These people are all leads. Some of them will upgrade and become paying customers.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to generate leads for your business.
But first, some fundamentals…
- What is a lead?
- What types of leads are there?
- What is lead generation?
- Why is lead generation important?
- Why generate leads and not buy them?
- How to generate leads
- Lead generation tactics
A lead is anyone who has expressed interest in a company’s product or service by sharing their contact information (e.g., email address) with the company.
Getting your sales team to contact every lead would be inefficient because some people are closer to buying than others. That’s why many companies divide their leads into subcategories. These vary from company to company, but the two most common are marketing-qualified leads (MQLs) and sales-qualified leads (SQLs).
1. Marketing-qualified leads (MQLs)
Marketing-qualified leads (MQLs) are leads that have interacted with your marketing but are not ready to buy. For example, they might have attended your webinar or downloaded a free eBook.
2. Sales-qualified leads (SQLs)
Sales-qualified leads (SQLs) are leads that have taken actions to indicate their desire to buy. For example, they might have signed up for a trial or requested a quote. Most businesses hand SQLs over to a sales team.
Lead generation is the process of attracting, engaging, and capturing the interest of people who might want to buy your product or service.
Lead generation is important because it gives you the permission and ability to contact potential customers directly. You can then build and nurture your relationship with them until they’re ready to buy.
Generating leads is usually better than buying leads because generated leads have expressed an interest in your product or service and permitted you to contact them. That’s not the case for bought leads. They might belong to a relevant list, but the messages you send them are unwanted, and they probably aren’t familiar with your brand.
Spamming bought leads with calls or emails can damage your reputation.
Generating leads for your business involves three steps. You’ll need a way to:
- Attract people to your website or webpage.
- Engage them so they’ll be willing to share their contact information with you (we call this the “offer”).
- Capture this contact information.
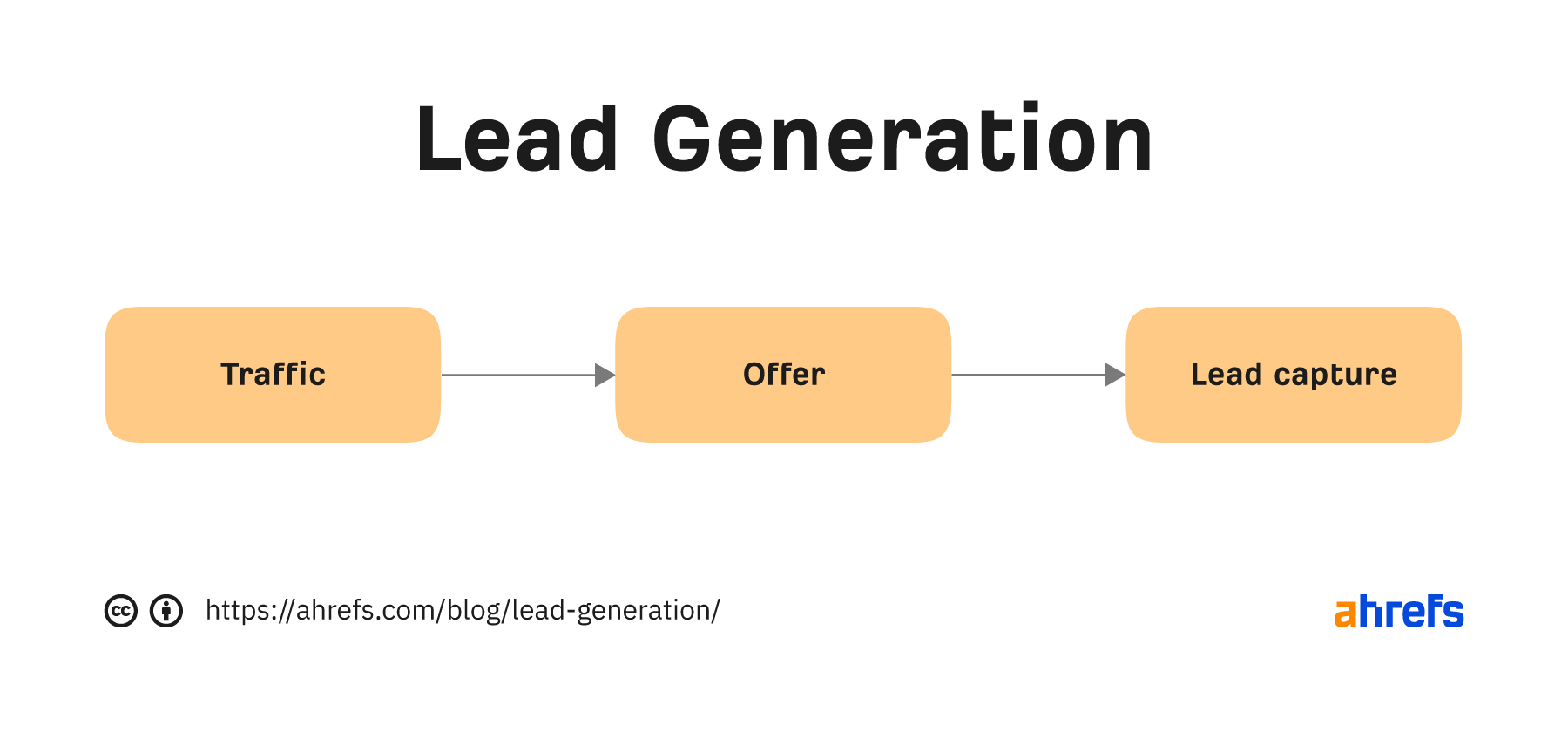
Most people set up their lead generation campaigns in reverse order, so let’s look at these steps in more detail, starting with the lead capture.
1. Lead capture
You’ll need a way to capture a potential lead’s contact information. This can be as simple as setting up a form on your site:
Precisely what information you ask for depends on your business’s needs. Common options include name, email, and phone number but you can ask for anything you like. Things like organization size and budget are common in B2B.
Just know that the more information you ask for, the less likely people are to fill in the form. This is not necessarily a bad thing because the people that make more effort are typically better leads.
2. Offer
A visitor to your website won’t hand over their contact information without some enticement. There are a variety of ways to do this. It all depends on your niche and who you’re targeting. You’ll also need to test multiple offers and see what resonates.
For example, ecommerce stores tend to incentivize visitors with discounts:

Bloggers usually give away free eBooks or downloads:

And software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies often create free tools as we did with Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT):
3. Traffic
Nobody will magically discover your page and offer. You need a way to market it.
For example, let’s say you sell soccer boots. You have a landing page offering a free eBook on how to improve penalties.
To drive traffic to this page, you could:
- Run PPC ads, e.g., FB/Twitter/Google ads.
- Create content that ranks on Google and link to that page.
- Promote the page on social media.
- Appear on podcasts and promote the page.
- Promote the page on communities, like Quora.
This is merely a sample of what you can do. The choices are endless.
Recommended reading: 11 Proven Ways to Drive Traffic to Your Website
Here are some common tactics you can apply to get more leads for your business. You’ll notice that all lead generation tactics are variations of this three-step process.
1. Blogging
Many companies use blogging as a primary lead generation tactic. It’s the basis of what is known as inbound marketing.
Traffic
For your posts to get traffic month after month, you’ll have to make sure they rank high on Google. To do this, target topics that people are actively searching for.
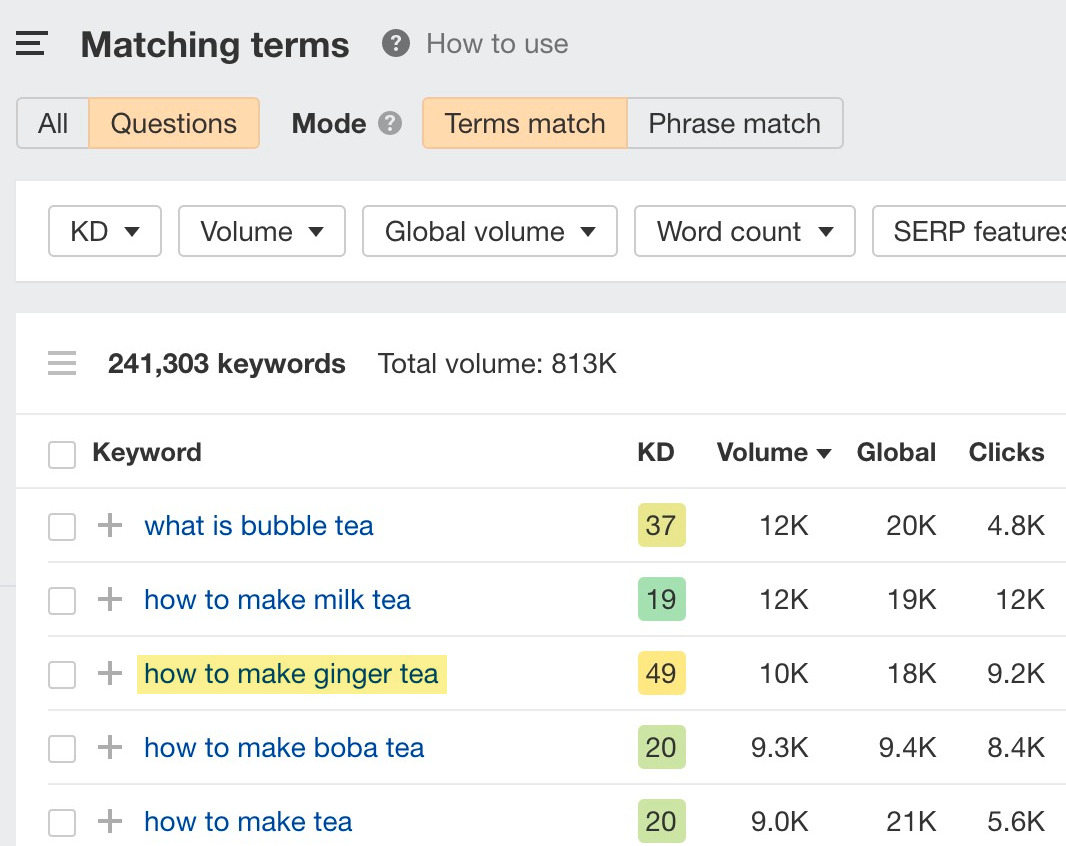
You can find these topics with Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer:
- Enter a relevant keyword into Keywords Explorer.
- Go to the Matching terms report.
- Toggle the “Questions” switch.
- Look for high-volume questions that your target marketing are likely to be searching for.
For example, if you sell tea online, “how to make ginger tea” would probably be a good topic for a blog post:
From there, it’s just a case of creating a post that deserves to rank. Watch this video to learn how:
Offer
Entice readers with free downloadable bonus content related to the post. This is known as a content upgrade. Checklists, worksheets, templates, and free courses all work well.
For example, Intercom offers an “ultimate guide to conversational support” in their post about global customer support:

Lead capture
Display a lead capture form when the reader clicks the content upgrade. You can do this with a popup or link to a landing page.
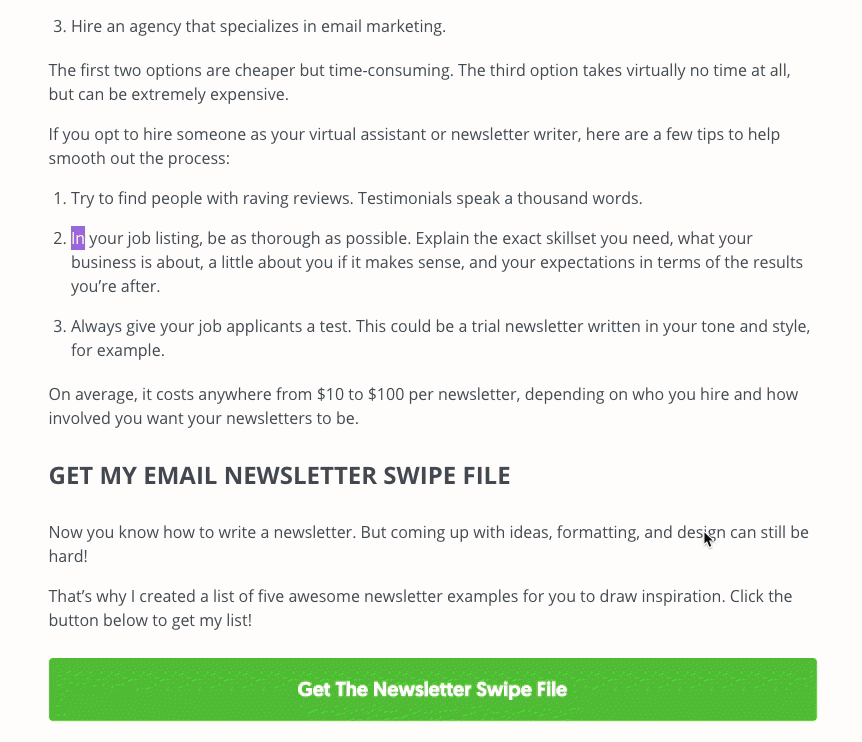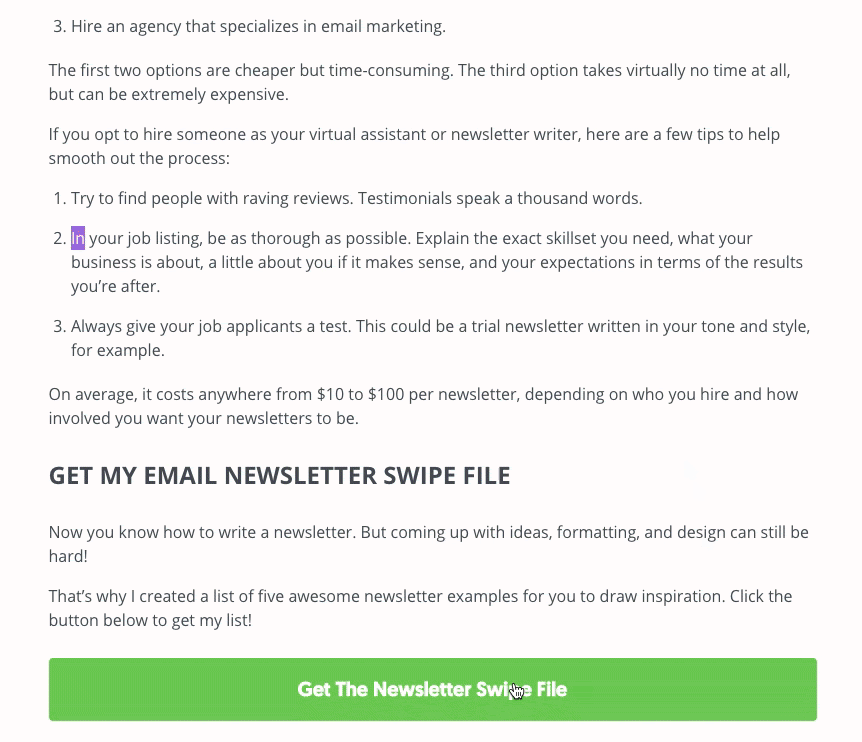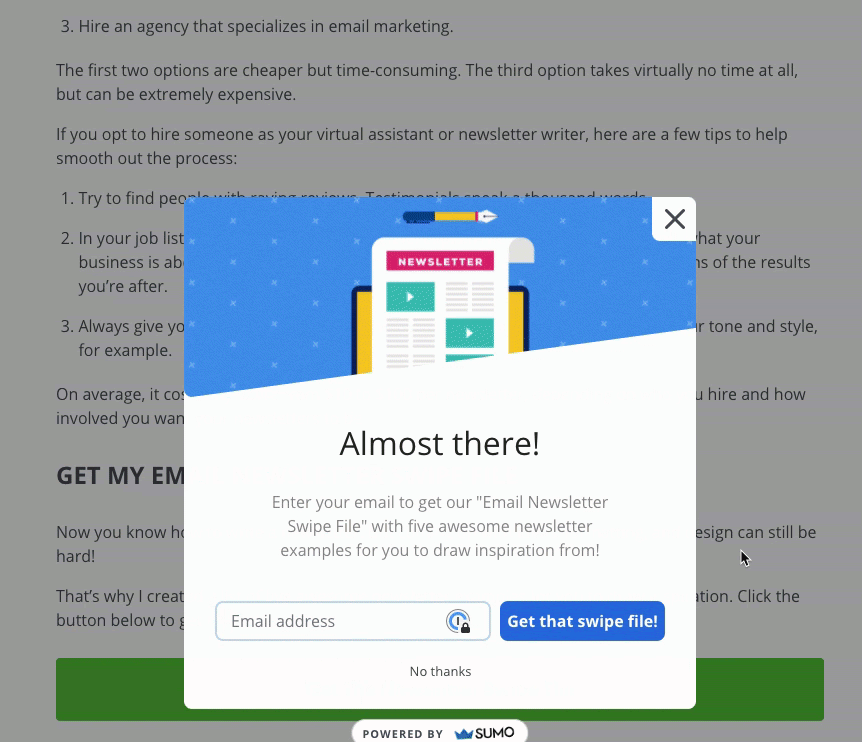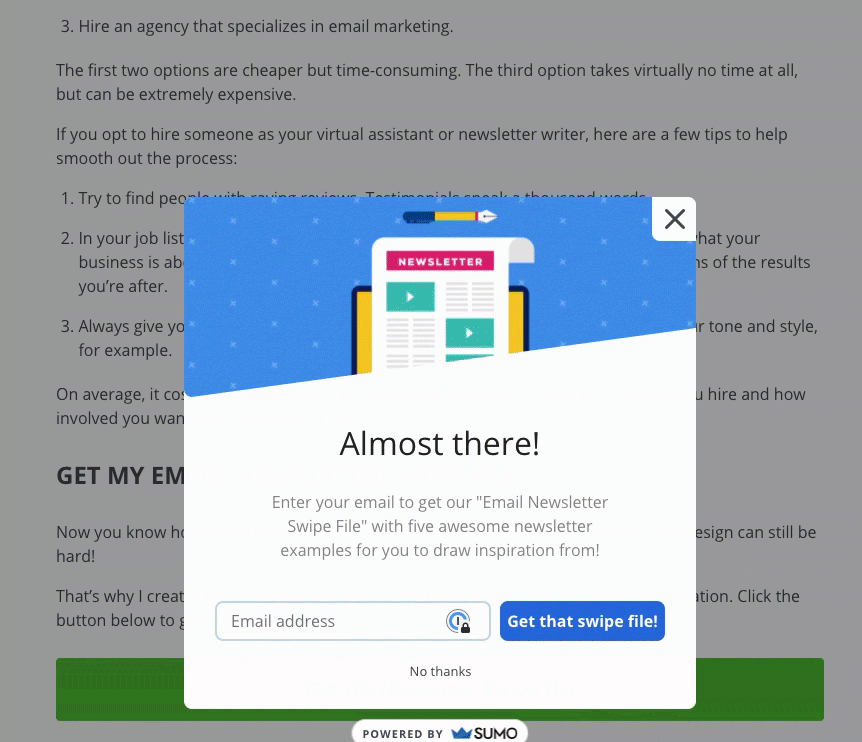
For example, Sumo delivers their content upgrade via a pop up:
You can choose whichever method you like. Try testing both ways to see which works best for your business.
2. Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising
PPC is when you pay for clicks to your website.
Traffic
Pay a platform like Google or Facebook to show your ads to their users. You’ll pay a fee each time someone clicks your ad. Use their targeting options to ensure the right people see your ad.
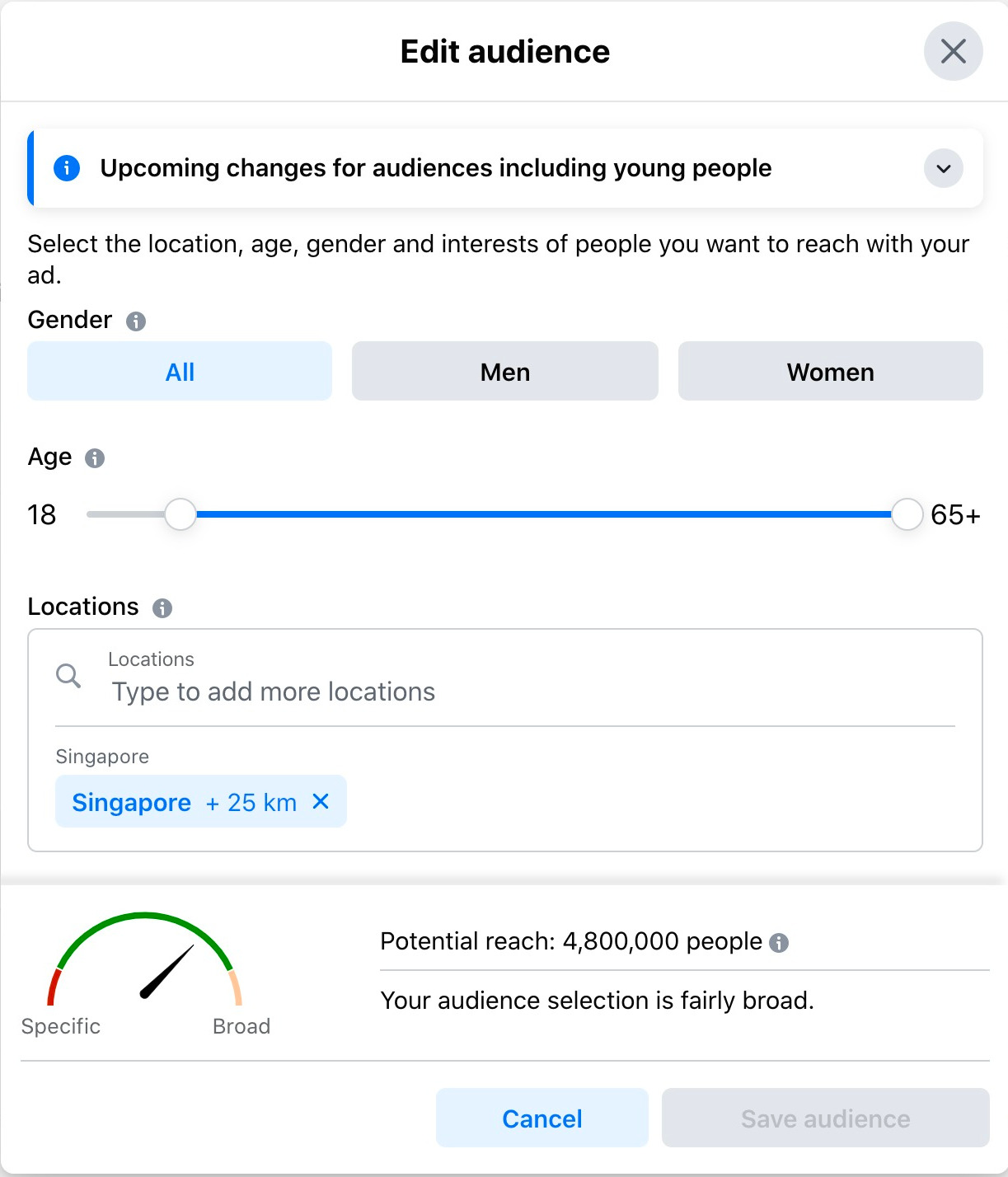
For example, Facebook lets you target ads by age, gender, location, interests, and more:
Offer
Entice people to click your ad with a compelling offer. Popular examples include webinars, free trials, and free downloads.
Here’s an example from HubSpot:

Lead capture
Send paid traffic to a landing page with more details about your offer. Include a form to capture leads.
Here’s the landing page that HubSpot sends their paid Facebook traffic to:

3. Partnering with other companies
Your company wants leads. Other companies want leads too. Why not collaborate?
Traffic
Find a company in a similar industry with a sizable audience that isn’t a direct competitor. Offer to create something useful for their audience, like a webinar, eBook, or course. You’ll get traffic to your offer when they promote it to their audience.
We did this a couple of years ago with Buffer, a social media scheduling tool.
Offer
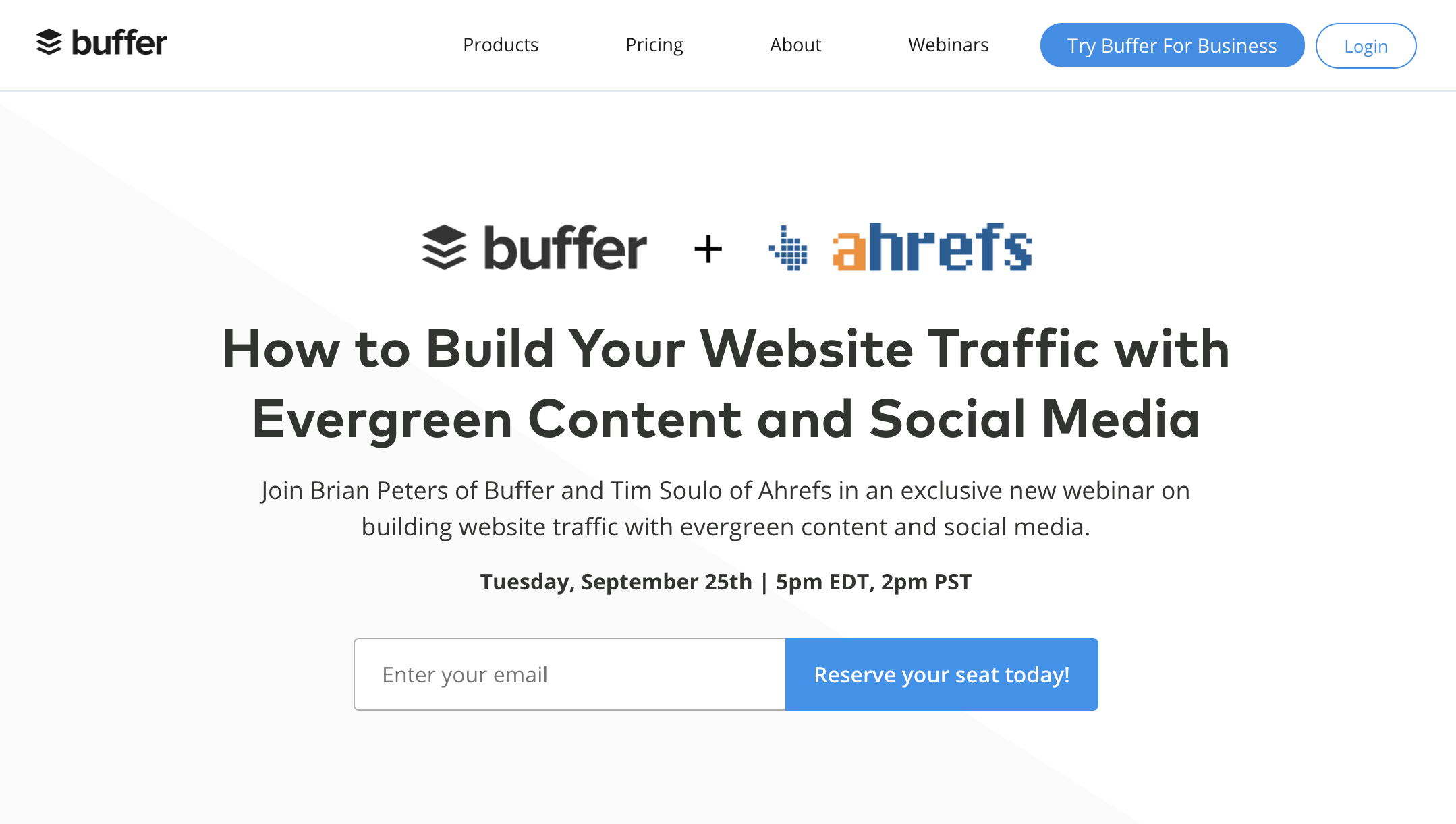
Tailor your offer to the audience of your business partner. For example, in our webinar with Buffer, we talked about getting traffic with content and social media marketing:
Lead capture
Create a co-branded landing page with more details about your offer and a lead capture form.
Here’s the landing page for our webinar with Buffer:
Recommended reading: 10 Lead Generation Tactics That Work (With Examples)
Final thoughts
Every lead generation tactic follows the same fundamental three-step process: traffic, offer, capture. The beauty of this is that it’s easy to identify and fix holes in your lead generation funnel.
If your landing page converts well but doesn’t get much traffic, focus on getting more traffic.
If your landing page has traffic but isn’t converting, create a better offer or experiment with the lead capture mechanism.
Did I miss out on anything important? Let me know on Twitter.




