Visibility in AI search is still in its early stages, which means you’re not late to the game—you’re actually early. Most businesses haven’t even started tracking their AI mentions, let alone optimizing for them. This creates a genuine first-mover advantage for those who act now.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about building and improving your AI visibility.
AI visibility is how discoverable your brand is and how often your content gets referenced across AI platforms like ChatGPT, Claude, Google AI Overviews, Google AI Mode, and Perplexity.
For example, here I’m using Ahrefs’ Brand Radar to analyze Tesla’s AI visibility and benchmark it against competitors.
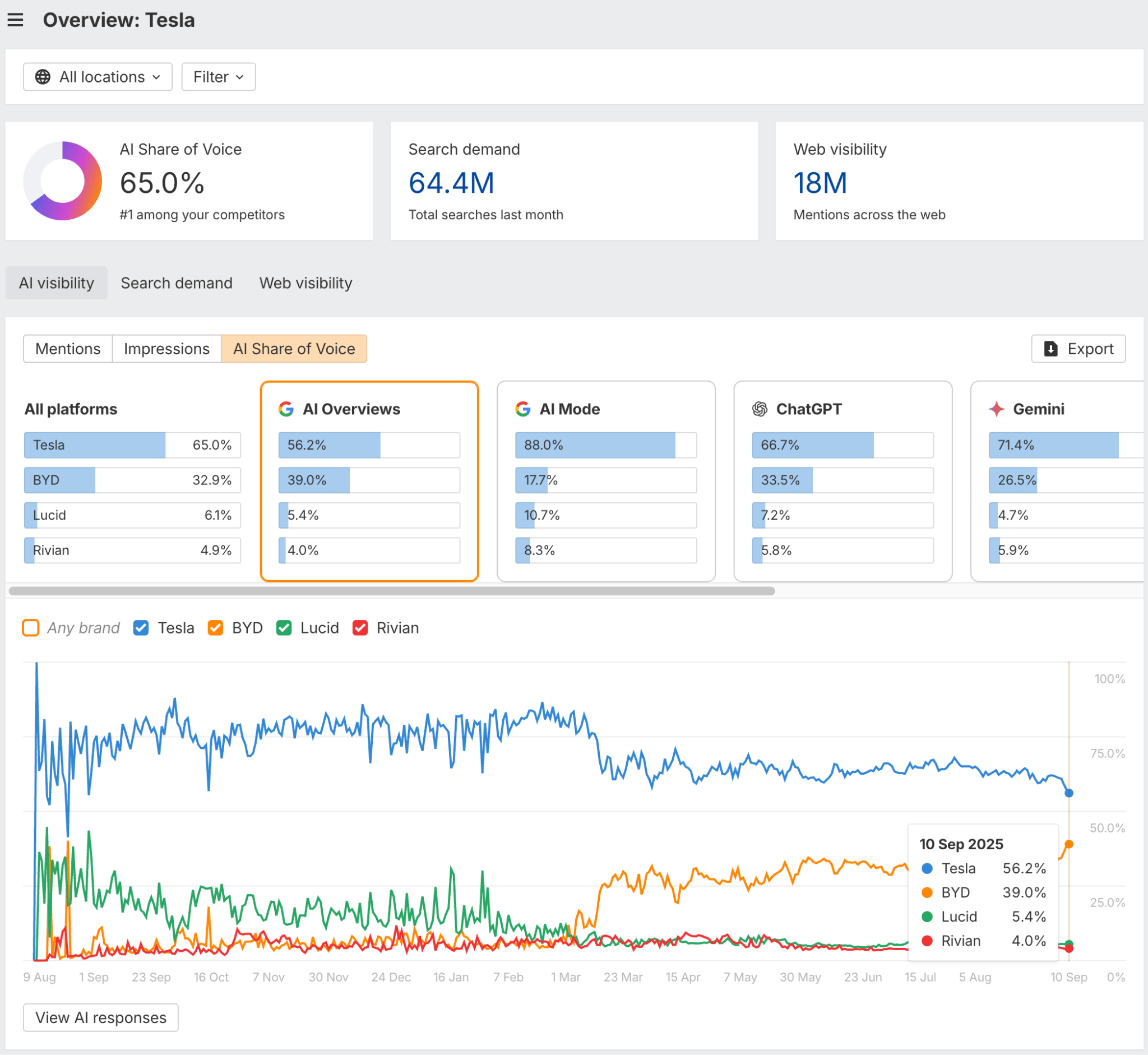
The data tells us that while Tesla has dominated the AI Share of Voice for the past year, its leadership is narrowing. The primary story is BYD’s explosive growth since March 2025, which has fundamentally shifted the competitive landscape from a single dominant brand to a two-brand race. Meanwhile, Lucid and Rivian remain marginal players with negligible AI visibility.
This rise of AI search and AI visibility is creating some important changes in marketing:
- You may get fewer visitors, but they may be more likely to buy. That’s because AI answers most basic questions directly, filtering out “tire-kickers” who were just browsing for information. So, people who actually click through to your site have moved past the research phase and are closer to making a decision.
- AI can provide personalized recommendations in a way traditional search never could. Instead of showing the same results to everyone, it can suggest solutions tailored to a person’s exact budget, industry, or use case. This opens up new opportunities for niche tools and services aimed at very specific audiences. But there’s a trade-off: unlike search results where your brand appears alongside many others, AI may only present a single recommendation—without showing all the alternatives it considered. That means less visibility for some businesses.
- Attribution is getting trickier because AI often drives traffic or awareness without leaving the usual digital footprints. In many cases, people hear about your brand through AI mentions, but those interactions don’t show up in traditional web analytics. Here’s Simon Heaton, Director of Growth at Buffer, explaining why and how they deal with that:
Attribution is challenging because not all referrals happen linearly from LLMs. Right now, the cleanest quantitative method we have is by capturing the referrer sources from sessions landing on our site. Looking up domains like chatgtp, perplexity, etc.
We’re also looking at qualitative methods to augment this as well: asking users how did they hear about us? This is emerging so less of how we landed on the data above.
The reality is that how users get to your site often involves various touchpoints. LLM visibility helps generate awareness, though only some of that is quantifiable. We realize the influence is much larger than what we’re able to track.
The rise of AI visibility has sparked conversations about Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and even doubts about the future of traditional SEO. Instead of just trying to rank high on search engines, the goal now is to get your brand mentioned and recommended by AI assistants when people ask questions related to your business.
SEOs, this is mostly for you. The metrics you rely on—click-through rates, organic impressions, rank tracking—miss this entire discovery channel.
GEO requires new tactics: earning mentions instead of just rankings, building authority through PR and media coverage, and optimizing for being cited rather than just being found. The tactics that worked for traditional search still matter, but they’re not enough anymore.
This is also a first-mover opportunity. Companies that figure out how to show up in AI recommendations early will have a big competitive edge—long before everyone else catches on.
Brand managers, executives, and business owners should also understand this shift. While you focus on traditional channels, competitors who figure out AI visibility first could build advantages before you realize what’s happening. Again, this requires coordination across PR, content, and marketing teams.
This section covers the three fundamentals that will shape your AI visibility strategy: how people search differently now, which AI platforms actually matter for your business, and how AI platforms source their information.
How AI search changes customer behavior
Traditional search gives you a list of links to click to get answers. AI search gives you direct answers immediately.
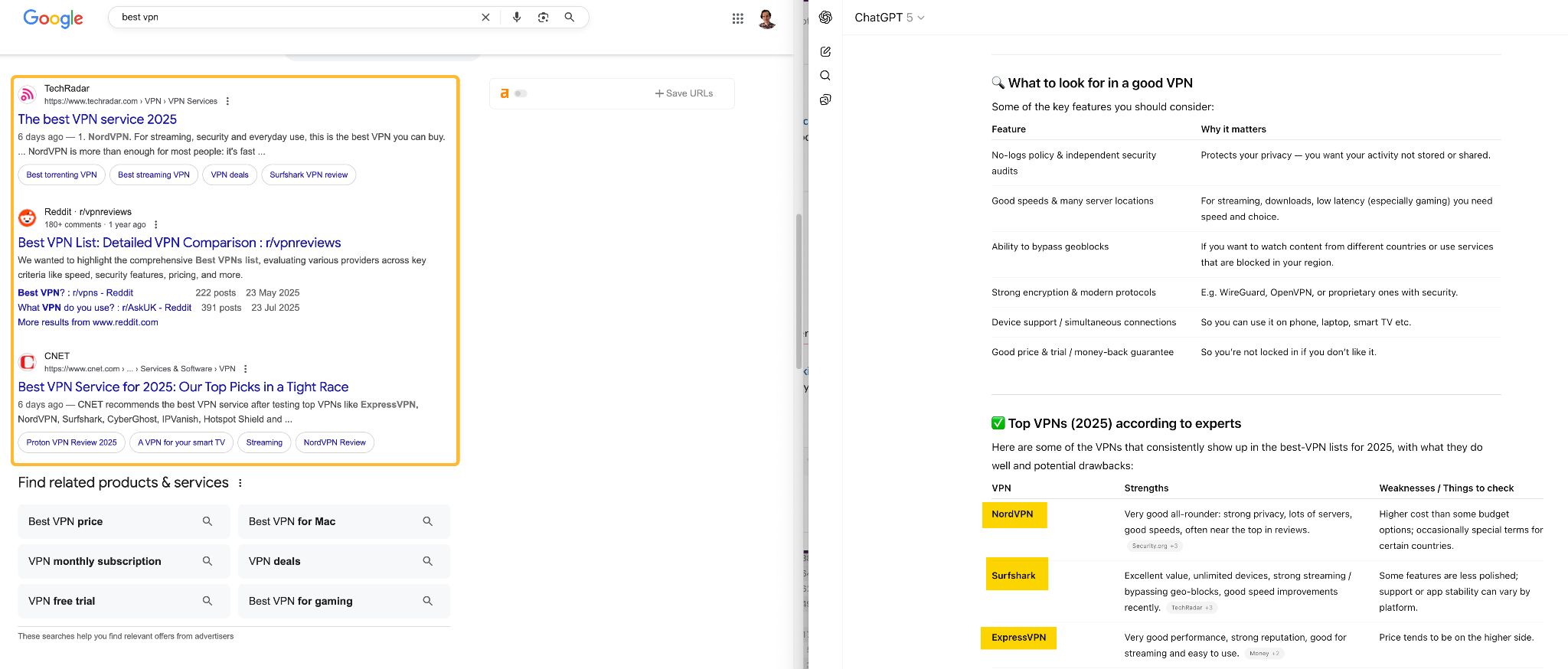
This changes user behavior. People get conversational with their queries (e.g., “I have a budget of around $200 and I’m looking for the best email tool. Can you compare some options and recommend which one gives the best value?”) and can ask follow-ups (“What about one with social media add-on?”). Most importantly, they get comprehensive answers without clicking through to websites, which means fewer visits overall but potentially higher-quality visitors who do click through.
This seems to be confirmed by the latest study from Kevin Indig. People use the new AI answers as a shortcut for simple facts, like a quick definition or a measurement conversion. It saves them a click.
But for anything important, anything involving a purchase, a big decision, or high-stakes topics like health and finance, they don’t fully trust the AI. They see the AI summary as a starting point, and then they scroll down to the traditional blue links to find a trusted brand or authoritative site to get the real story.
Major AI platforms you need to know
When it comes to sending traffic, a few AI search platforms stand out:
- ChatGPT. The dominant player, driving 0.21% of total website traffic.
- Perplexity. Smaller but growing fast, contributing 0.02% of traffic share.
Together, these tools account for nearly all AI-driven traffic today.
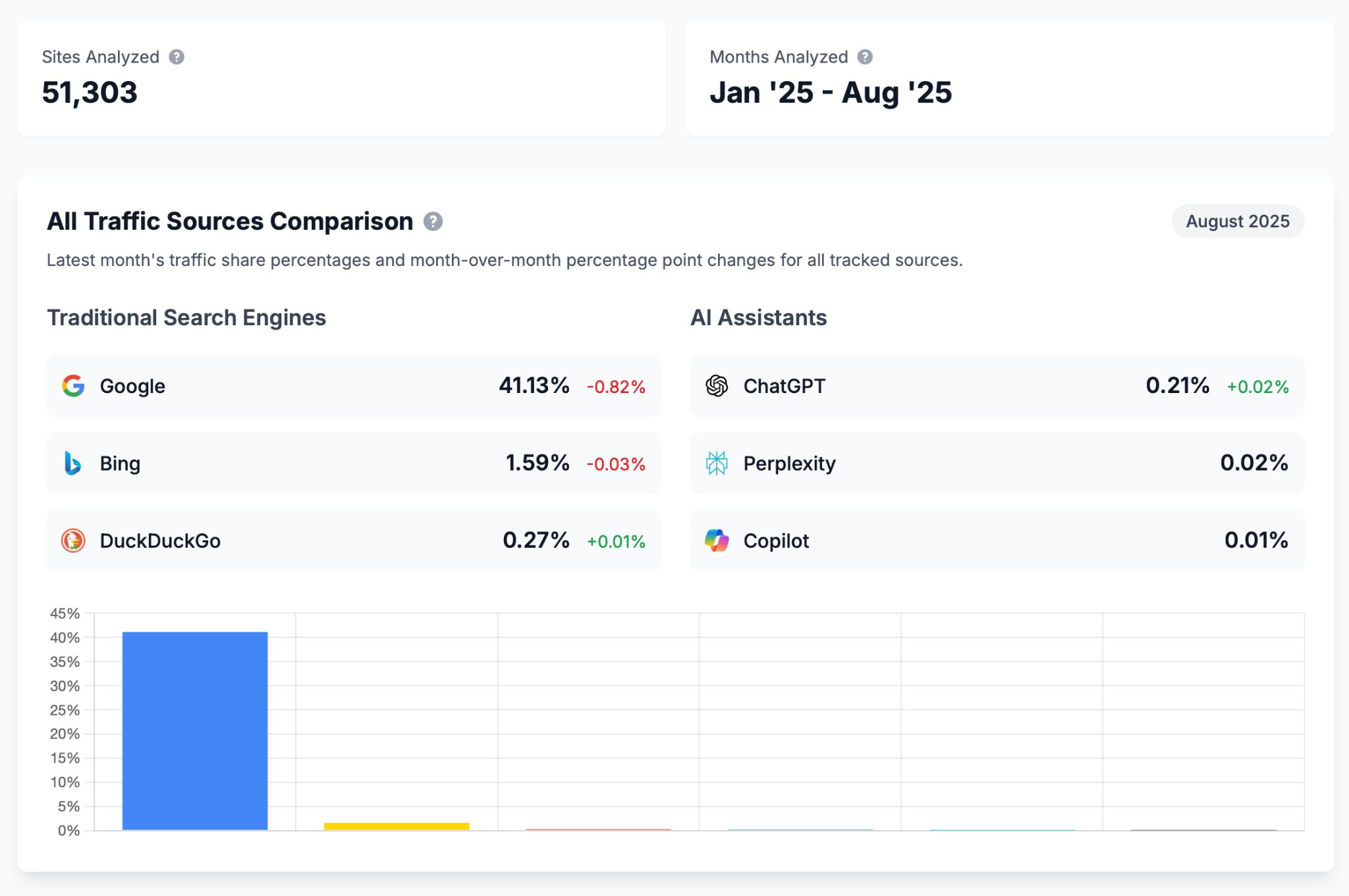
The numbers come from our AI vs. Search Traffic Analysis dashboard (based on over 50k sites), where you can explore the data yourself for free and track how the trends shift over time.
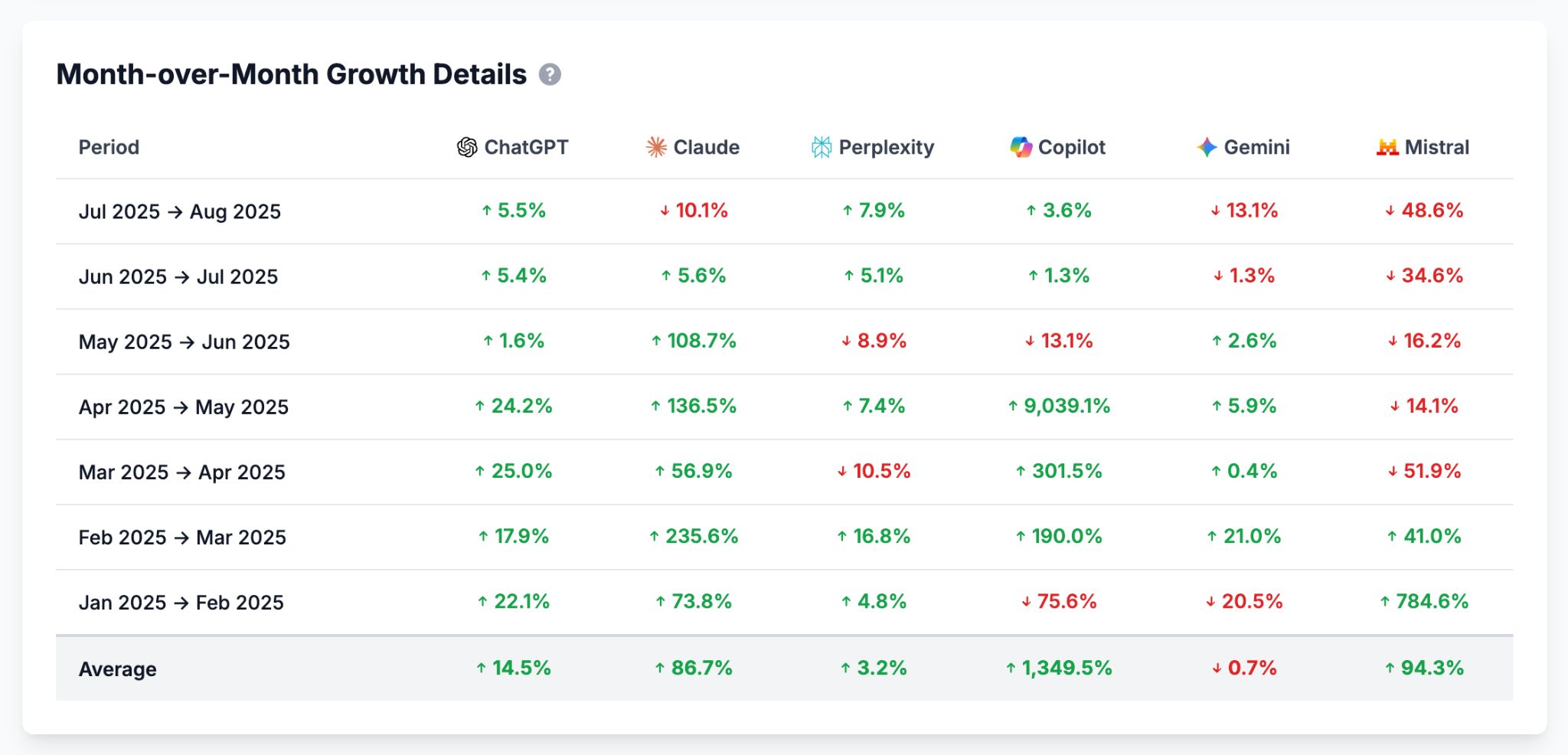
Another AI system to watch is Google’s AI Overviews (AIOs)—a new AI feature built directly into Google Search. As of May 2025, AIOs appear for 9.46% of all desktop keywords, and in the US, that number jumps to 16%.
According to Ahrefs Brand Radar, their presence is steadily increasing, showing a clear upward trend.
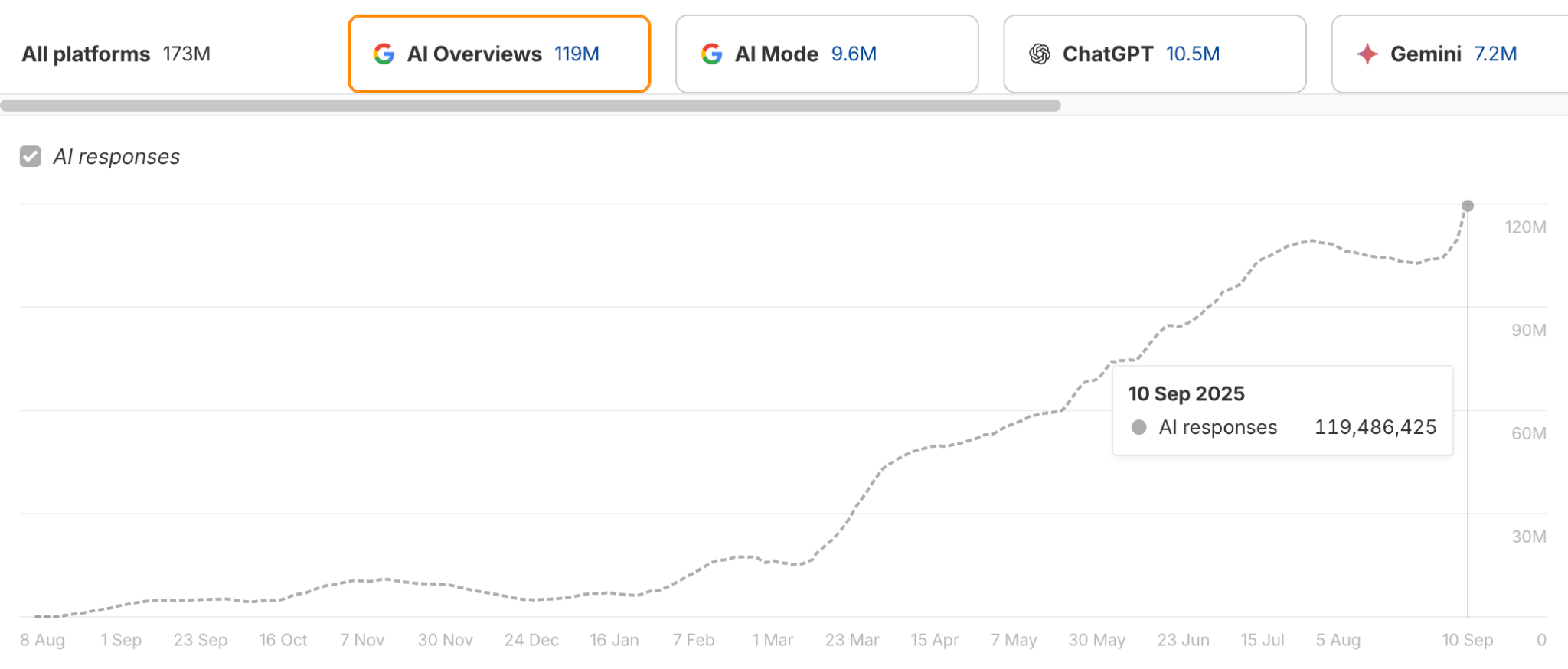
AIOs mostly show for informational queries and source 76% of citations from top-10 ranking pages. When present on a search engine result page, they reduce clicks by ~34.5%.
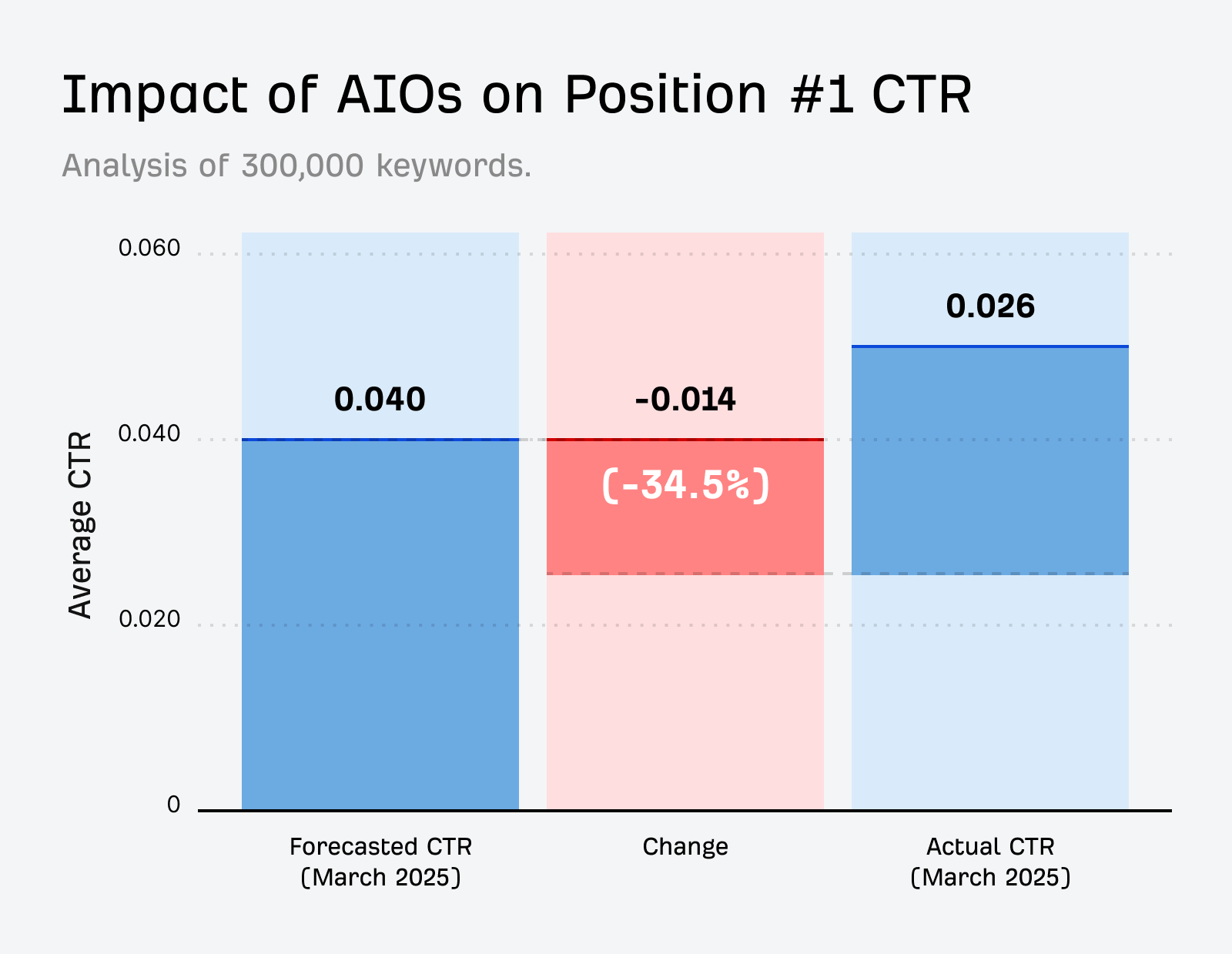
At the same time, AIOs may increase organic search impressions, creating what the industry calls the great decoupling—more visibility doesn’t mean more clicks anymore.
Training data vs. real-time search in AI search
AI platforms use two information sources, sometimes combining both:
- Training data: Foundational knowledge with cutoff dates—this is the information AI learned during its initial training, which typically includes content from across the web up to a specific point in time (often 6-12 months ago). Established brands with strong historical presence have advantages here because they were well-represented in the training data and tend to be mentioned more frequently in AI responses about established topics.
- Real-time search: Current information for recent events, products, and pricing. This levels the playing field for newer companies with effective SEO and GEO strategies.
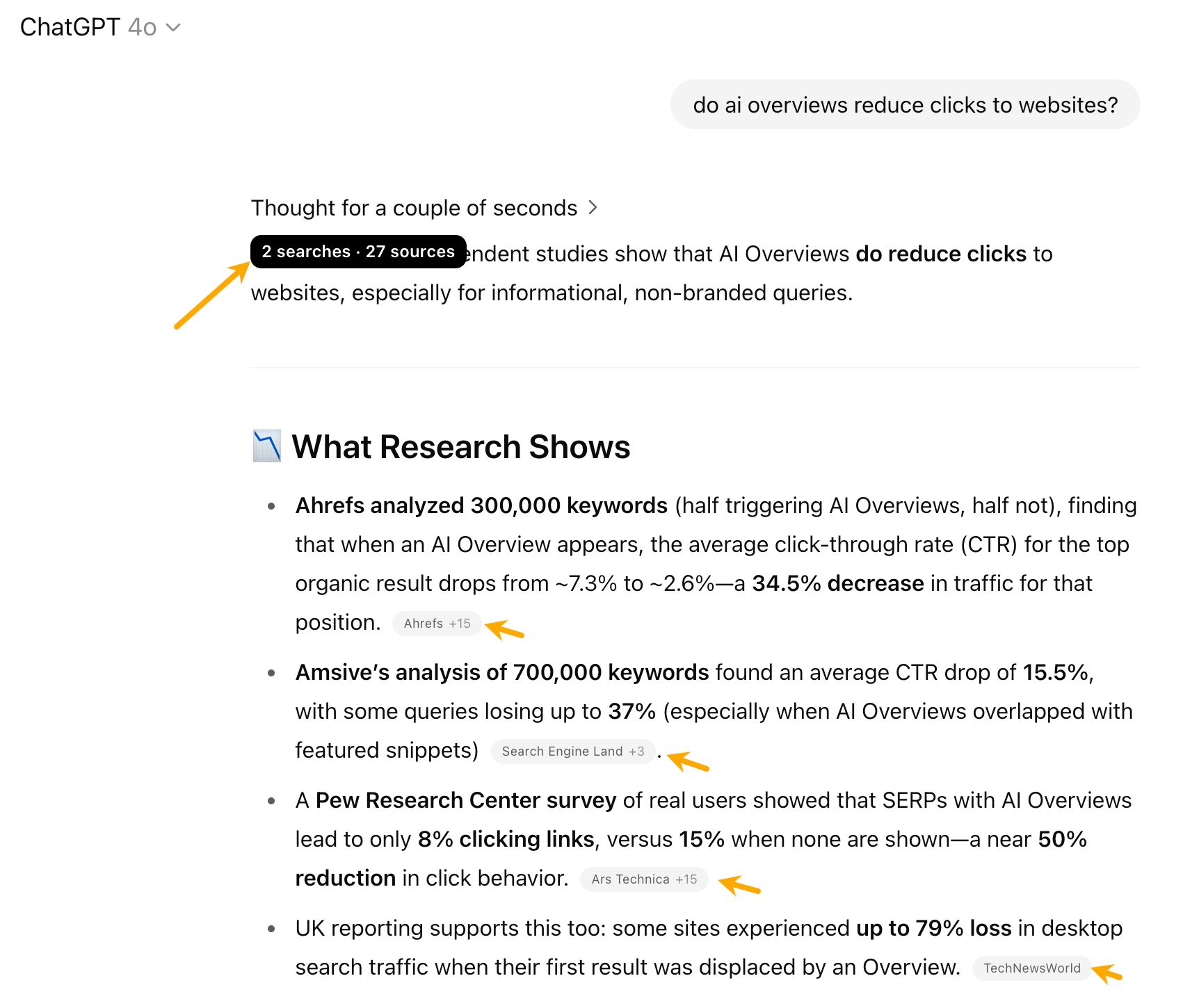
Future models starting from GPT-5 will probably rely more heavily on real-time search, making optimization more important.
Start with simple questions your customers might ask. Try obvious ones first: “What’s the best [your type of business]?” or “How do I choose [your product category]?” Then get more specific based on what you actually do. If you sell email marketing software, try “affordable email marketing for small businesses” or “email marketing vs newsletters.”
Don’t know what to test? Here are some ideas:
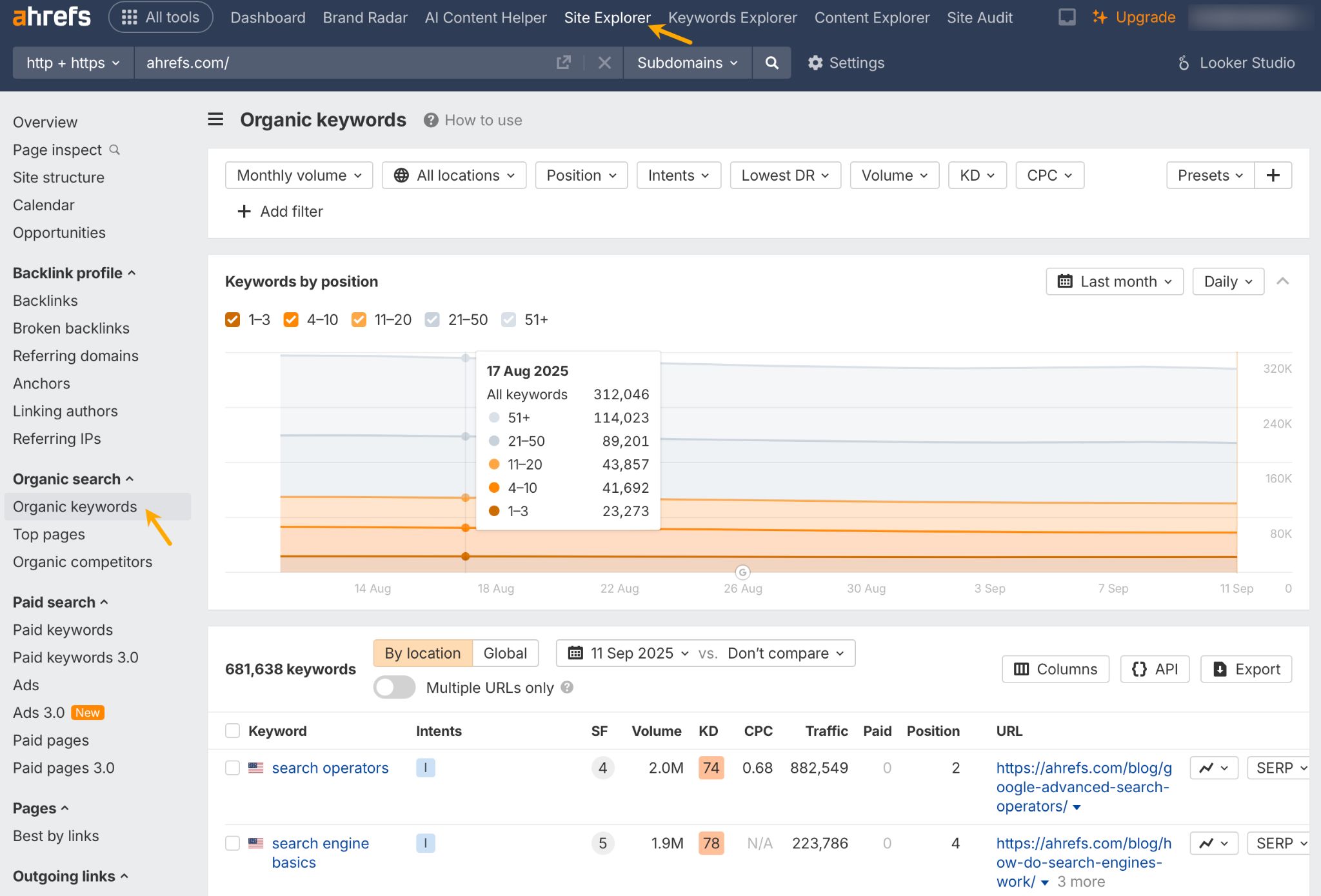
- Check the top search terms your site ranks for. You can use the free Google Search Console or AWT for that. If you use AWT, head to the Site Explorer tool and open the Organic keywords tab (screenshot below).
- Use a free keyword tool like Ahrefs’ Free Keyword Generator or AlsoAsked to see what search terms people may use to find your site.
- Think about the questions customers ask you most often.
- Check Google’s autocomplete suggestions for keywords related to your business.
Test on different AI platforms. Create a free account on ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity (Google AI Overviews appear automatically in some Google searches). Ask the same question on each platform—you’ll be surprised how different the answers can be. One might mention your brand, while another completely ignores you.
Also, AI assistants may recommend different products from your lineup for the same query, as in the example below.
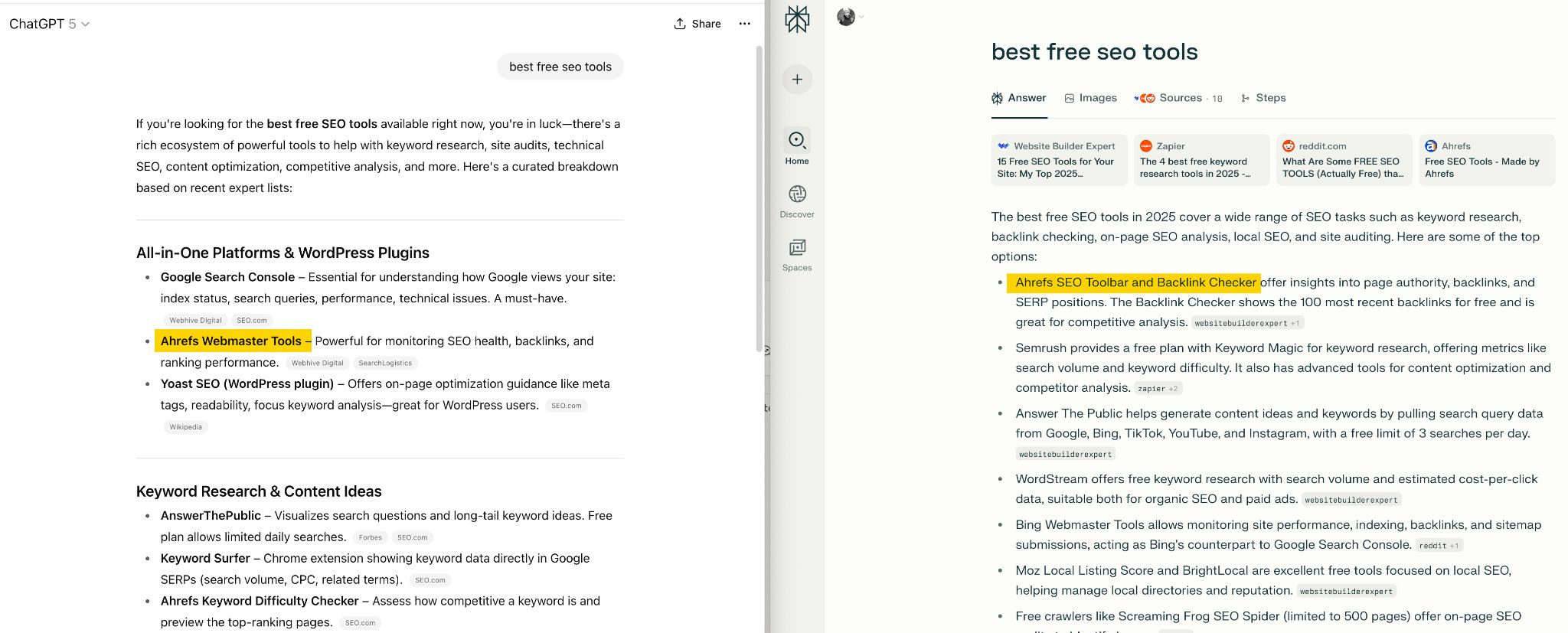
Ask the same question multiple times. This sounds weird, but AI gives different answers even to identical questions. Try the same prompt 2-3 times on each platform. Yes, this means a lot of conversations, but you can spread this over a few weeks, and it gives you a realistic picture.
For example, when I ran the same prompt again in ChatGPT, it gave me a slightly different response; this time with a new way of categorizing the tools and offering different recommendations.

Take a close look at how visitors referred by AI behave. They may act differently from regular search traffic. In our recent study, we found that these visitors stayed longer on our site and were likely to convert—probably, they’ve usually done their research before clicking through.
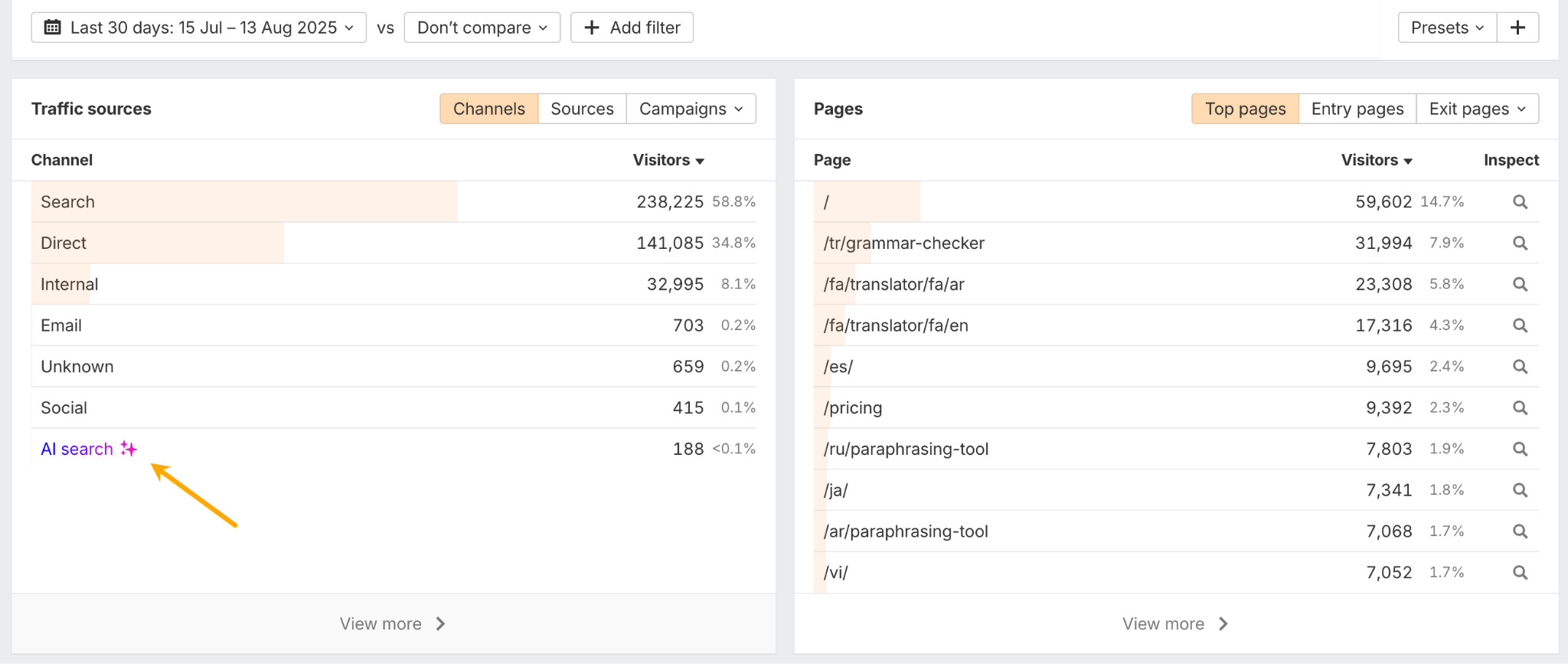
Another thing you can do with Ahrefs’ free Webmaster Tools is check which types of content drive visitors to your site and how they interact with it (do they stay longer, do they click through). For context, I recently ran this check on ahrefs.com, looking at a 3-month data period:
| Content category | Total views | Engagement | Strategic insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| How-to guides | 7315 | 184 sec time on page | Bread-and-butter traffic drivers; AI assistants favor clear, actionable guides. |
| Data studies | 6134 | 207 sec time on page | High engagement; authoritative research performs well in AI results and invites further clicks. |
| Homepage | 2875 | 0.53 bounce rate (low) | Captures navigational queries; AI assistants surface brand entry points. |
| Listicles (tools) | 976 | 0.84 bounce rate (high) | Strong time on page; useful for tool discovery via AI assistants, but high bounce suggests single-visit utility. |
| Definition | 747 | 173 sec time on page | Fulfills direct informational queries; AI assistants use these for concise answers. |
| Listicles | 585 | 0.79 bounce rate (high) | Good at attracting curiosity clicks from AI summaries. |
| Product | 530 | 0.24 bounce rate (low) | Low bounce rate; AI assistants can drive qualified visitors directly to product-related pages. |
| Opinion / thought leadership | 282 | 214 sec time on page | Engaging for deeper reads; niche but valuable for brand authority in AI contexts. |
To get this data, click on AI Search in the Web Analytics tool (part of AWT). Then, you can export it and ask your favorite AI assistant to help you do the data analysis.
Manual tracking becomes unmanageable very quickly. You’re dealing with multiple platforms, hundreds of query variations, and a lot of response variability. For competitive analysis, you need consistent tracking over time, which is almost impossible to do by hand.
However, the bigger limitation is discovery versus tracking. When you manually test “best email marketing tools,” you’re only checking one specific query you already thought of. You’re tracking what you know to look for, not discovering what you don’t.
Tools like Brand Radar automate monitoring across millions of prompts and various AI platforms, which means they can uncover opportunities you never would have found manually. They reveal queries where your competitors get mentioned, but you had no idea those conversations were even happening.
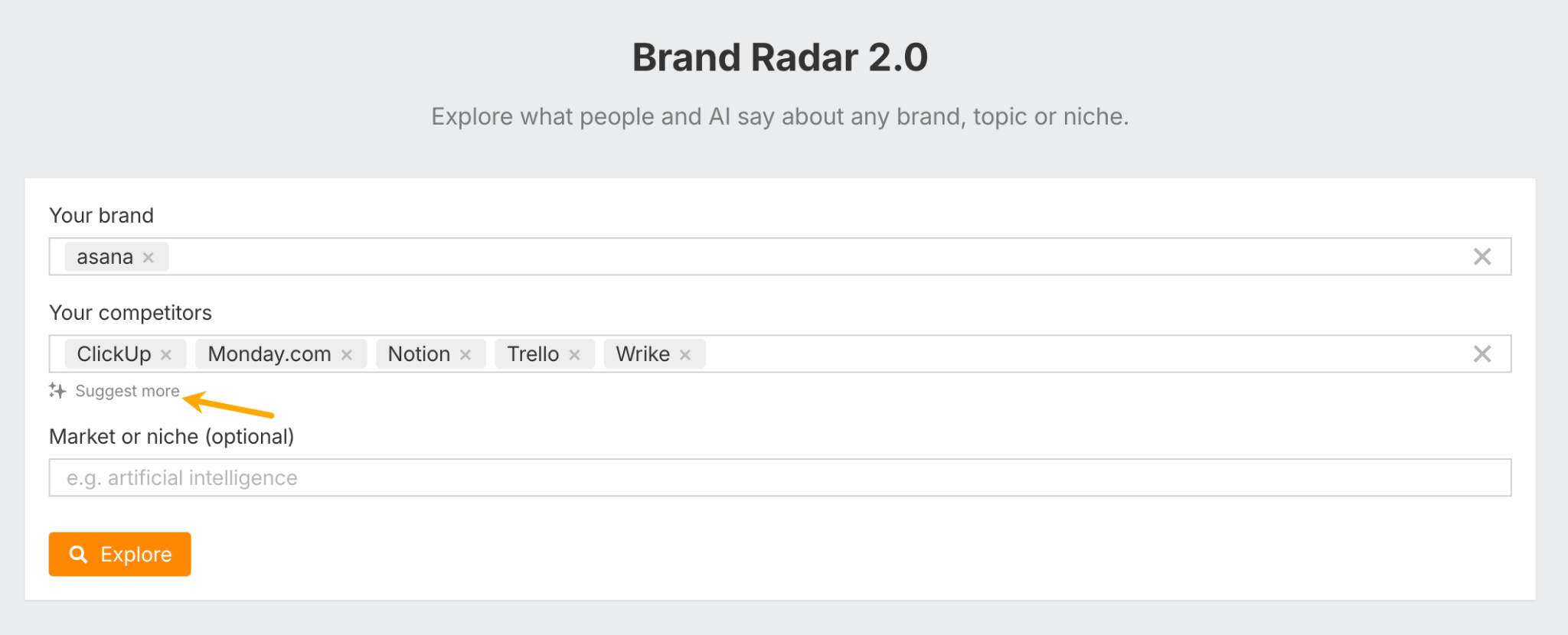
To start using Brand Radar, just enter your brand name and your competitors’ names (the tool can even use AI to suggest similar brands).
You’ll get a dashboard with data on:
- AI mentions: When your brand appears in AI responses.
- Impressions: Mentions weighted by search volume to estimate reach.
- AI share of voice: Your brand’s reach percentage versus competitors.
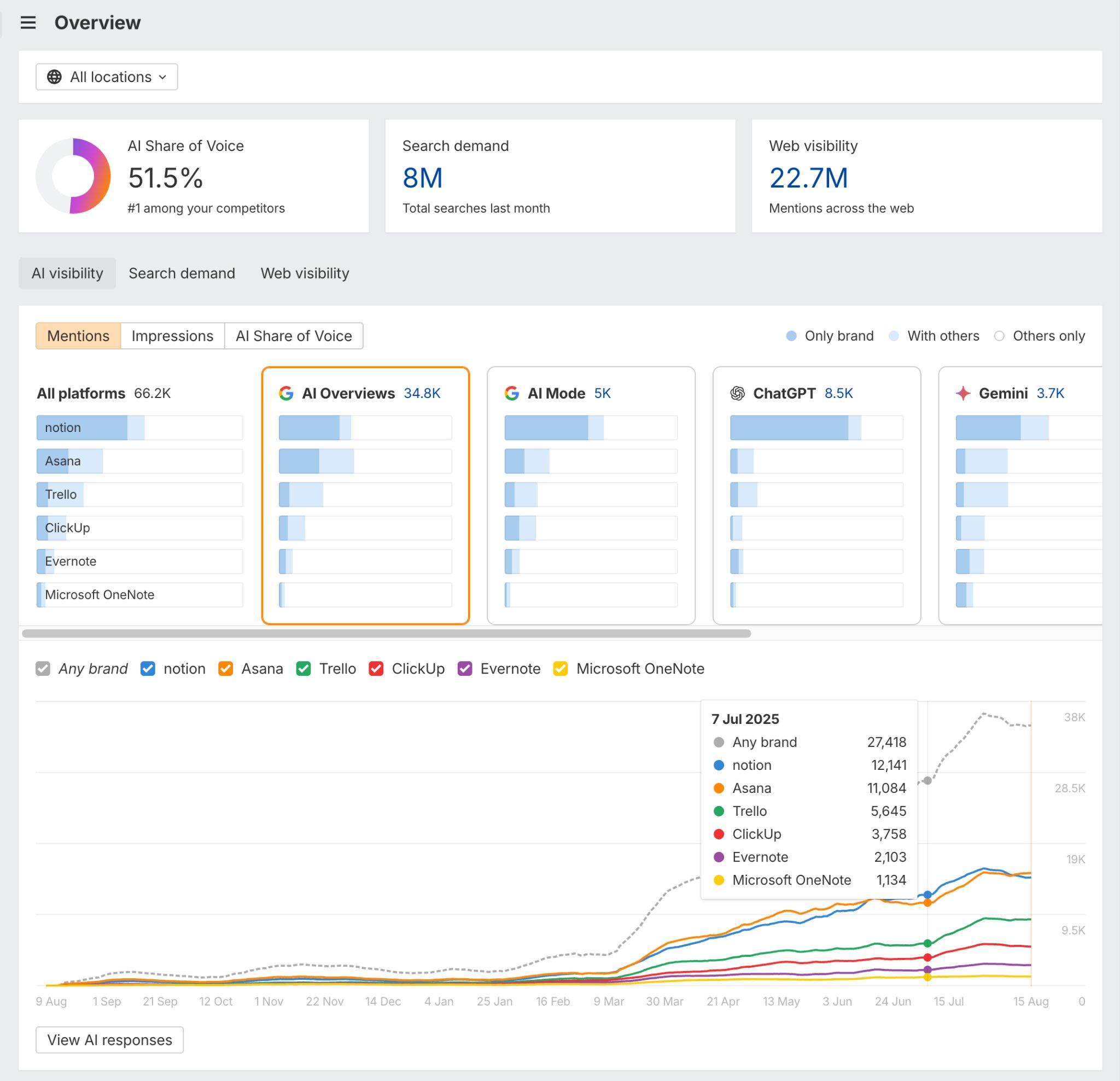
For example, imagine you’ve just launched a new product that expands your brand into a bigger market, and now you want to see how your AI visibility stacks up against new competitors. That’s exactly what happened with Monday.com when they introduced their CRM feature—up until then, they were mainly known as a project management tool.
- Enter your brand and competitors.
- Go to the Topics report.
- Enter the topic in the Filter window.
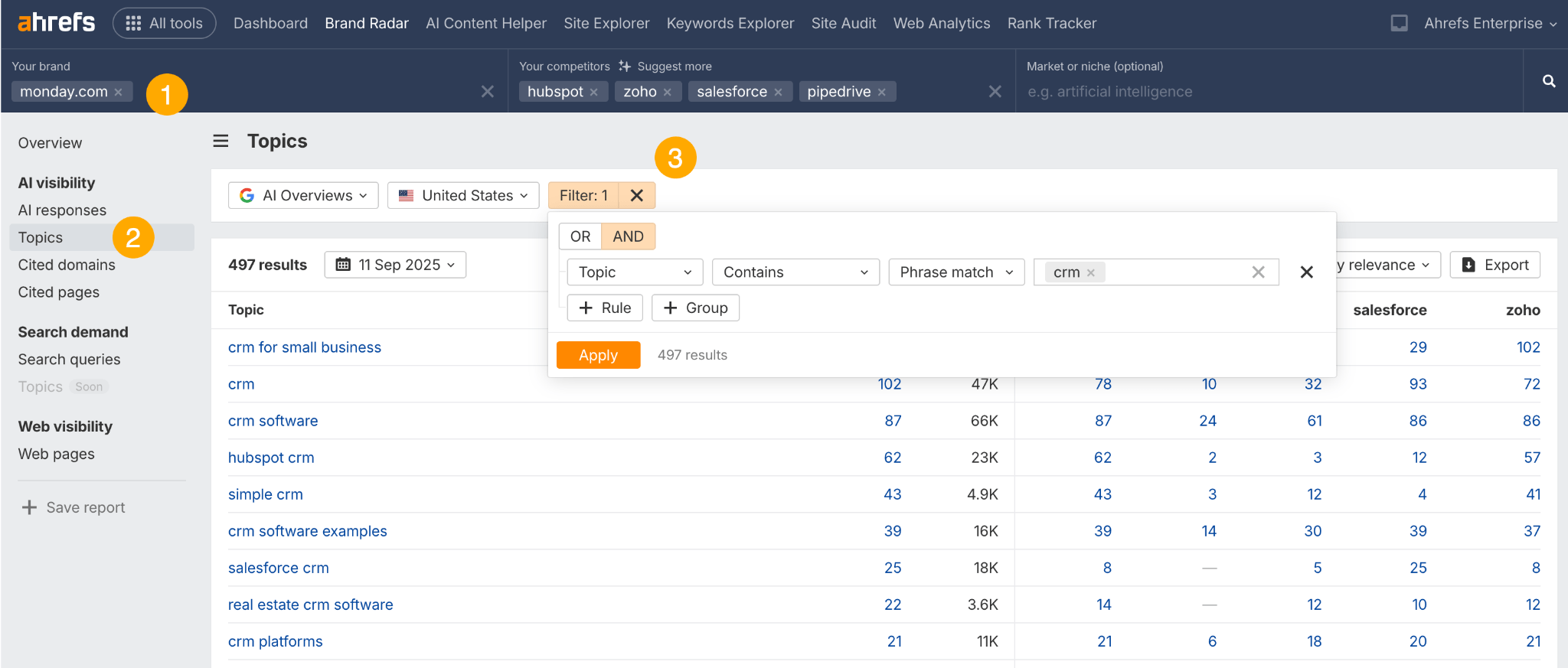
You can also save your reports, so you’ll always have access to the same data whenever you need it.
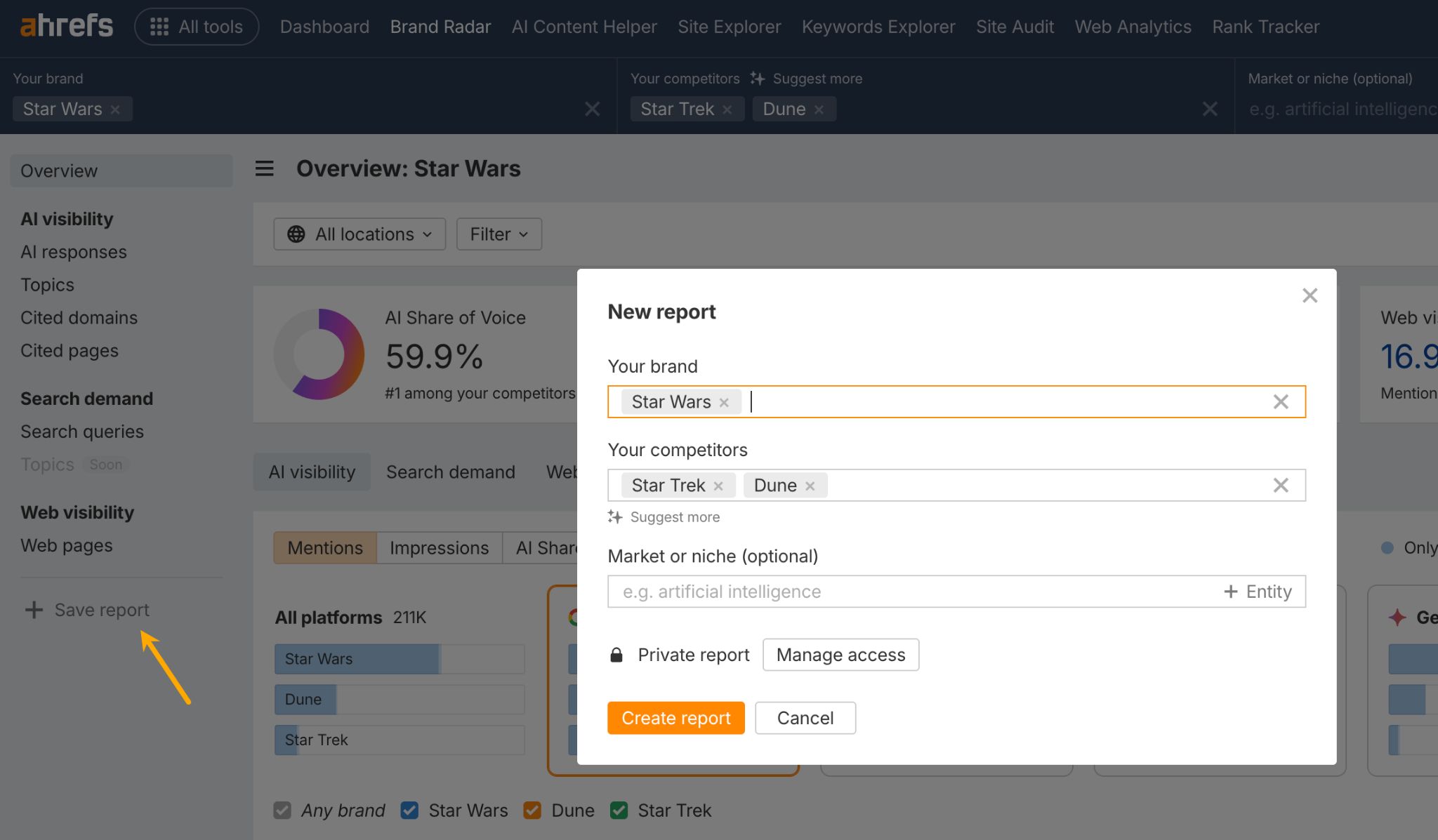
If you need to share updates with stakeholders or clients, you can add AI visibility data to a live dashboard using the Report Builder. It will keep everything updated automatically, so the data is always current.
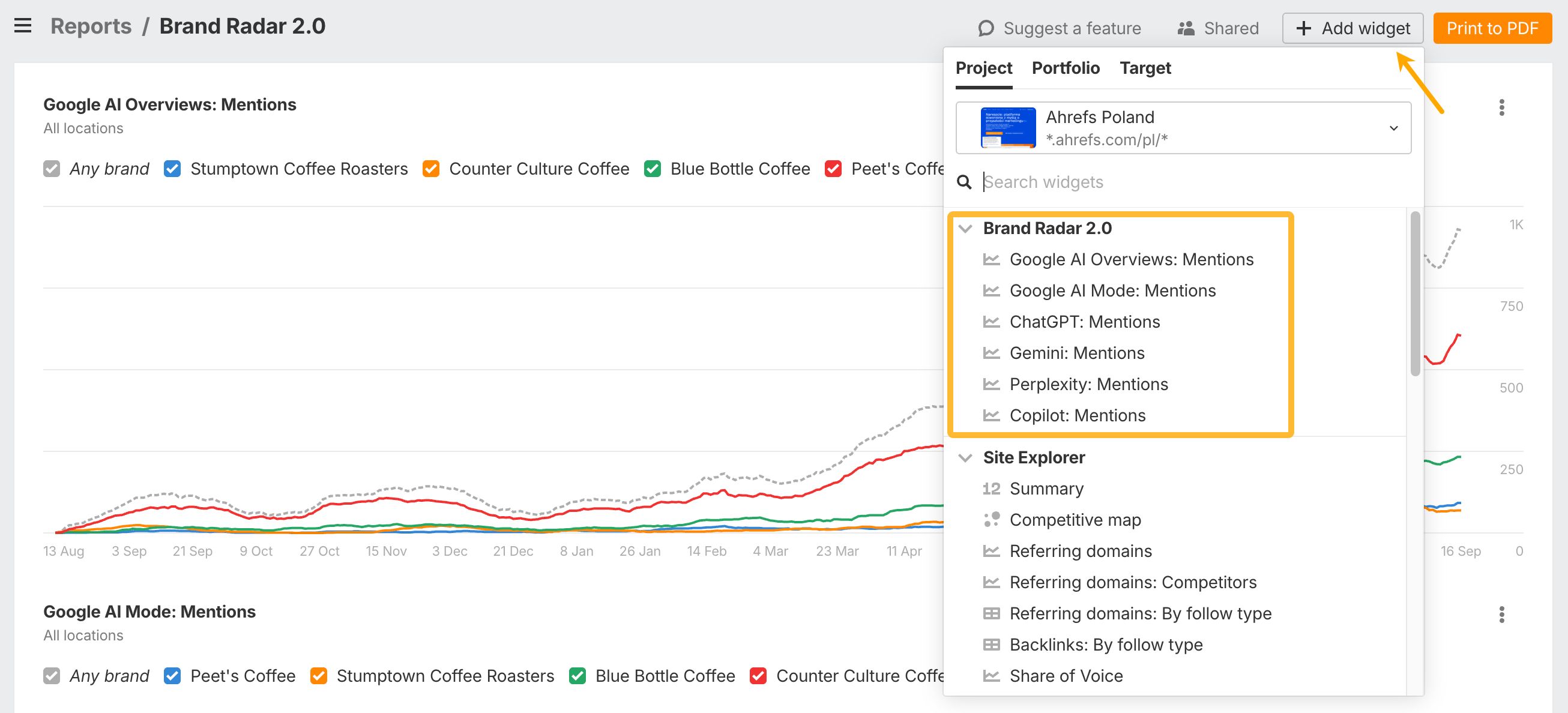
In this article, we cover even more use cases of Brand Radar, including how to:
- Measure how closely AI links your brand to a topic or product category.
- Identify which of your pages get the most visibility in AI search.
- See which content formats AI tends to cite most often for your topic.
- Find the most-cited pages in your niche—and learn how to get mentioned in them.
Another handy tool is Ahrefs’ Site Explorer. One of its many features lets you quickly check the AI visibility of any website.
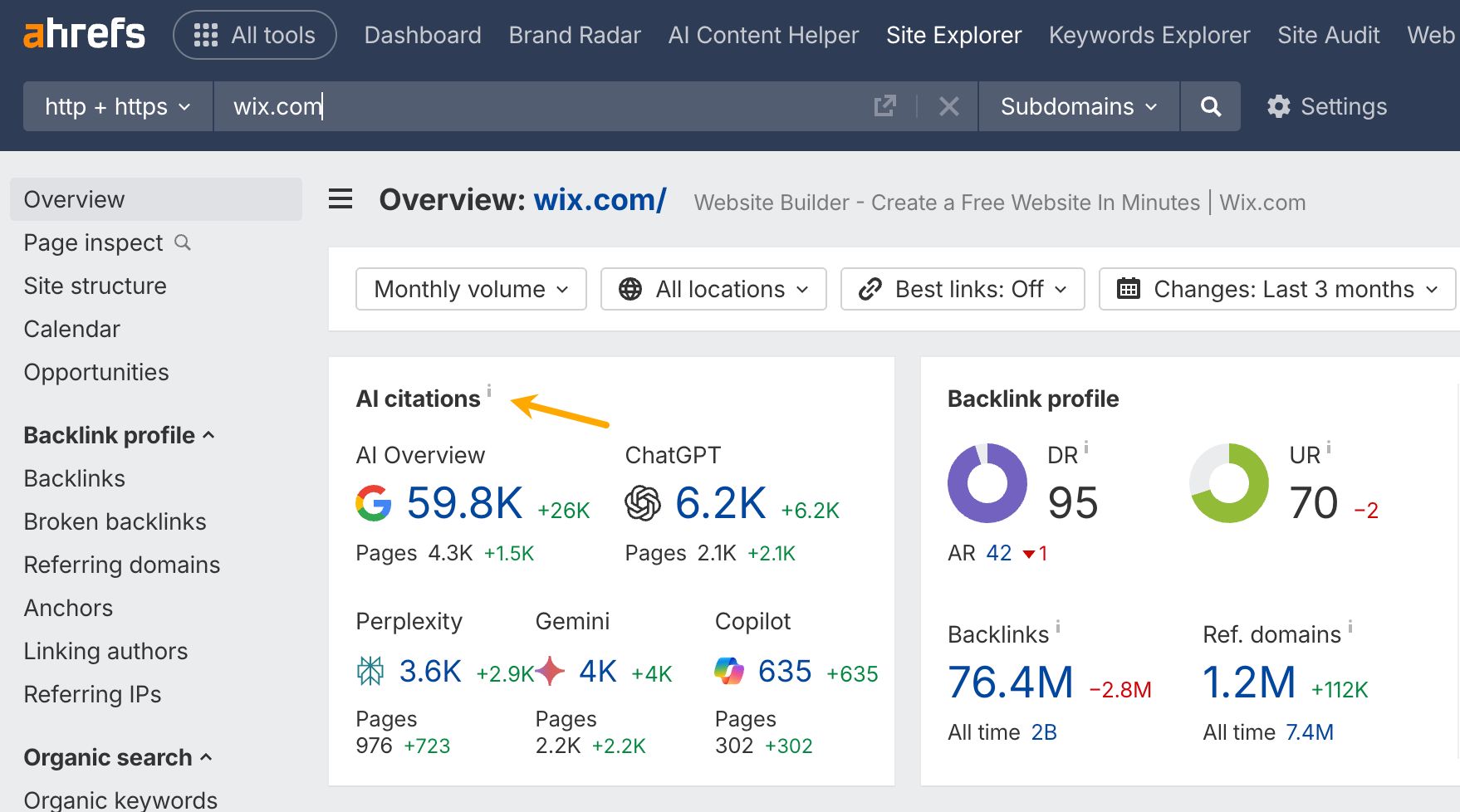
AI tracking tools are not perfect
The AI search landscape is still developing, which means the data and methodologies have some significant constraints you should be aware of.
- No real demand data exists. No company has access to actual search volume data for ChatGPT or other AI platforms (yet).
- All tools use synthetic prompts since real user query data isn’t available. At Ahrefs, we base our prompts on real questions from our keyword database and People Also Ask data, but they’re still “artificial”.
- AI responses vary significantly due to personalization, different models, and inconsistent responses.
- Attribution remains challenging. Tracking direct conversions from AI mentions is nearly impossible due to complex user journeys.
Bottom line: While no tool is perfect, dedicated AI visibility tools remain your best option for systematic tracking and competitive analysis at scale.
This new practice of optimizing for AI search is known as Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). The idea is to ensure your brand is visible and accurately represented in AI-generated answers—so it shows up even when users don’t click a link.
You might also see it referred to as LLMO or AEO, but the goal is the same: making sure AI assistants include your brand in their responses.
Think of it this way: traditional SEO was like competing to have the best storefront on a busy street. GEO is like making sure the local tour guide knows about your business and recommends it to visitors.
The good news is that GEO builds on traditional SEO fundamentals—great content, clear structure, and topical authority work for both. You’re just expanding your definition of success beyond clicks to include AI citations and brand mentions.
Finally, you don’t always need it to get mentioned or cited by AI. Take Ahrefs, for example—our content and product pages have been referenced 7,470 times across 2,309 pages, all without any effort to optimize for AI visibility. It’s a good reminder that AI isn’t really a brand-new marketing channel; it’s built on the content that’s already out there.
Back to the core principles that drive AI visibility.
Build third-party authority
Most brand mentions will come from third-party sites, not your own domain. AI platforms seem to trust external validation over self-promotion. To illustrate, here are the top sources of our brand mentions (no ahrefs.com):

So, focus your efforts on getting featured in:
- Industry rankings and “best of” lists from authoritative publications. You can use Site Explorer to find those with high AI citation counts and domain authority.
- PR and media coverage in relevant trade publications.
- Customer reviews and case studies on third-party platforms.
Focus on high-citation content formats
According to our research, certain content types get cited by AI more frequently:
- “Best” and “top” lists. These comparison formats are exactly what AI needs to make recommendations.
- “Vs” comparisons and how-to guides help AI answer specific user questions about choosing between options or solving problems.
- Product and service pages with clear, factual descriptions get cited when AI needs to explain what companies offer.
- Data studies and authoritative research provide the facts and figures AI platforms love to reference.
- Definition and FAQ content answer the basic questions AI gets asked most frequently.
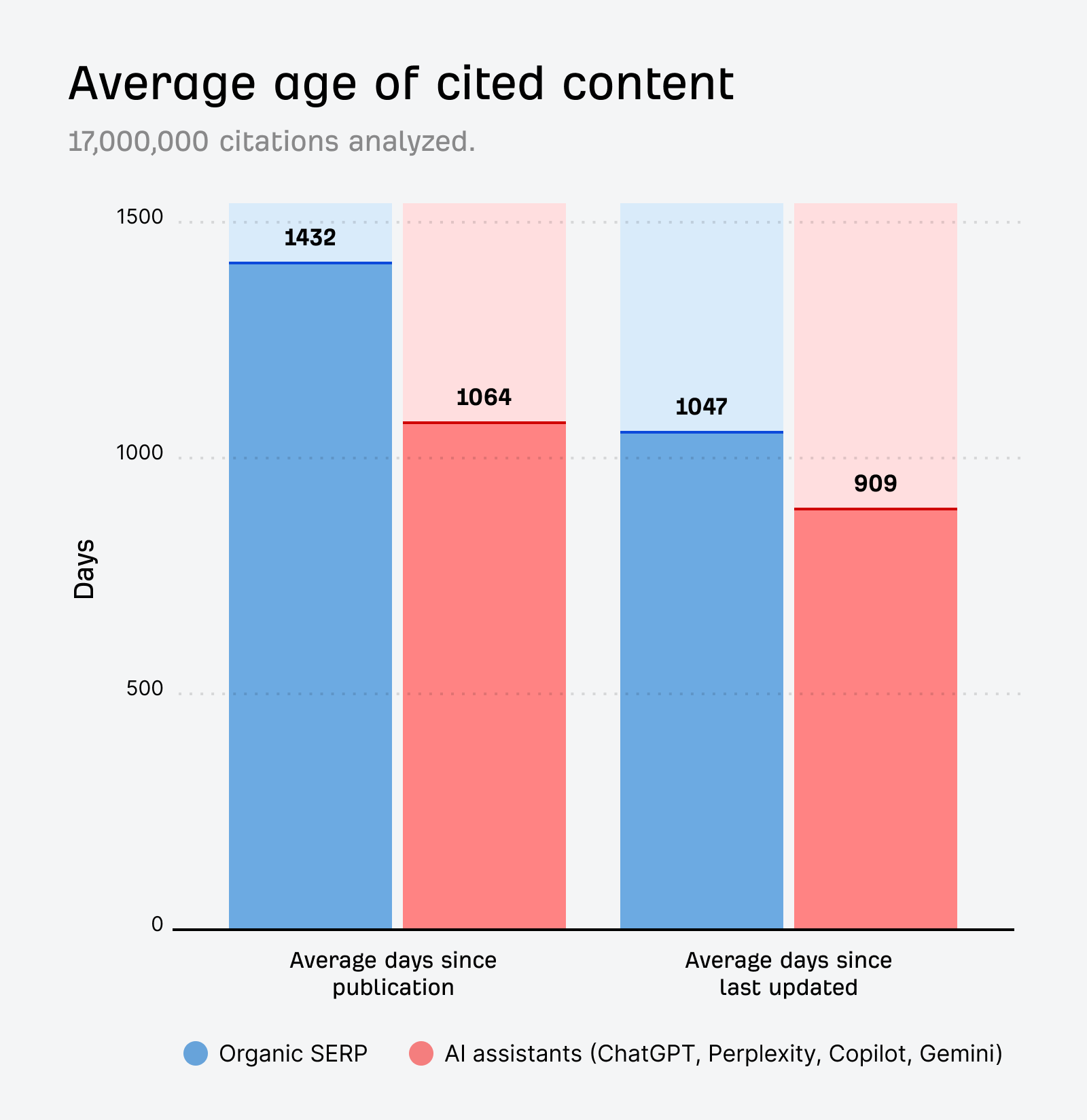
One more important note: compared to traditional search results, AI assistants tend to favor fresher content. Once you create these assets, make sure to keep them updated.
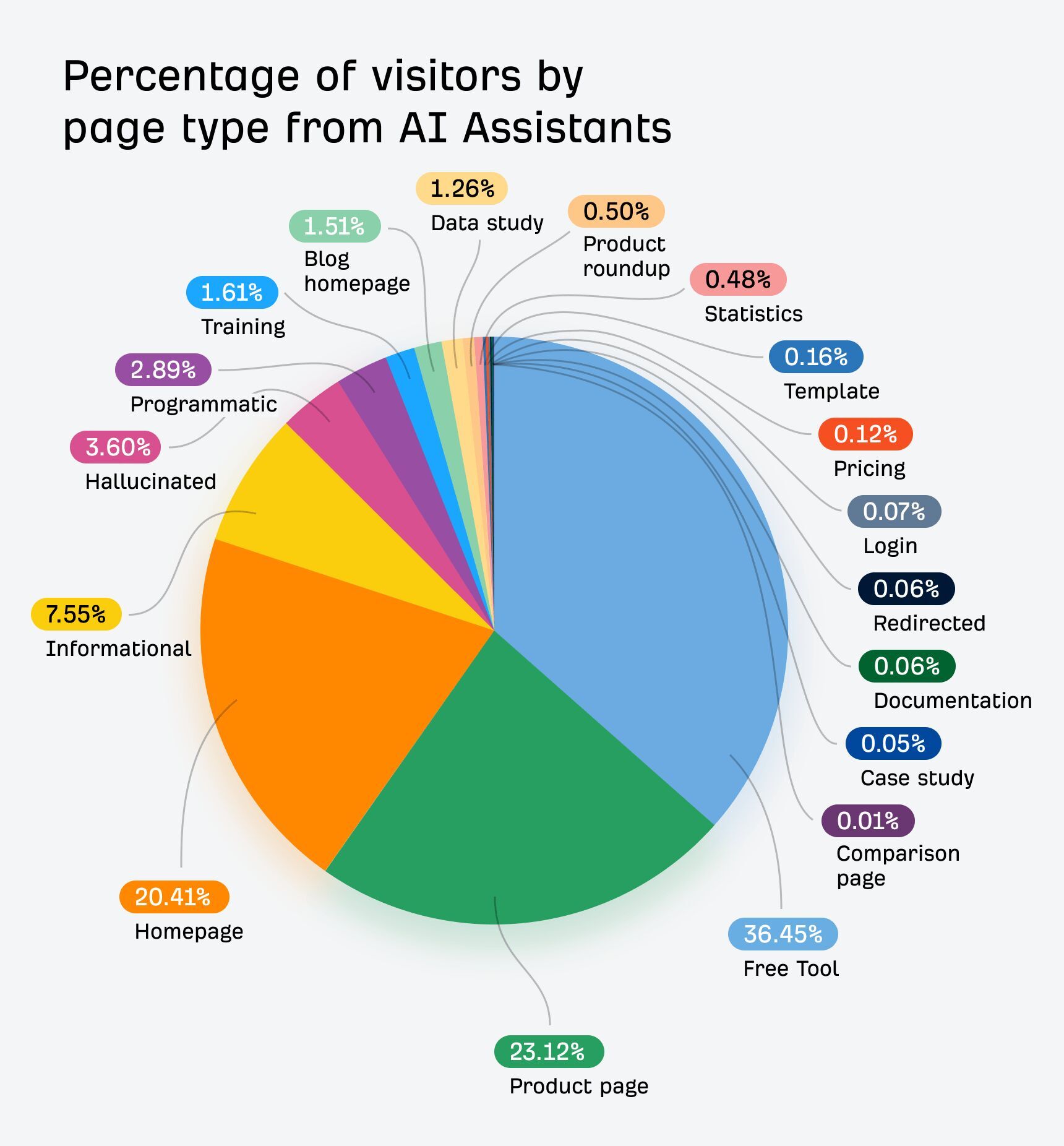
Perfect your primary touchpoints
We found that over 80% of AI traffic goes to homepages, product pages, and key tools. Chances are, AI traffic share on your site will look similar.
Make these pages AI-friendly:
- Make your value proposition immediately clear in the first paragraph.
- Create factual descriptions AI can easily parse and cite, avoid marketing fluff.
- Use structured formatting with headers, bullet points, and clear sections.
- Include easy-to-find contact information and key business details.
Format for AI readability
AI platforms prefer content that’s easy to understand and cite:
- Use hierarchical headings (H1, H2, H3) and bullet points for structure.
- Write in simple, direct language with short paragraphs. Answer common questions explicitly rather than making readers infer answers.
- Include specific facts and figures that AI can quote with confidence.
- Ensure fast loading speeds and mobile optimization. Likely more important for Google’s AI than other ones and by extension, AI assistants that use Google Search to improve results.
- Add schema markup for FAQs and product information.
- Finally, make sure you’re not blocking AI bots in your robots.txt file or in your firewall settings.
Post on high-authority user-generated content platforms
AI platforms clearly favor certain websites when pulling citations, which means you can lean on the platforms AI already trusts.
The data highlights some big winners:
- YouTube is the second most-cited domain in AI answers, with 3.7 billion monthly organic visits.
- Reddit shows up in 77% of product review searches and ranks third overall for AI citations.
The takeaway? Go where your audience already spends their time. If they’re asking questions in specific subreddits, that’s where you should show up. If they’re watching YouTube to learn about your industry, that’s where your focus should be.
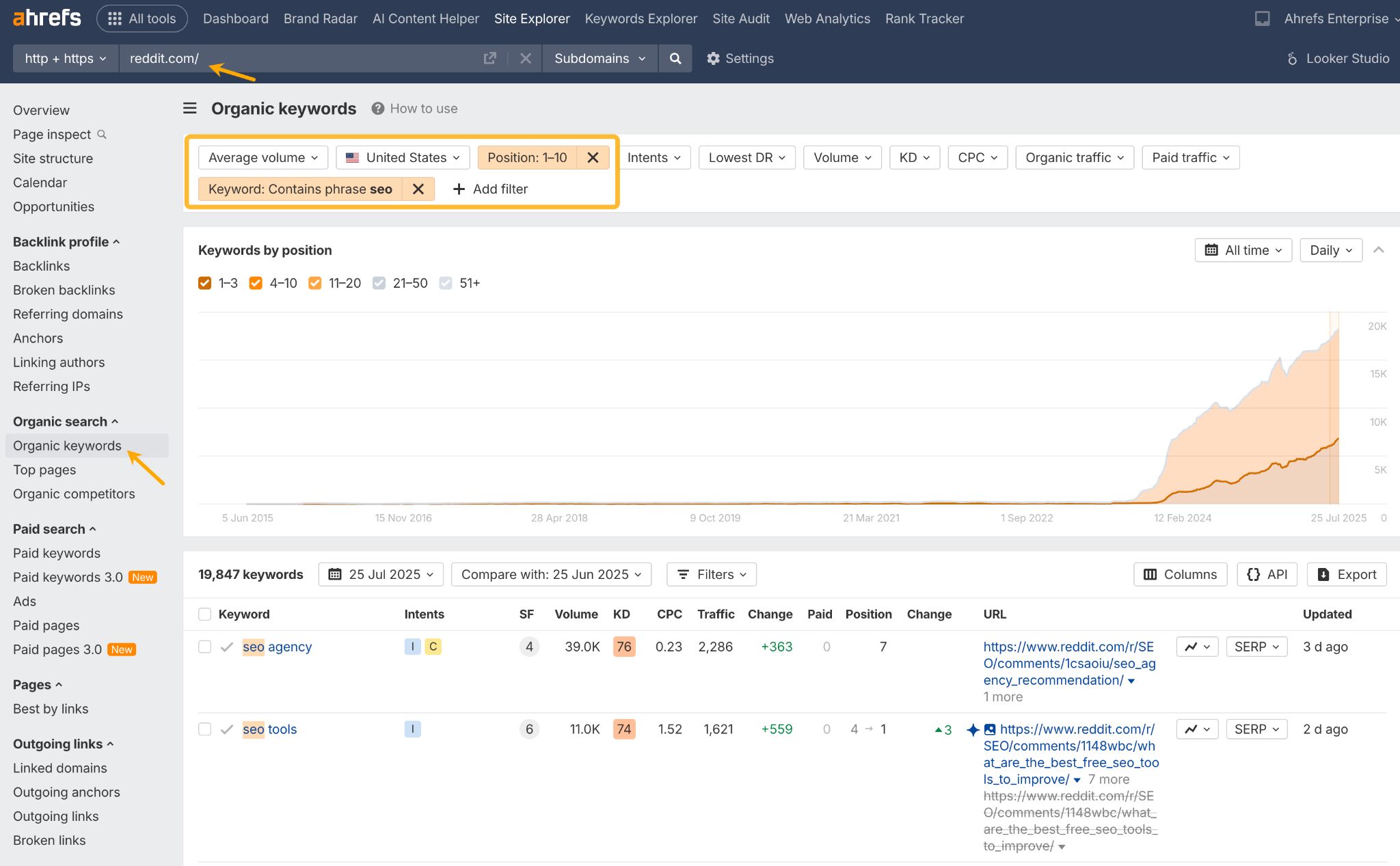
Here’s how you can use Ahrefs to find relevant Reddit threads:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer, enter “reddit.com”, and open the Organic keywords report.
- Use filters: positions 1-10, keyword includes (enter phrases related to your site). You can select a preferred location, too.
- Look for relevant keywords with a lot of traffic.
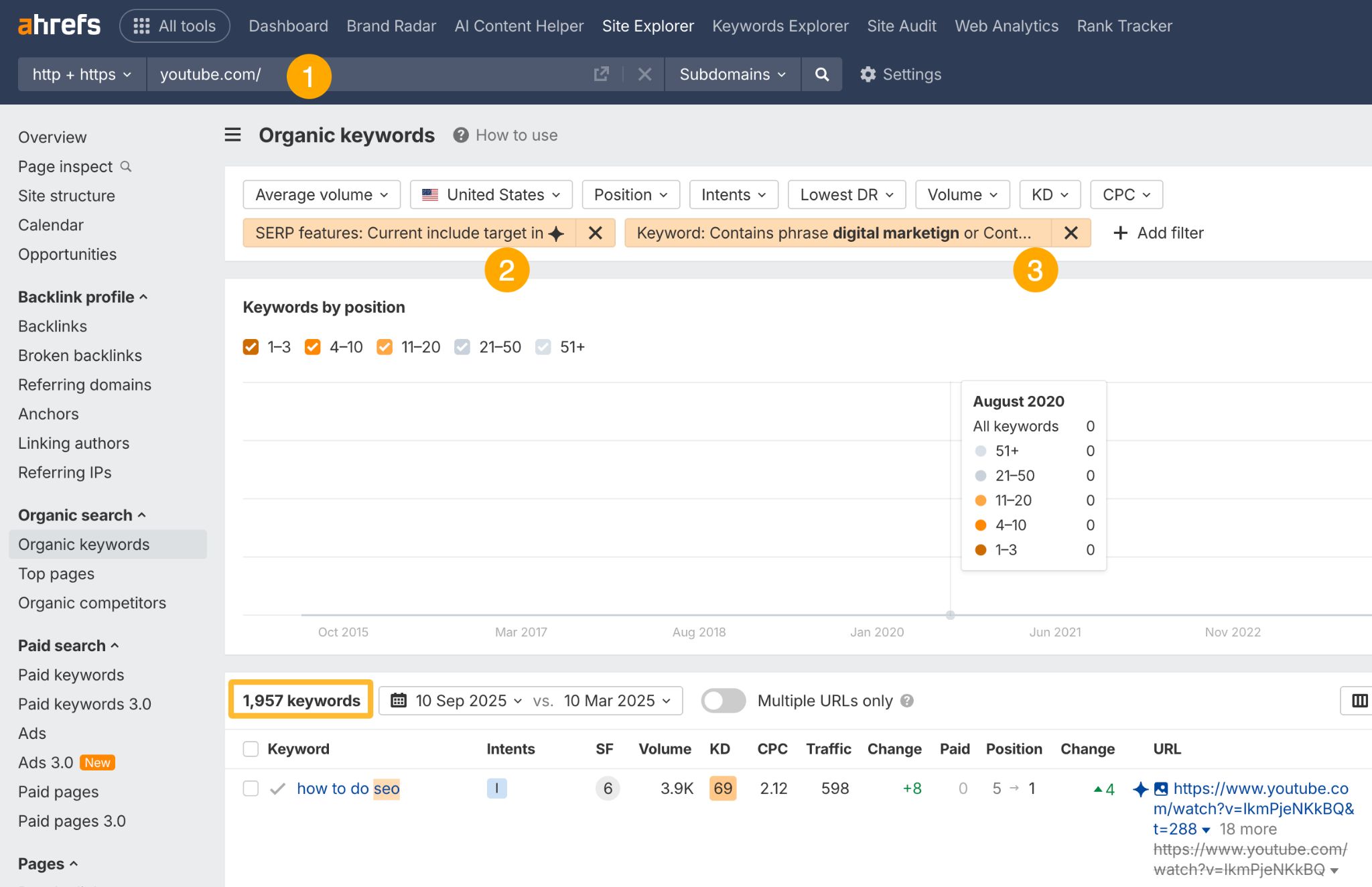
As for YouTube, here’s how to find topics where Google cites this platform in AI Overviews:
- Go to Site Explorer and enter youtube.com as the target.
- Set SERP features filter to “Current include target in AI Overviews”.
- Set the keyword filter to “Contain [your topics]”.
Find your AI mentions and citation gaps
AI mentions gaps are AI responses where competitors are mentioned, but you’re not.
By analyzing your AI mention gap, you’ll discover industry publications, review sites, and expert roundups that are warm leads for PR outreach because they’ve already demonstrated interest in covering your market.
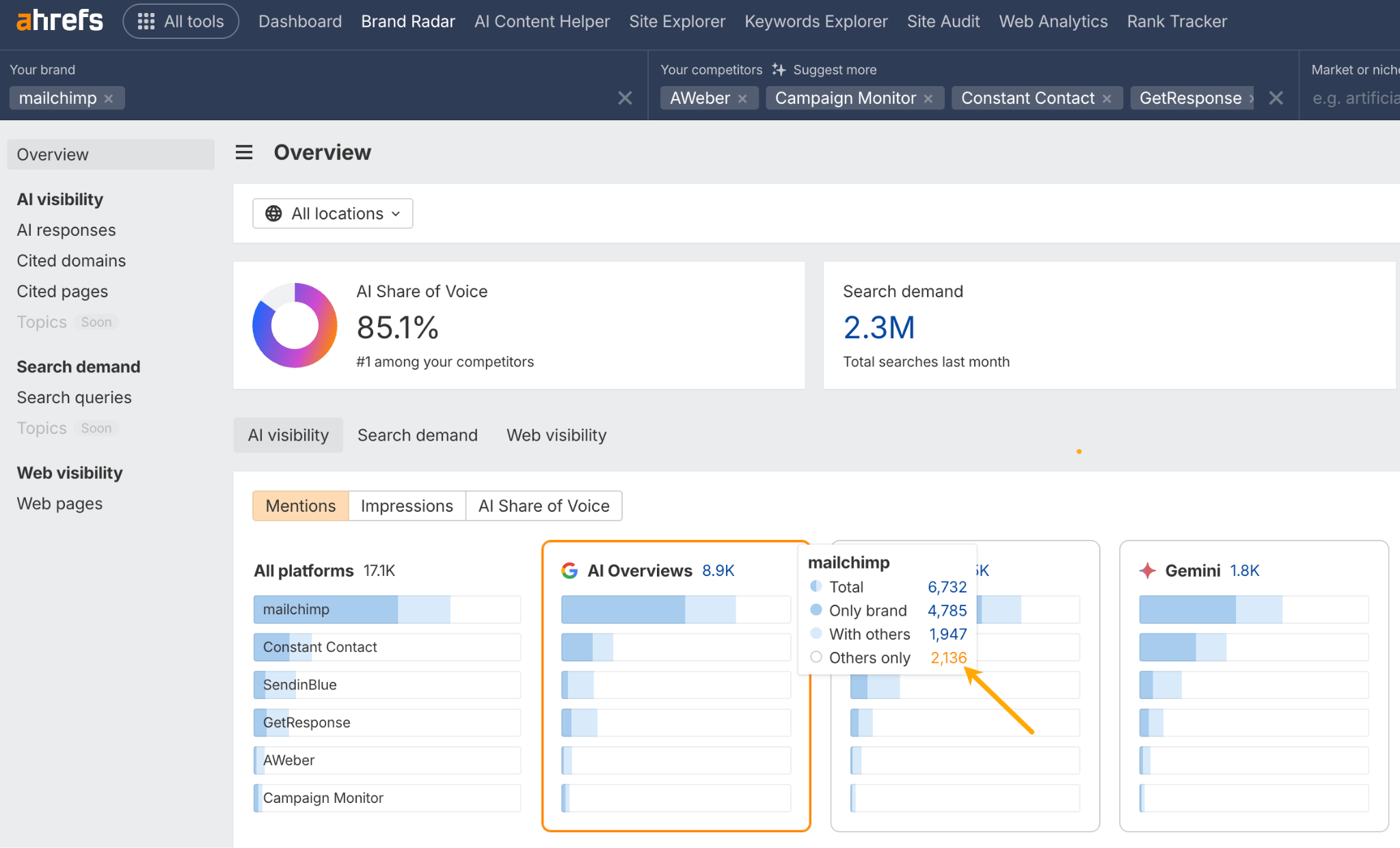
Here’s how to find your AI mention gap using Ahrefs’ Brand Radar:
- Enter your brand and competitors.
- Hover on your brand in the mentions graph section and click on “Others only”.
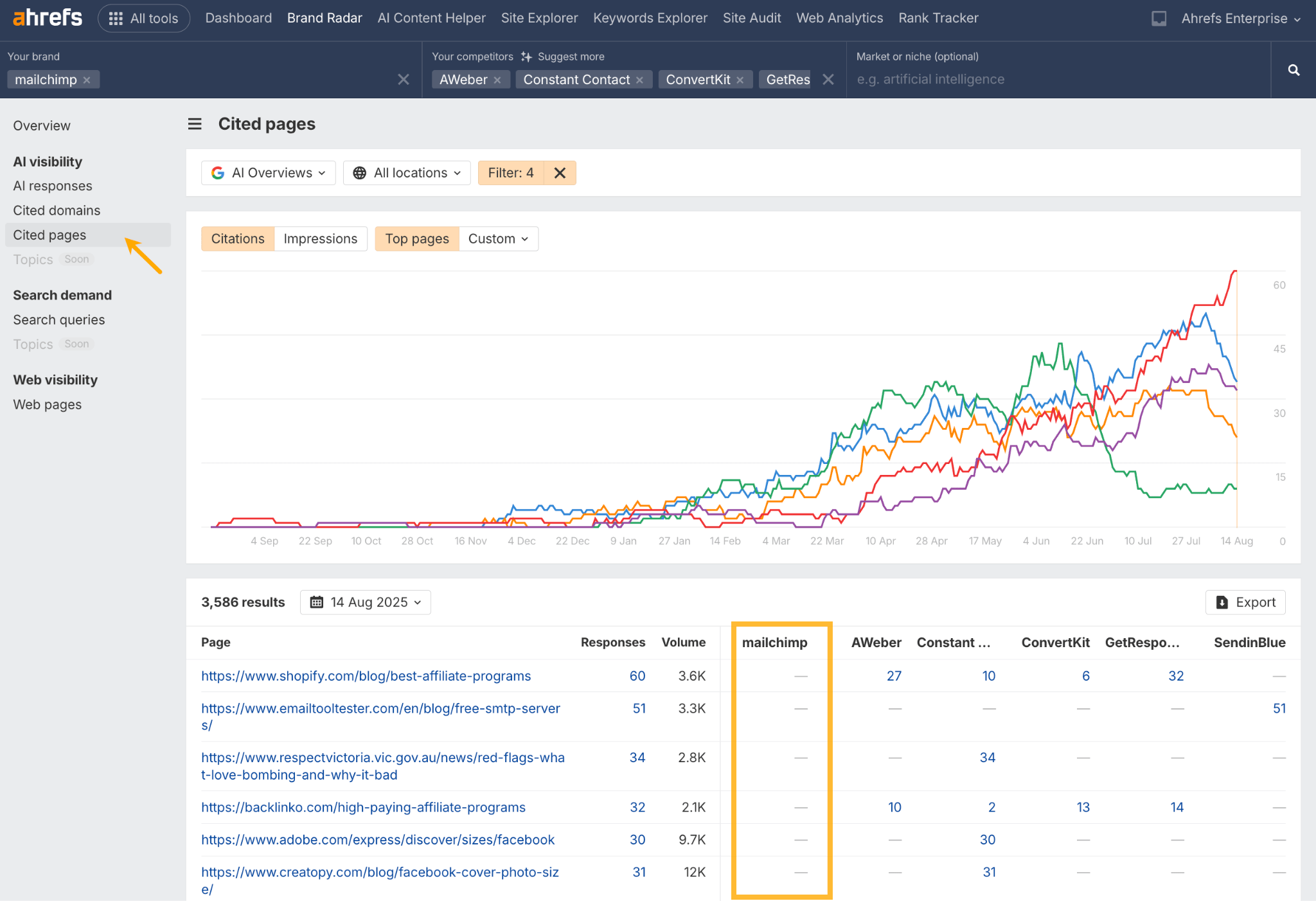
- Go to the Cited pages report.
- Repeat for each AI index.
AI citation gaps are AI responses where competitors’ content gets cited, but yours does not.
When AI cites your competitor’s research or quotes their expert opinion, it’s positioning them as the thought leader in your space. Over time, this builds their brand authority while yours remains invisible.
Use Brand Radar to show competitor citations without your brand, then identify high-search-volume queries where competitors dominate. Create superior content targeting these specific topics to earn your own citations.
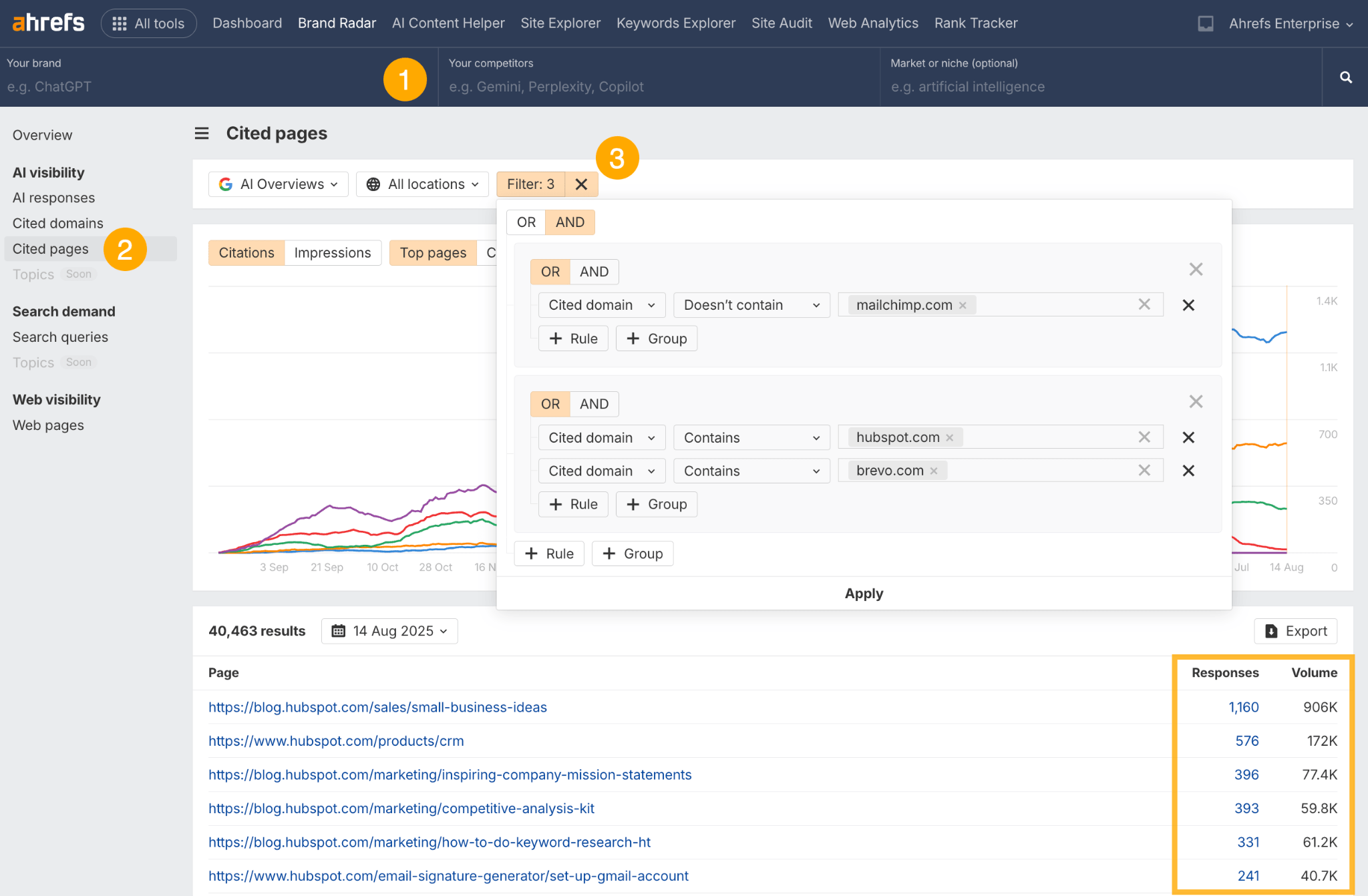
To identify your AI citation gap with Brand Radar:
- Make sure top-level filters are left blank.
- Go to the cited pages report.
- Set the lower filters to AND. Then, set the first rule to “Cited domain doesn’t contain [your domain]”. Add a new Group and set it to OR. Inside that Group, add separate rules for each competitor domain, using: “Cited domain contains [competitor’s domain].”
Final thoughts
AI search isn’t a completely separate marketing channel you need to add to your already-packed strategy. It’s how your existing efforts—content creation, PR, SEO, brand building—now have additional impact you weren’t measuring before.
The content you’re already creating can get cited by AI platforms. The PR coverage you’re already pursuing can lead to AI mentions. The industry relationships you’re already building can result in AI recommendations. You don’t need to start from scratch; you need to expand how you define success.
So, this isn’t about panicking or dropping everything to chase AI search. It’s about recognizing a timing opportunity and acting while the barrier to entry is still low. So, start testing, learning, and optimizing while there’s still room to make an impact.
Got questions or comments? Let me know on LinkedIn.



