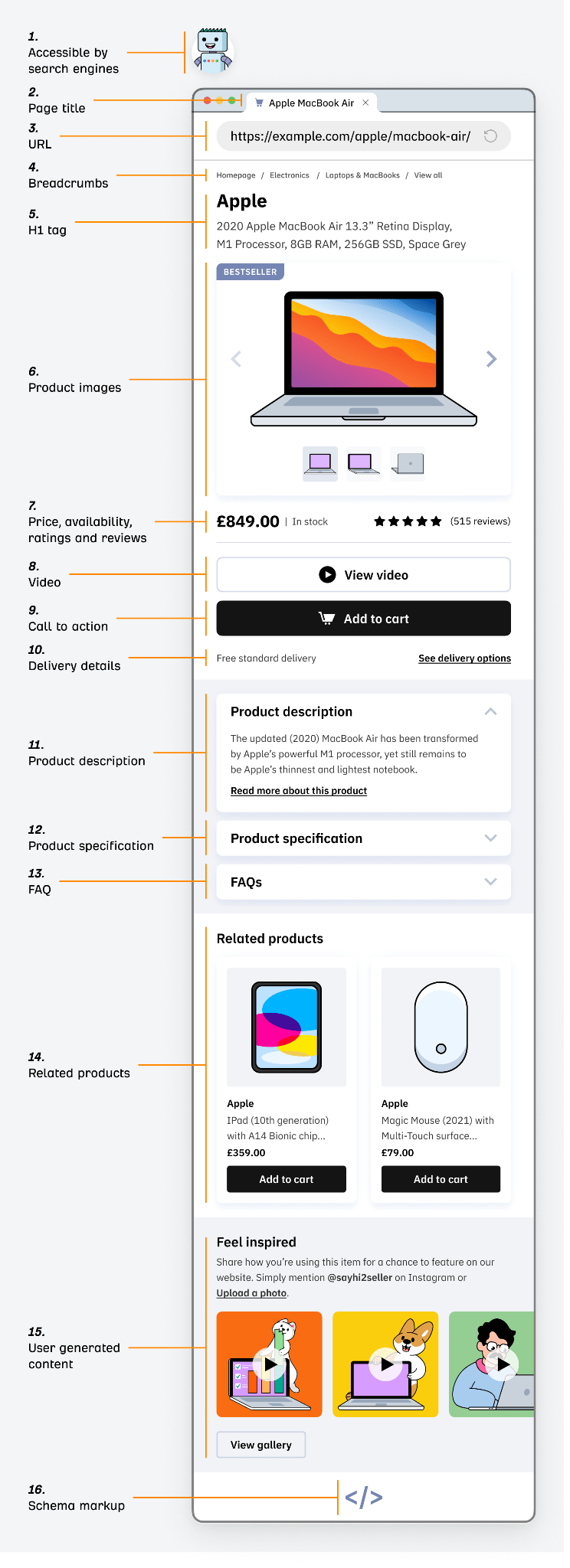
In this beginner’s guide, I’ll share 16 elements that collectively make up the anatomy of a well-optimized product page. I’ll also explain how to audit your product pages for issues.
What makes a great product page?
Product pages are one of the more definable content page types in SEO because they contain certain common elements people expect to see.
Let’s explore the anatomy of a well-optimized product page:
Before you start to check onsite elements, it’s a good idea to check if your product page is able to be crawled and indexed by search engines. If not, you’ll be wasting your time optimizing your product page for everything else.
The quickest way to check this is to navigate to the product page and open it up in the Ahrefs’ SEO Toolbar. Then click on the Indexability tab.
If there are any issues, the toolbar will flag them in a red circle in the sidebar.
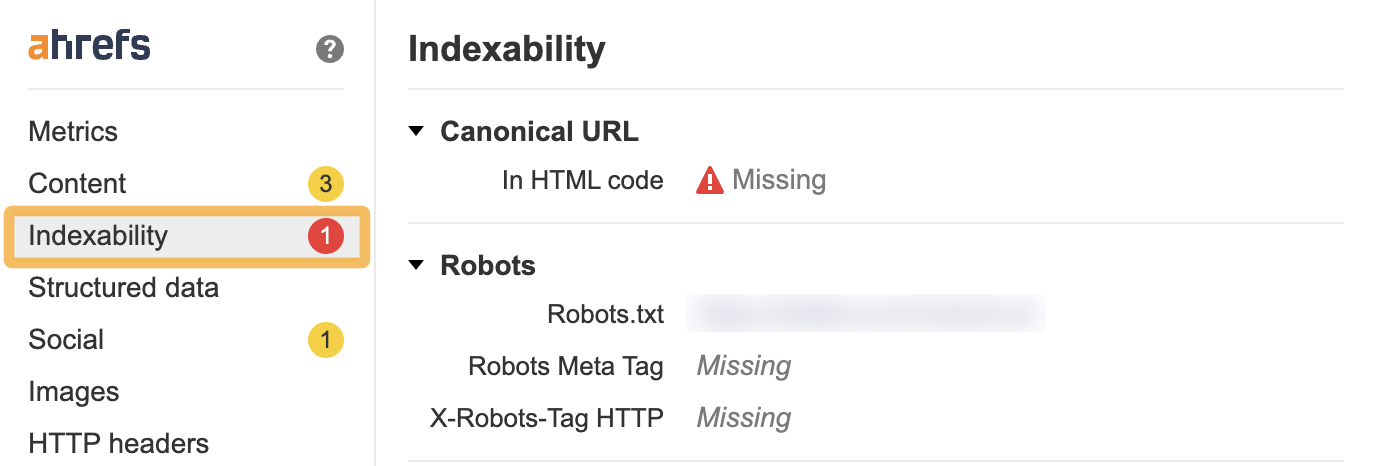
There are a few basic checks you should make. Make sure that the product page:
- Is not blocked in robots.txt
- Has no noindex tags on the page
- Has a canonical in the head of the HTML code (in most cases, it will be self-referencing)
- Included in your sitemap.xml file
Once you’ve passed these initial technical SEO hurdles, it’s time to get started.
A title tag (also known as a page title) is a piece of HTML code that specifies the title of a webpage. They appear in Google’s search results and are a minor Google ranking factor.
They look like this:
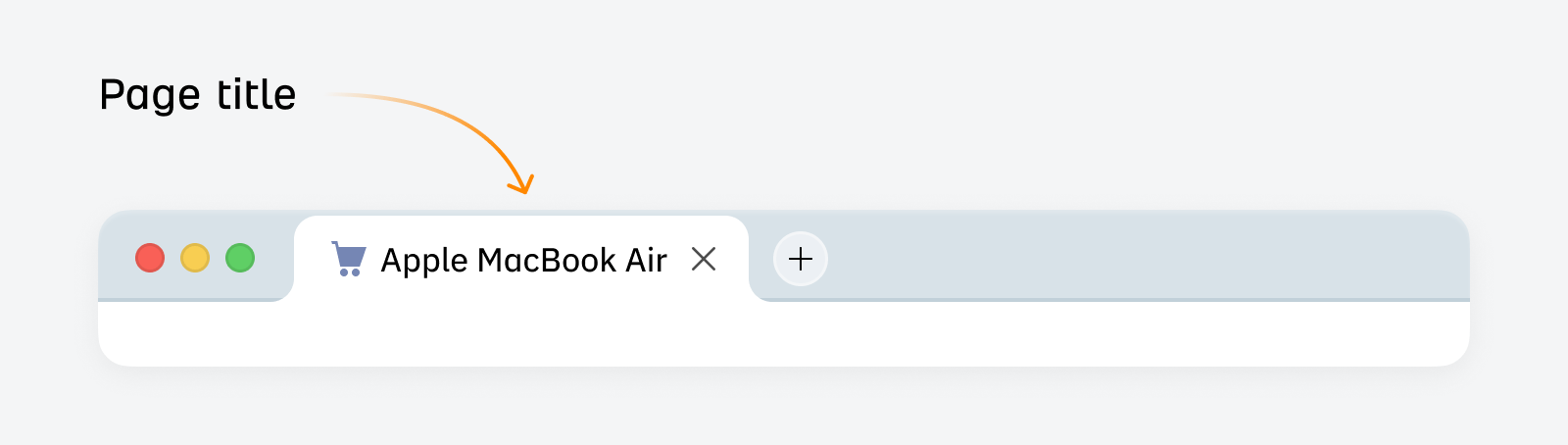
Your product page title should be clear, say what the product is, and use relevant keywords that accurately describe the product. This helps searchers and search engines understand what your product page is about.
You can use Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer to get inspiration from competitors’ product page titles in the SERP overview.
If users search for your products using stock-keeping units (SKUs) or other product identifiers, then it’s a good idea to include this information in your product page title tag and your URL.
One of the best examples of where this would be important is for a brand like Lego.
Here’s an example of the Lego Land Rover Classic Defender 90 product. The SKU is included in both their page title and their URL:

Even if you just search for “10317” using a tool like Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer, you can see that their site appears at the top of the SERP.
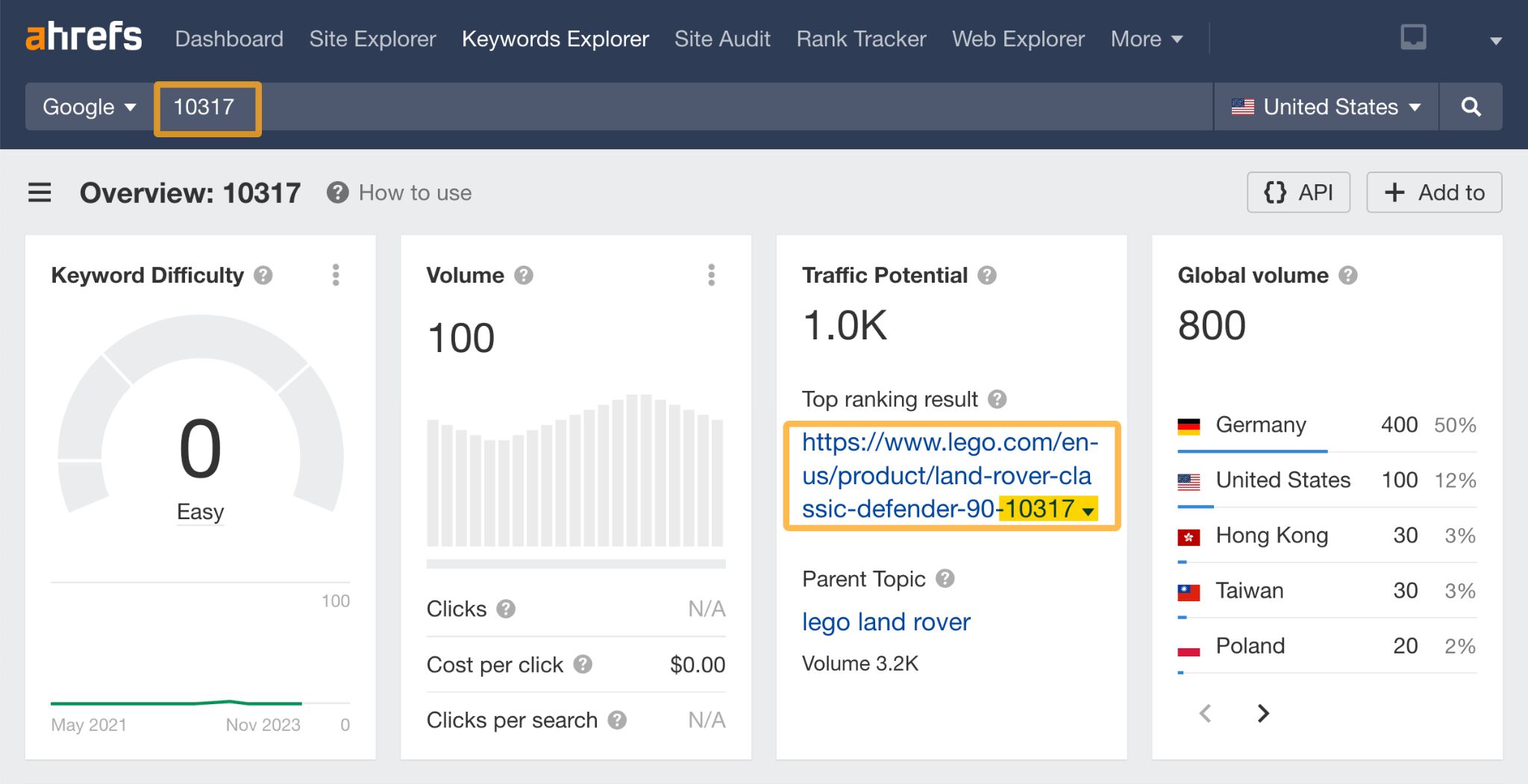
TLDR; if SKUs or product identifiers are important for your business—and customers are searching for them—then it may be useful to include them both in the URL and title tags of your products.
URLs are located in the address bar of your browser. An SEO-friendly URL should be easy to understand and clearly indicate the page’s content. Creating well-thought-out URLs early on will help create a logical website structure in time.
Google’s advice when it comes to URLs is:
“Create a simple URL structure. Consider organizing your content so that URLs are constructed logically and in a manner that is most intelligible to humans.”
Here’s what a well-structured URL looks like:

And here are some more tips for creating URLs:
- Use relevant keywords that accurately reflect the product to help search engines understand the page’s context
- Keep URLs concise and avoid unnecessary characters or complex structures, as simpler URLs are easier for users to digest
- Use hyphens to separate words rather than underscores or spaces to make the URL easily readable
- Be consistent in your URL structure — it’ll make your website easier to navigate and enhance the user’s experience by providing a clear idea of what to expect on the page
- Don’t bury important keywords lower down in your URL hierarchy
In the SERPs, there are complicated and seemingly illogical URL structures in every SERP that rank well—especially in ecommerce land. This doesn’t mean you should ignore URL structure completely, but try to establish a consistent structure early on and stick to it.
Breadcrumbs are internal links that show users their location in the site’s hierarchy and help them navigate quickly through the website.
They look like this:
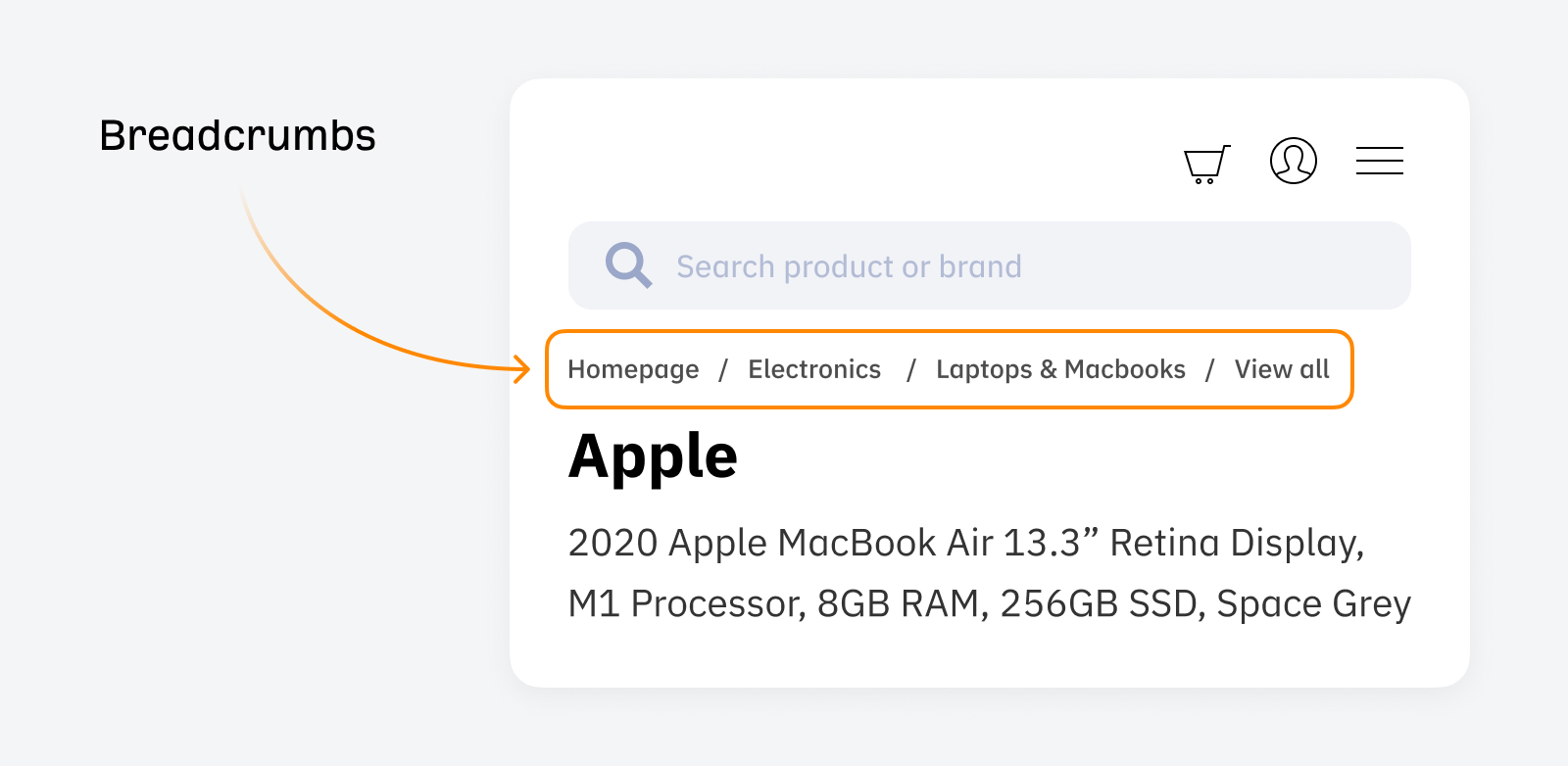
They’re useful for SEO because they create a logical structure that search engines can crawl and understand.
Breadcrumbs allow users to check their position on your site and to backtrack if necessary. This is useful for ecommerce stores because users often navigate between category pages and many product pages when deciding which product to buy.
Implementing schema markup for breadcrumbs can help optimize them for search engines.
The H1 tag is an HTML element that signals to users and search engines what the page is about.
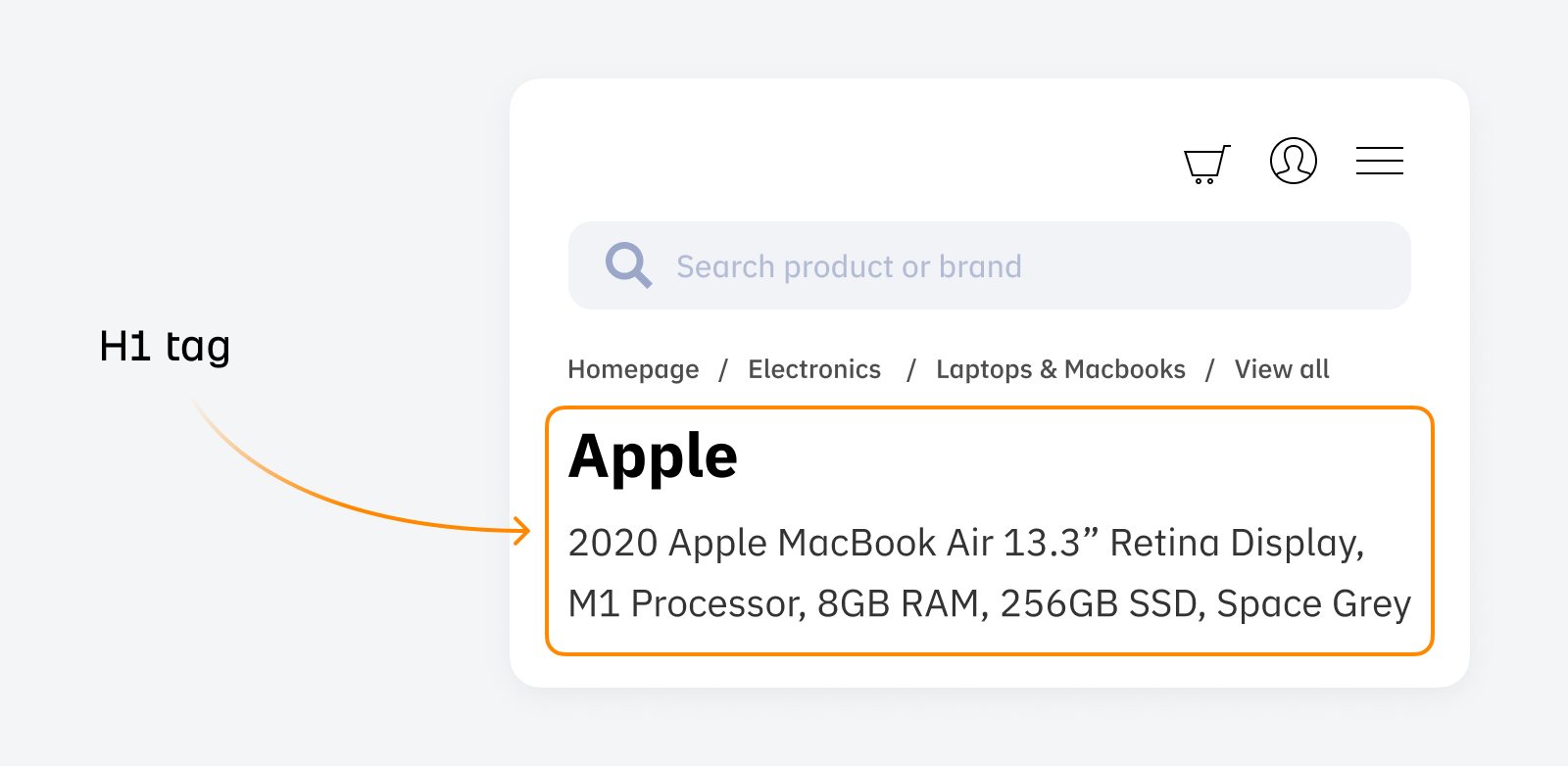
The main difference between H1 tags and title tags is where they appear—H1 tags do not appear in Google search results, but appear on the page.
This is what an H1 tag looks like in the code:
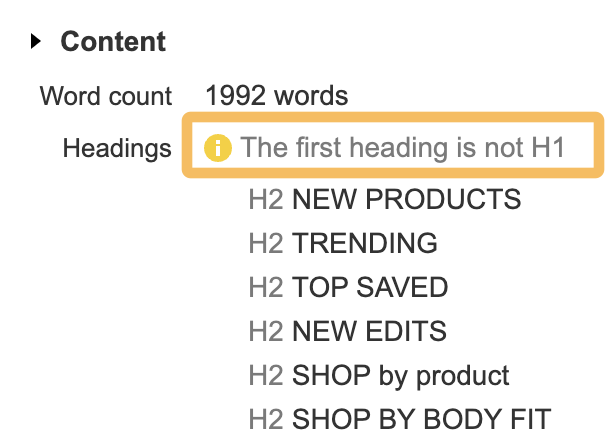
<h1>This is the h1 tag</h1>The fastest way to check whether a page has an H1 is to use the Ahrefs SEO Toolbar. Here, you can easily spot-check the hierarchy of the headings.
Product images are photographs or digital representations of your products. Usually, one image or a gallery is shown on a product page to showcase the product.
They’re essential because they provide extra detail about the product that written descriptions can’t always capture—like how the product should be used, the exact color of the product, and so on.
From a search perspective, product images are essential as they can rank in Google’s image search results—so there’s a traffic incentive to optimize your product images for SEO.
So, how can you optimize your product images for SEO?
Here are the basics you need to optimize for:
- Add alt text
- Use descriptive file names
- Use responsive images
- Compress your images and use image formats like jpg, jpeg, png, webp, or avif
Alt text is a brief description of the image, which is not only crucial for search engine indexing but also vital for accessibility, allowing screen reader users to understand the image content. Like file names, alt text should be descriptive and include relevant keywords naturally.
You can do many things to improve your image’s performance in search engines. Check out our image SEO guide to learn more.
Videos increase user engagement with your product pages—and like images, they’re valuable as they can independently drive traffic to your site.
Videos can appear in four places on Google:
- Google’s search results
- Google Images tab
- Google Videos tab
- Google Discover
But, to become indexed, videos must fulfill certain criteria.
Before investing time and effort in creating videos, consider whether it would benefit your audience.
For example, in the fashion industry, visitors expect to see a video to get a better look at how the clothes fit, so it’s no surprise that clothing stores like ASOS have short videos prominently placed on their product pages.
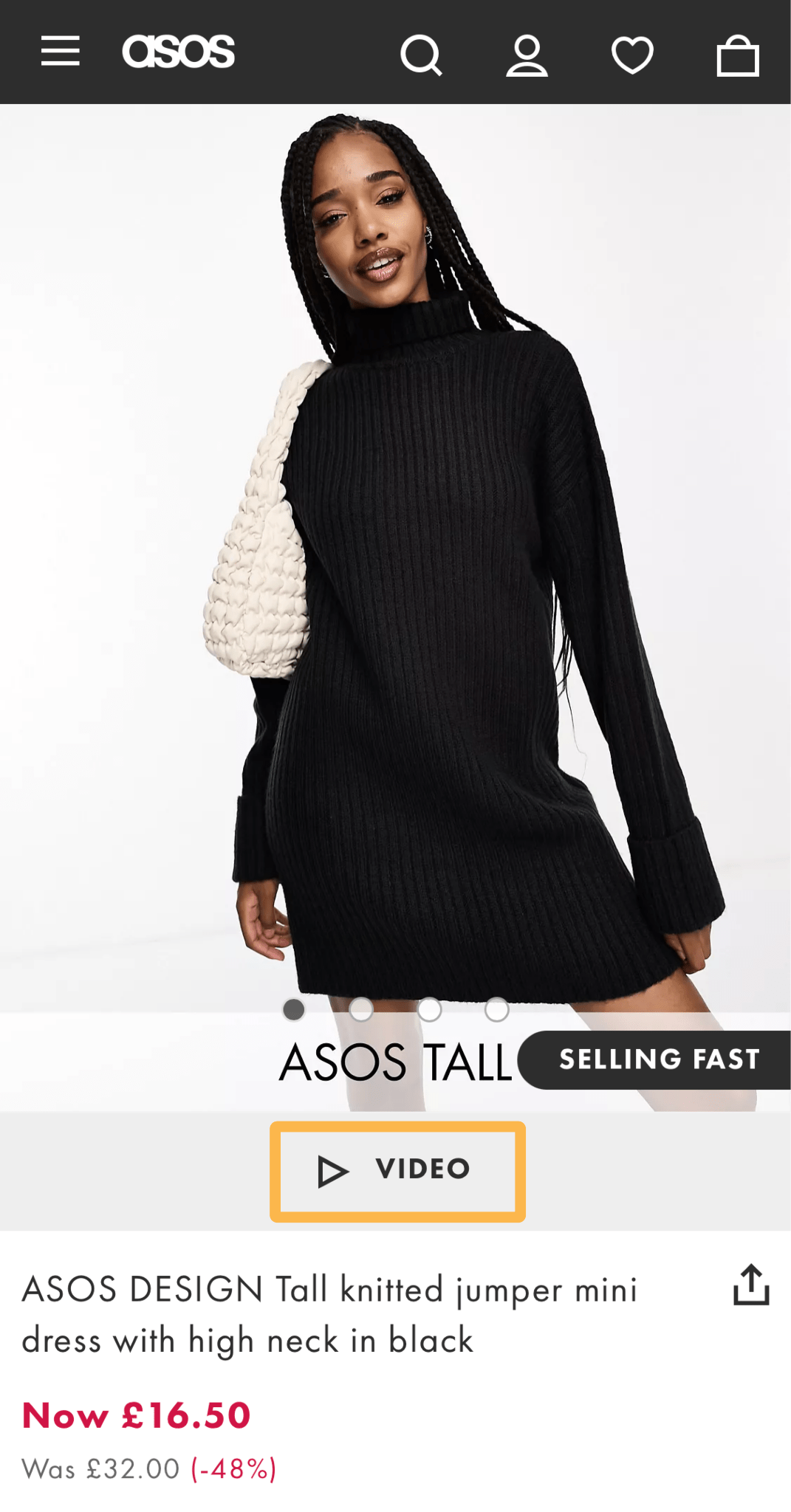

But if you were in the business of selling storage sheds—there’s not much additional benefit for your audience of including a video, as most people know what a storage shed looks like.
Using a platform like Wistia can help you optimize your videos for SEO as well as receive more detailed analytics on your product video’s performance.
Product price, availability, ratings, and reviews are an essential part of the user experience. If you don’t have these elements, users will bounce from the page, impacting your rankings and weakening your SEO efforts.
The good news is that most ecommerce-focused CMSs like Shopify or Wix handle this out of the box, so there’s usually little configuration required to get these elements set up.
If you want to optimize further, adding product schema helps increase visibility in Google of this information and make it look like this in the Google search results.
The rating and reviews are essential for potential customers as they can get an idea of what the product is like before buying it.
Therefore, it’s a good idea to prominently display customer ratings, as they offer valuable social proof, which can help influence purchasing decisions.
Ensure they are easily accessible and readable to enhance user experience and credibility, which can lead to increased engagement and sales.
This user-generated content enriches your site with diverse, relevant keywords and phrases, further boosting SEO efforts.
You’ve probably clicked a million call-to-action (CTA) buttons in your online life—but unless you’re well-versed in user experience (UX), you probably aren’t aware of how important they are in encouraging visitors to buy your products.
For example, Amazon.com has some of the most recognizable CTAs on the internet:

To create an effective CTA, use concise, strong, actionable verbs such as:
- Buy Now
- Learn More
- Add to Cart
This direct approach makes it clear to users what they should do next.
While CTAs don’t directly impact SEO rankings, they play an important role in user experience of your product page. Without obvious CTAs, visitors might get confused and bounce from the page. This type of behavior, if repeated, could signal to search engines that this page is not a good experience.
Ensure your delivery information is visible and easy to find; don’t make your visitors hunt for it—otherwise, they might leave the page before they buy the product. If visitors consistently bounce from your page, your rankings may suffer over time.

Most ecommerce content management systems (CMSs) automatically add delivery information to your product pages.
Position your delivery information near the purchase button or price, and use icons or brief bullet points to make it easy to understand. Regularly update the delivery section with current shipping times, costs, and options to build customer confidence and satisfaction.
Clear, easy-to-understand delivery details reassure customers and create a positive user experience. Doing so will reduce visitors bouncing from the page before buying your product.
A good product description is content that describes the product and sells it.

But what makes a product description stand out?
- Create a unique product description instead of copying from other manufacturers’ websites.
- Be direct in your product description to avoid wasting time and effectively sell the product to potential buyers.
A well-written product description enhances user experience and can increase conversion rates, positively impacting your site’s SEO performance.
It’s best to avoid using AI tools like ChatGPT for product descriptions, as the potential reputational risks often outweigh the benefits. AI tools sometimes provide inaccurate “hallucinated” information, leading to confusion and mistrust.
Product specifications help humans and search engines understand the nuances of your product. For search engines, including these specifics means that the page can rank for more topically relevant longer-tail search queries.
Product specifications are best presented clearly and concisely using HTML bullet points to make them search-friendly.
Product page FAQs help visitors answer questions they have before they make a purchase. If you often get the same sets of questions asked about specific products, then it might save your business time.
If your products come with many customer questions, adding a FAQ section to your product pages is a good idea. FAQs help your visitors answer any questions they may have and increase the chances of ranking for related keywords.
You can discover the types of questions people are searching for your product by putting it into Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer and casting your eyes over the Questions section.
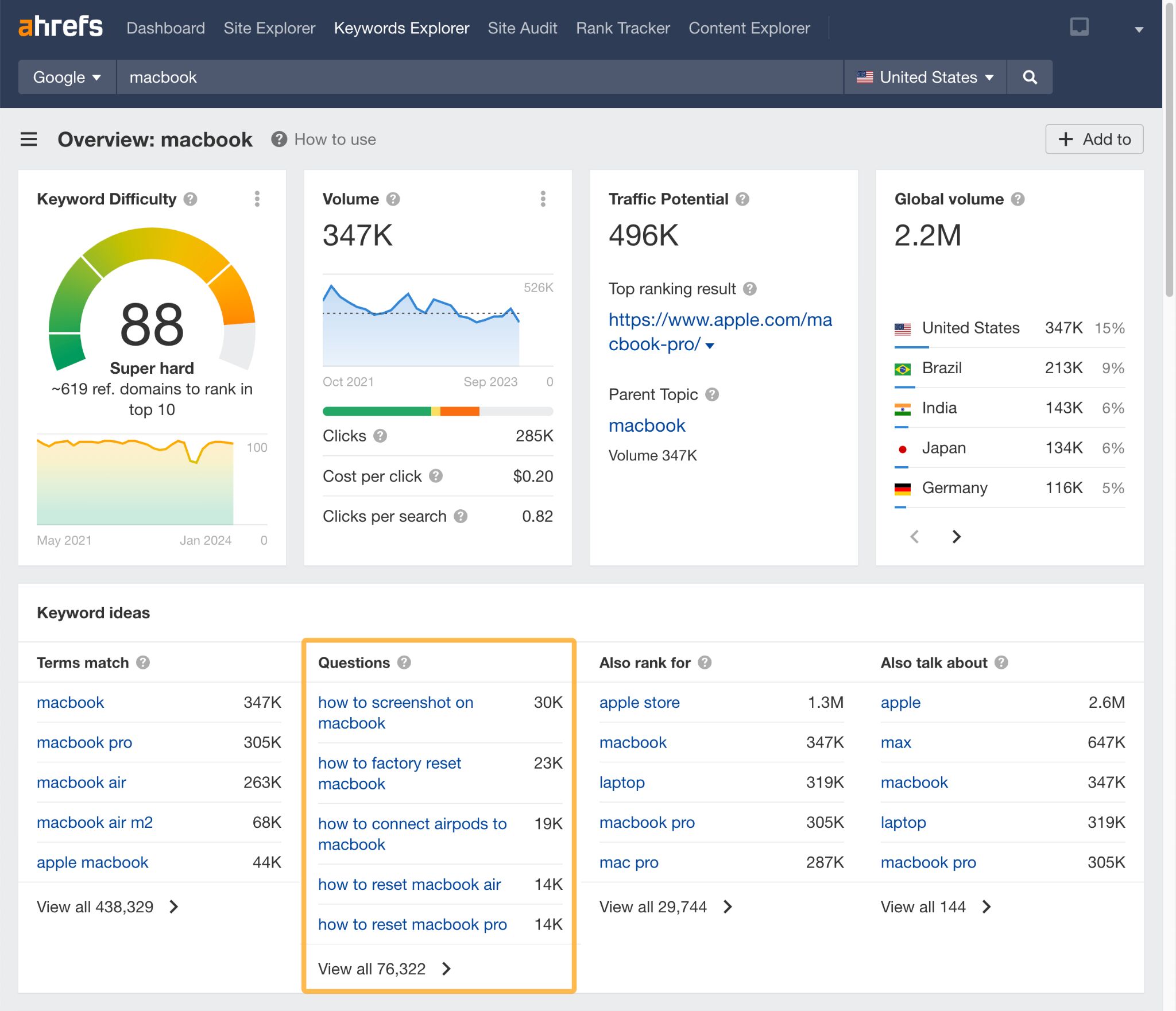
FAQs can help improve visitors’ user experience by answering questions you have on the product page, rather than having them return to Google to find the answer.
Displaying related products improves user experience and encourages clicks on other related products.
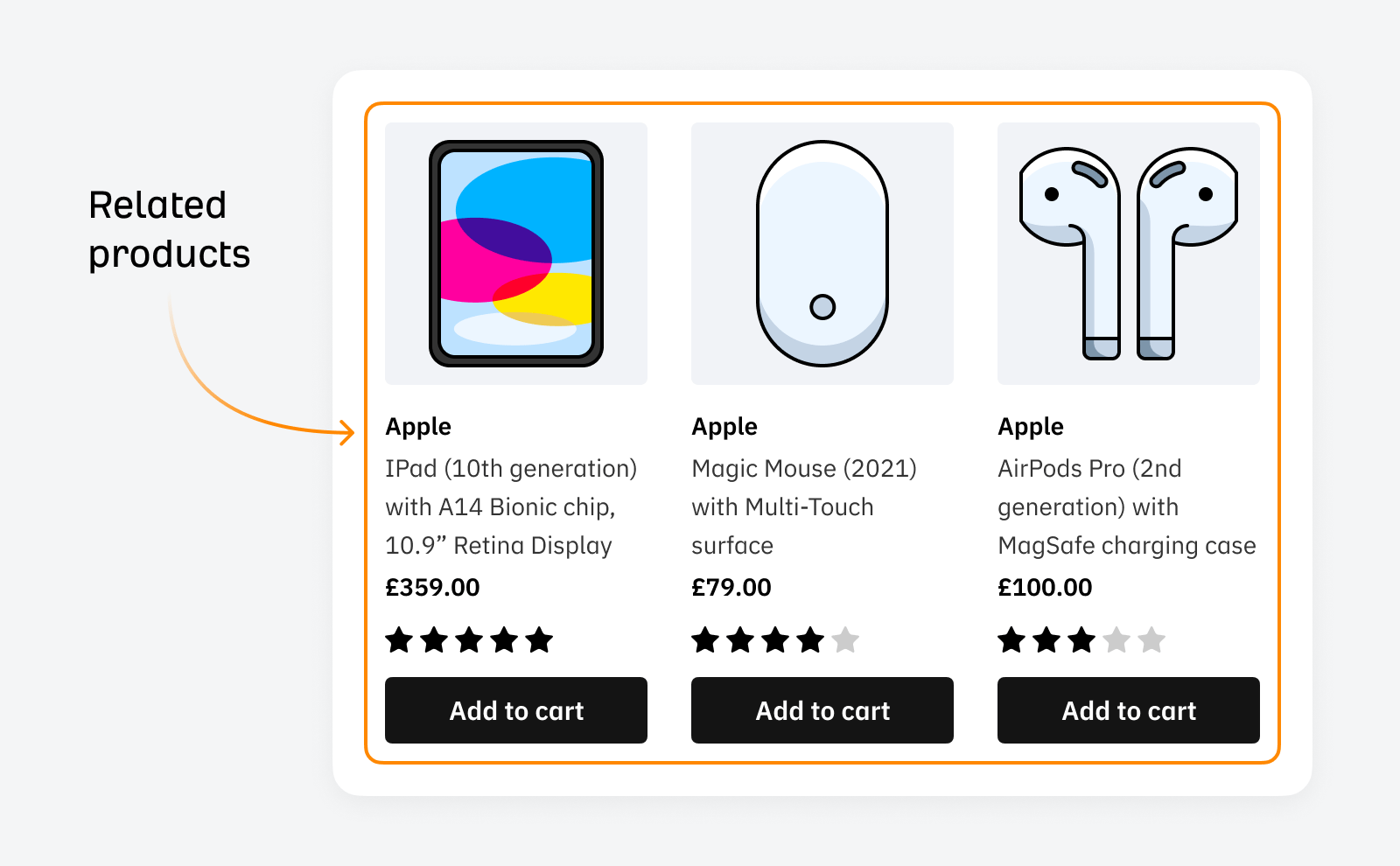
You can encourage product upsells by showcasing relevant, complementary items while naturally using internal links to link to relevant products.
This improves user engagement and contributes to SEO by passing link equity and increasing page views and time spent on the site.
This strategy not only boosts the potential for cross-selling but also enriches the overall user experience on your site.
User-generated content (UGC) is one of the most compelling ways to show potential customers what the products look like away from the carefully crafted product images and videos.
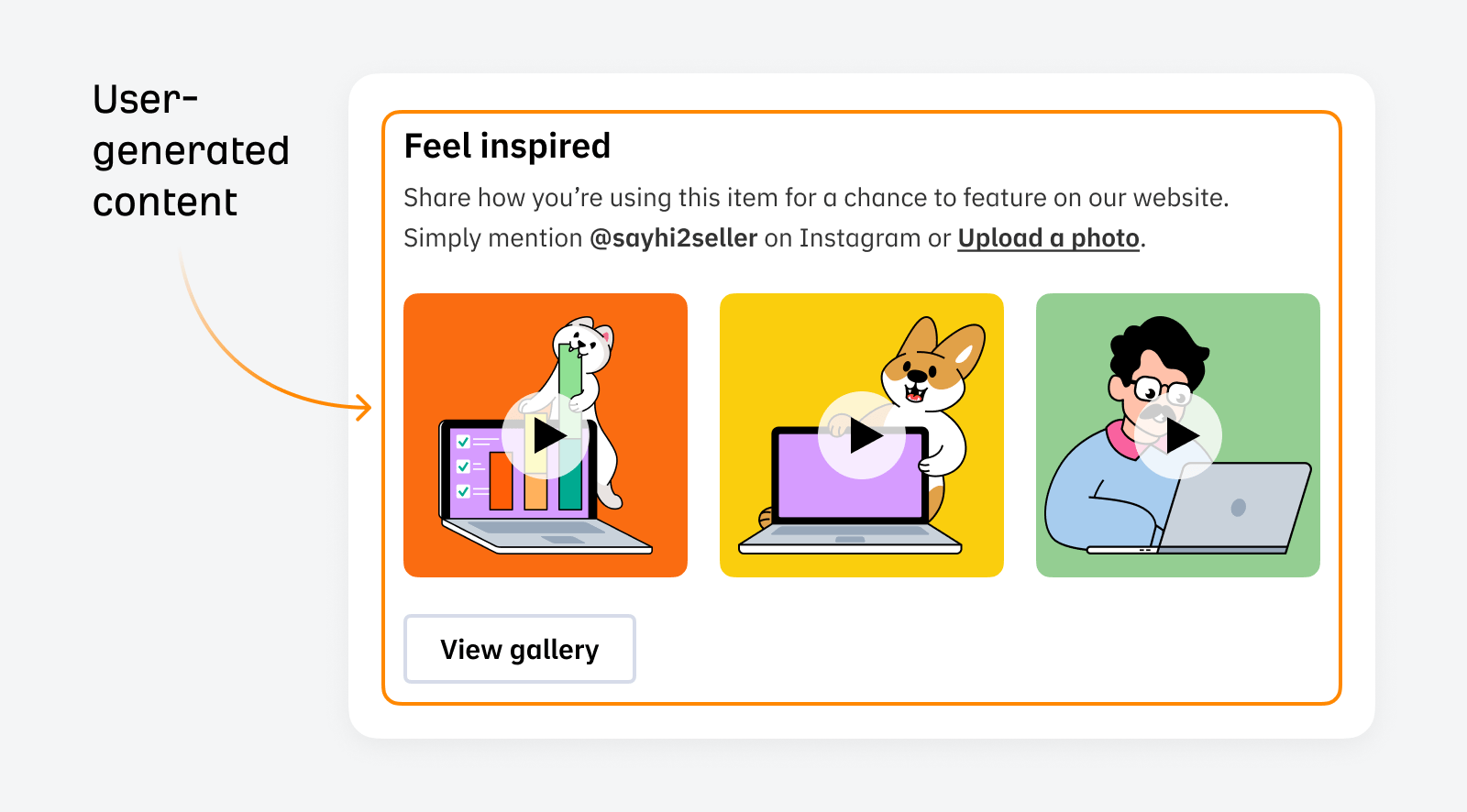
User-generated images are essential for industries like fashion—when you want to see the fit of the clothes on people who are not professional models. Adding UGC is a strong signal for customers as it shows your shop is trustworthy and not a scam.
Schema markup is code that can be used to visually enhance elements of your website within the search results. Google uses it to display rich snippets.
The main advantage of adding it is that products with schema markup are much more likely to get a higher click-through rate due to their size and visual appeal.

When we talk about schema with product page SEO, I would always include product schema myself.
- Breadcrumb schema – enhances breadcrumbs
- Video schema – if videos play an important role in your content
- Review schema – if you have reviews, you can add review schema to enhance them
We’ve covered what you should include in your product pages, but how can you audit them?
Here are the two approaches I’d recommend:
1. Use Ahrefs’ SEO toolbar for quick spot checks
The fastest way to check product pages for common SEO issues is with the Ahrefs’ SEO toolbar.
- Navigate to a product page
- Open up the toolbar
- Look for any potential issues
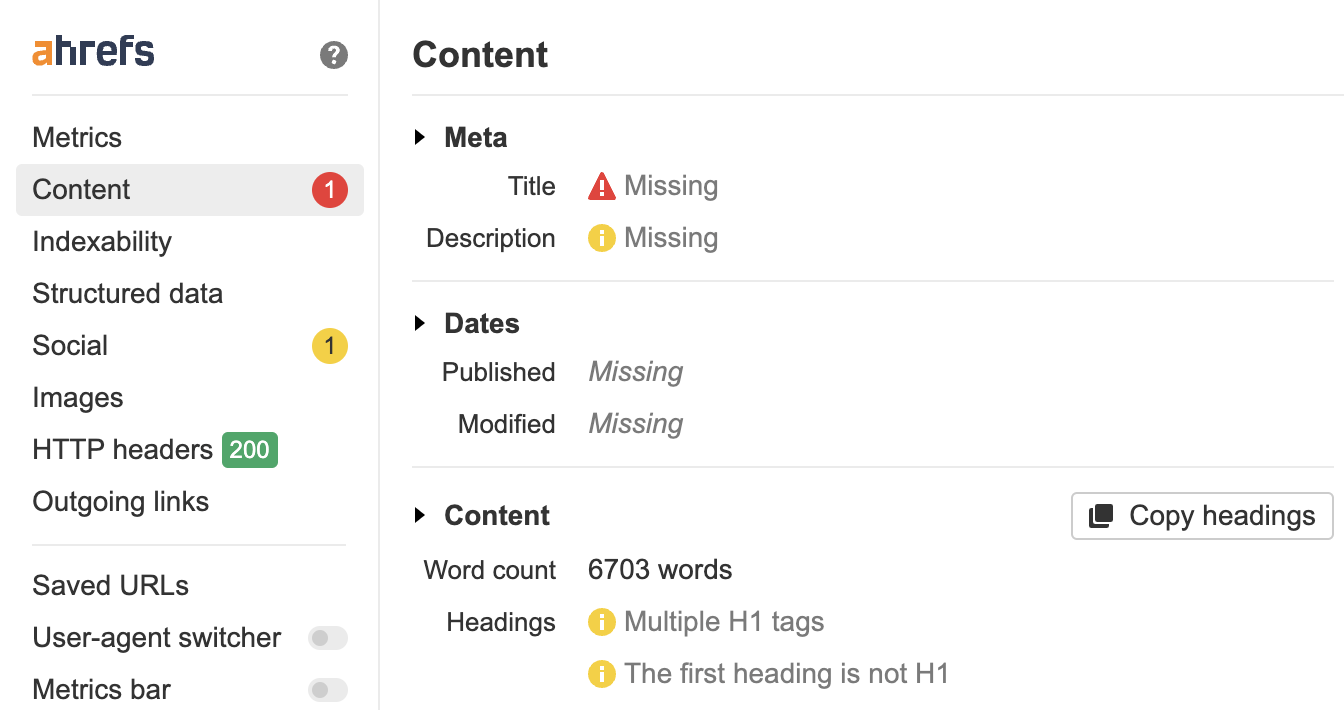
Product pages usually follow a templated structure, so chances are, if you spot a problem on a product page, it could also apply to other product pages.
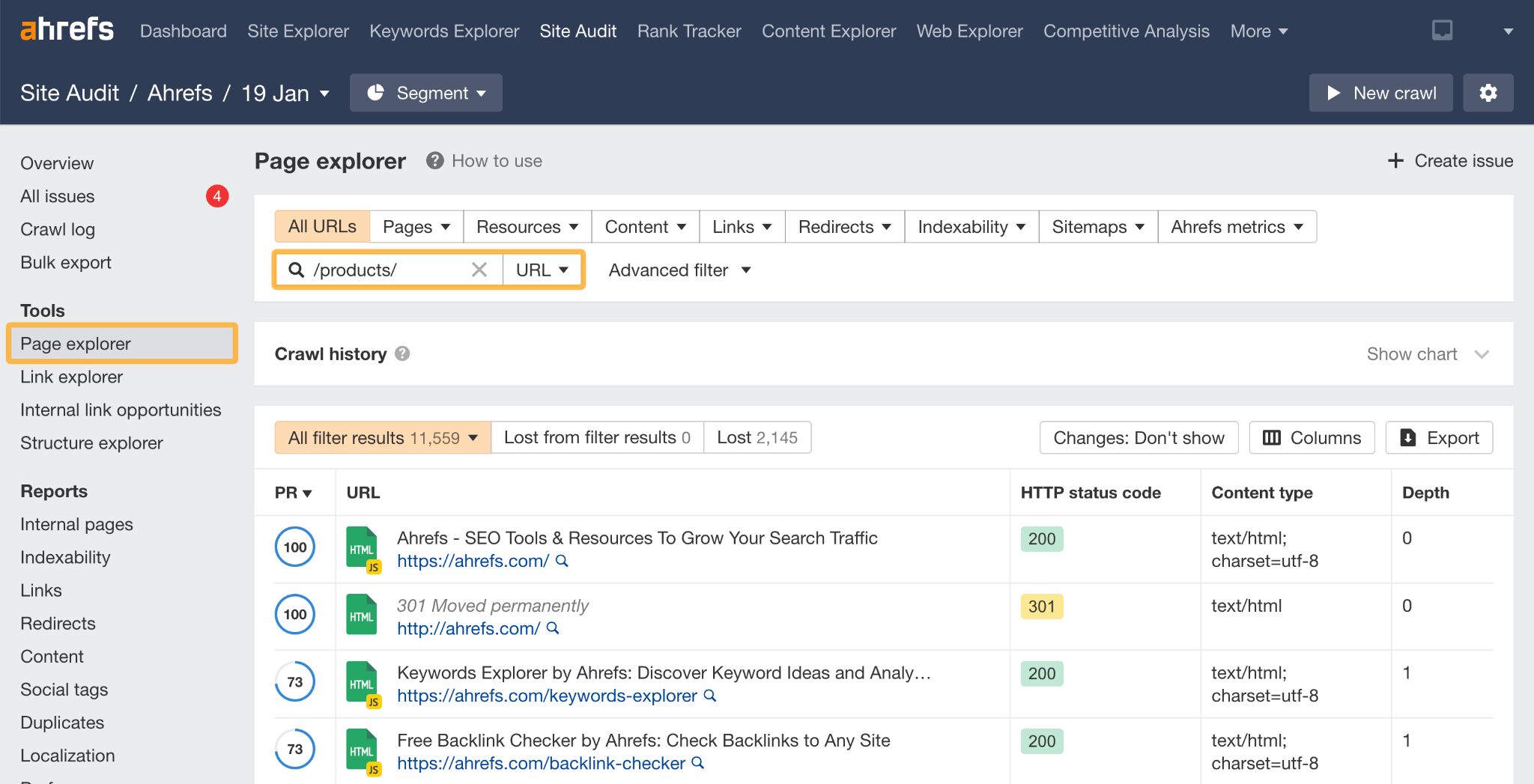
2. Get a site-wide view with Ahrefs’ Site Audit
If you’re completing an SEO audit, you’ll want to understand the current state of all products on the website. The best way to do this is with a tool like Ahrefs’ Site Audit.
- Run your crawl
- Once it’s finished, head to Page explorer in the sidebar of Site Audit
- In the search bar, enter your product URL identifier, e.g. /products/
- Order by Organic traffic to see the most popular pages
- Click on Columns to add other elements you want to examine
- Analyze!
Final thoughts
Optimizing product pages for SEO is important for any ecommerce business looking to enhance visibility and drive more conversions.
By integrating relevant keywords, crafting compelling and descriptive product titles, and ensuring high-quality, informative content, businesses can improve their product page’s rankings. This, in turn, leads to increased organic traffic and better user engagement, essential for boosting sales and customer loyalty.
Got questions? Ping me on X.