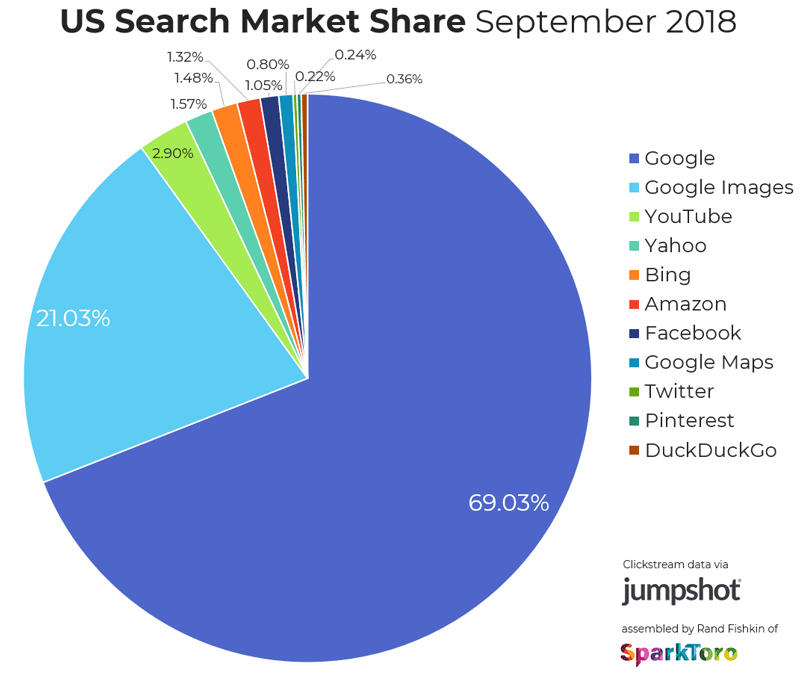
However, I want to point out that this is likely a minor issue. If you’re making any of the mistakes in this post, focus on fixing them first. As the saying goes, “don’t major in minor things.”
How to fix missing alt text
Run a crawl with Site Audit. This will tell you if you have any images with missing alt text.

Click the number to see the affected URLs. All that’s left is to fill in the missing ones. If you’re struggling, you can use our free AI image alt text generator.
Upload your image, select a tone, and you’re off to the races.
Keep learning
You now have an understanding of what common SEO mistakes you could be making and how to avoid and fix them. If you want to dig deeper and continue learning, check out these resources:



