If you make smart keyword choices, you’ll produce content with the potential to attract valuable organic search traffic month after month. If you pick the wrong keywords, your content will only attract low-value traffic or none at all.
So how do you choose the right keywords for SEO?
Many people overcomplicate this process, but the reality is that it’s not that hard.
Here’s how to do it in four simple steps:
- Find keywords with search traffic potential
- Make sure you create content that aligns with search intent
- Make sure the keyword has “business potential”
- Make sure you can rank for the keyword
Unless people are actually searching for a keyword, there’s no point in targeting it. That’s because ranking high for a keyword nobody is searching for won’t send any traffic your way. It simply has no traffic potential.
To find what people are searching for, you need a keyword research tool.
Google has a free one called Keyword Planner. The way it works is pretty simple: You enter a topic, and it kicks back relevant keyword ideas and search volumes.
For example, here are a few of the ideas and search volumes it gives us for “dog food”:
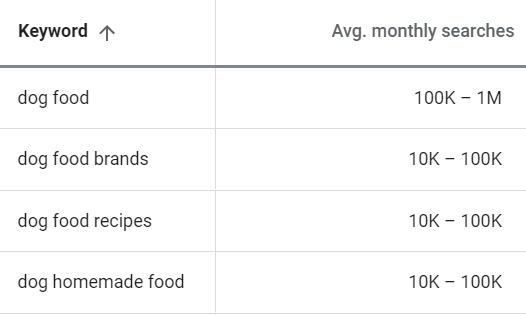
Unfortunately, Google Keyword Planner (GKP) has one major flaw: It only shows search volume ranges, not actual monthly search volumes (unless you’re running ads).
Some of these ranges are huge too. You can see above that a few keywords fall into the 10K-100K bucket. This makes it super hard to know which ones to prioritize because the range is so broad. The keyword could get 10k monthly searches, 40k, 80k, 100k—there’s just no way of knowing.
To get precise keyword search volume estimates, you’ll need a third-party tool like Keywords Explorer. This tool works in much the same way as GKP. You enter a topic/seed keyword, and it shows you keyword ideas and monthly search volumes.
The difference is that the search volume estimates are much more precise, and you also usually get way more ideas than in GKP.
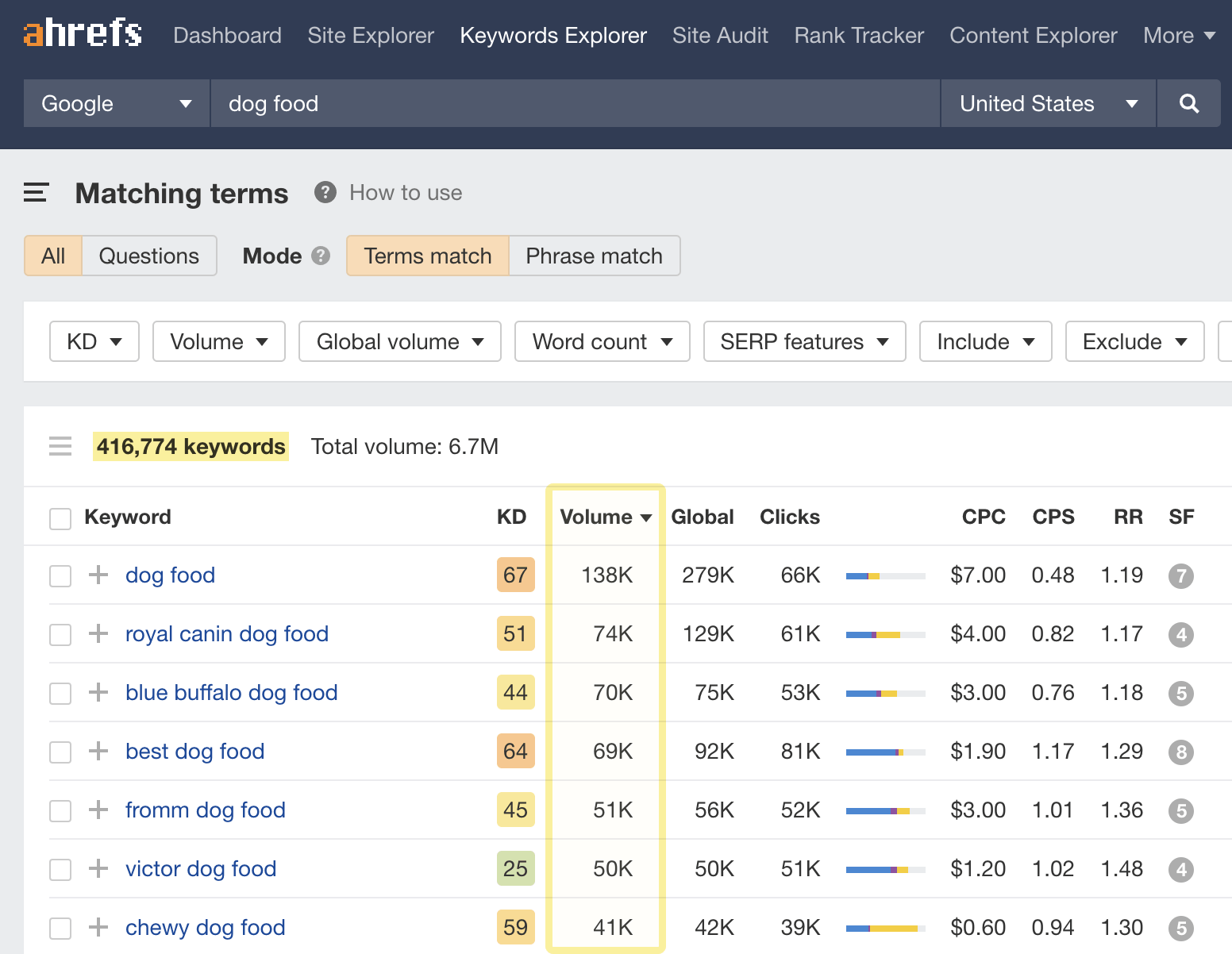
For example, if we enter the seed keyword “dog food” and check the Matching terms report, we get over 416,000 keyword ideas with search volumes and other data:
Generally speaking, keywords with higher search volumes have a higher traffic potential. However, ranking in pole position for some keywords gets you way more traffic than you’d imagine, given the search volume.
For example, here’s the search volume for “best dog food”:
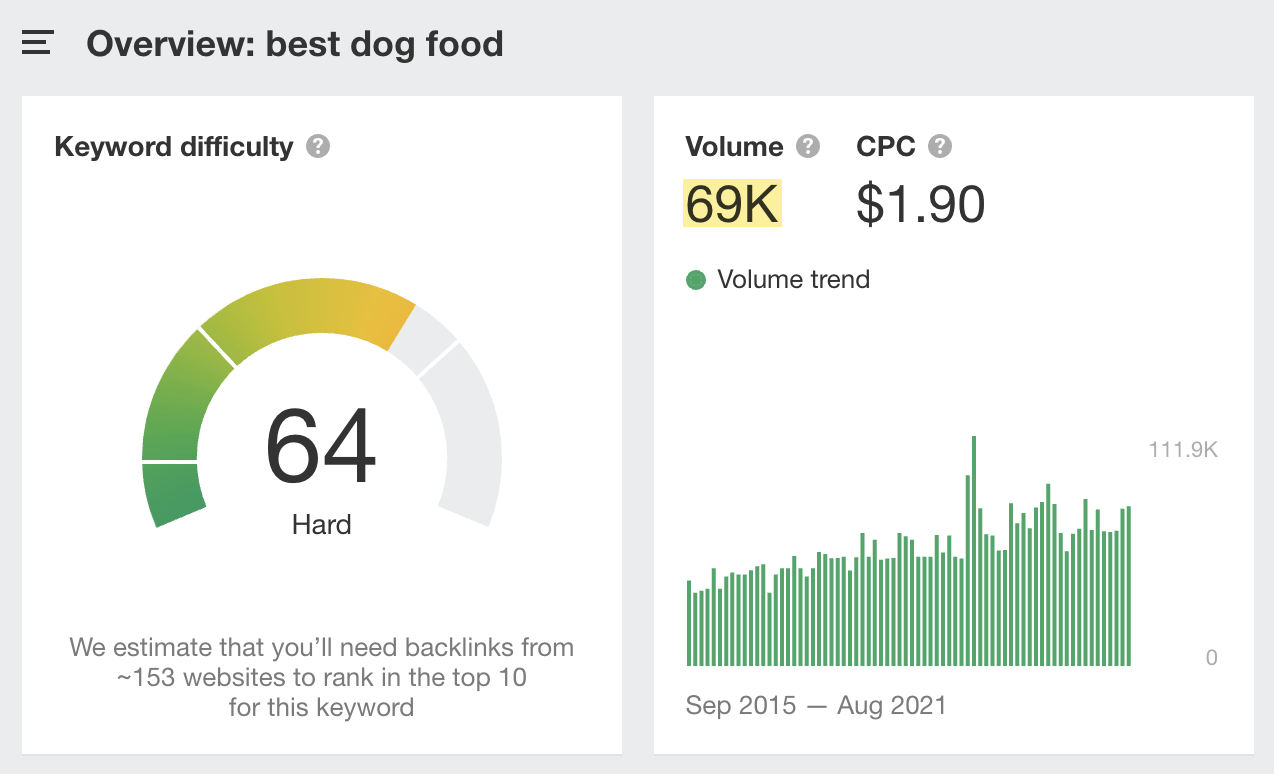
69K. Pretty high.
But if you scroll down to the SERP overview and check the estimated traffic to the top-ranking page, you’ll see that the traffic potential of this topic is actually much higher:
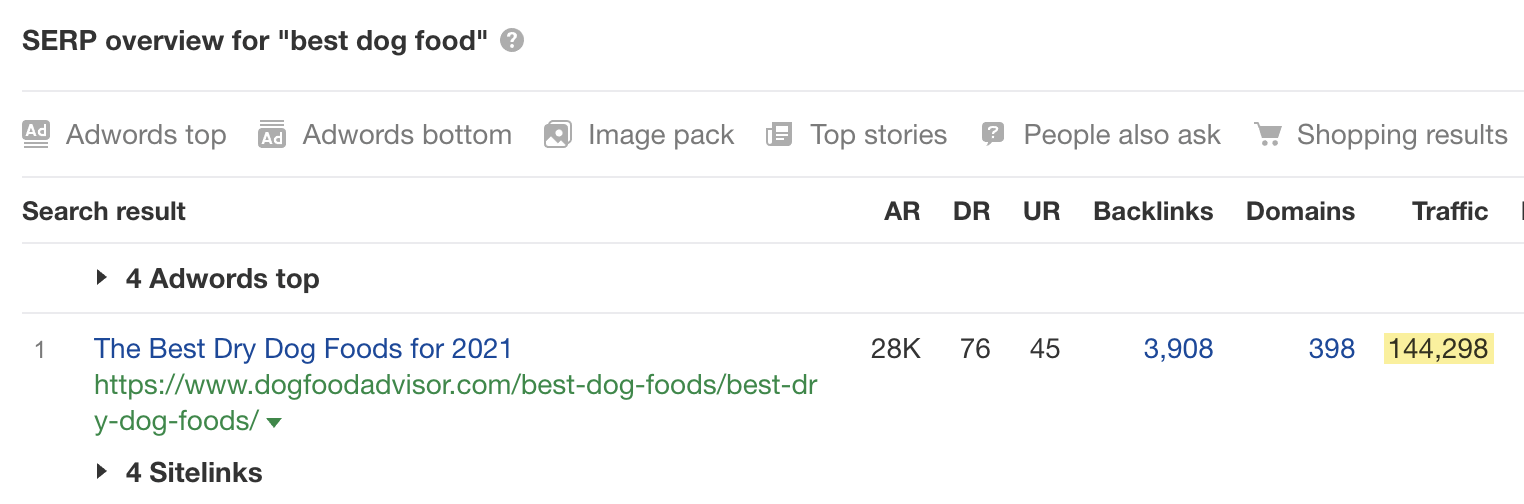
The top-ranking page gets an estimated 144,298 monthly organic search visits. That’s more than twice the search volume for “best dog food.”
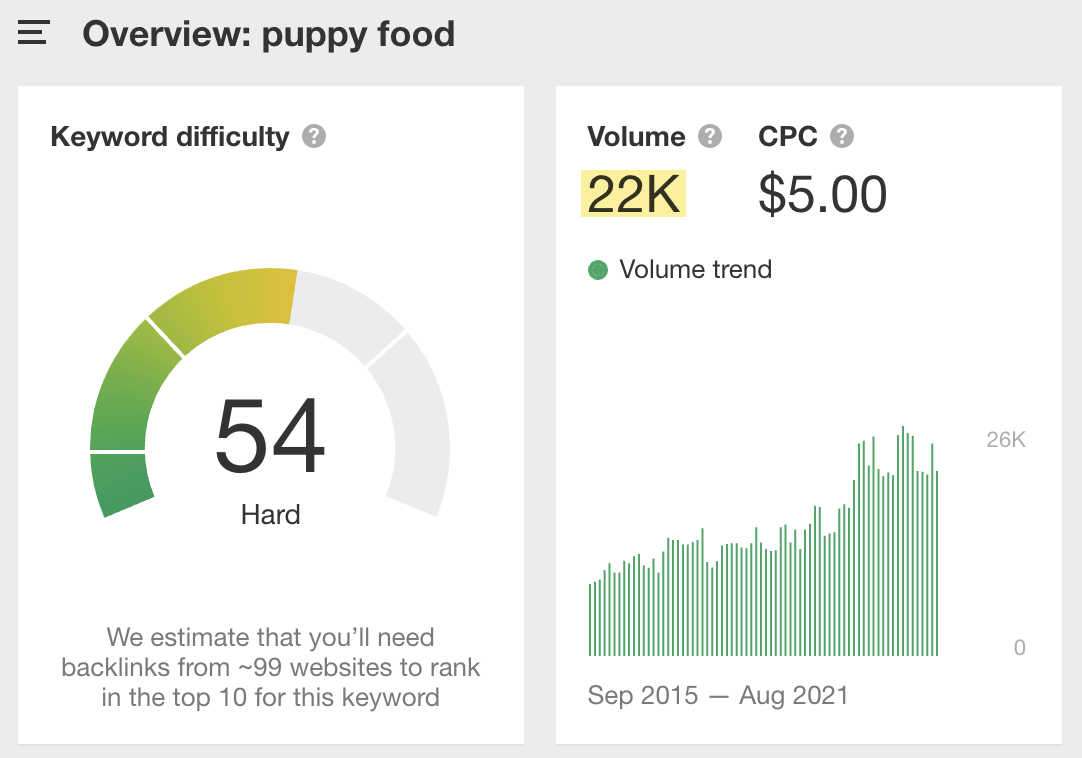
On the flip side, some topics will bring in way less traffic than you’d expect, given the volumes of their “head” keywords. For instance, the keyword “puppy food” has a search volume of 22K…
… but the top-ranking page only gets an estimated 7K monthly visits:
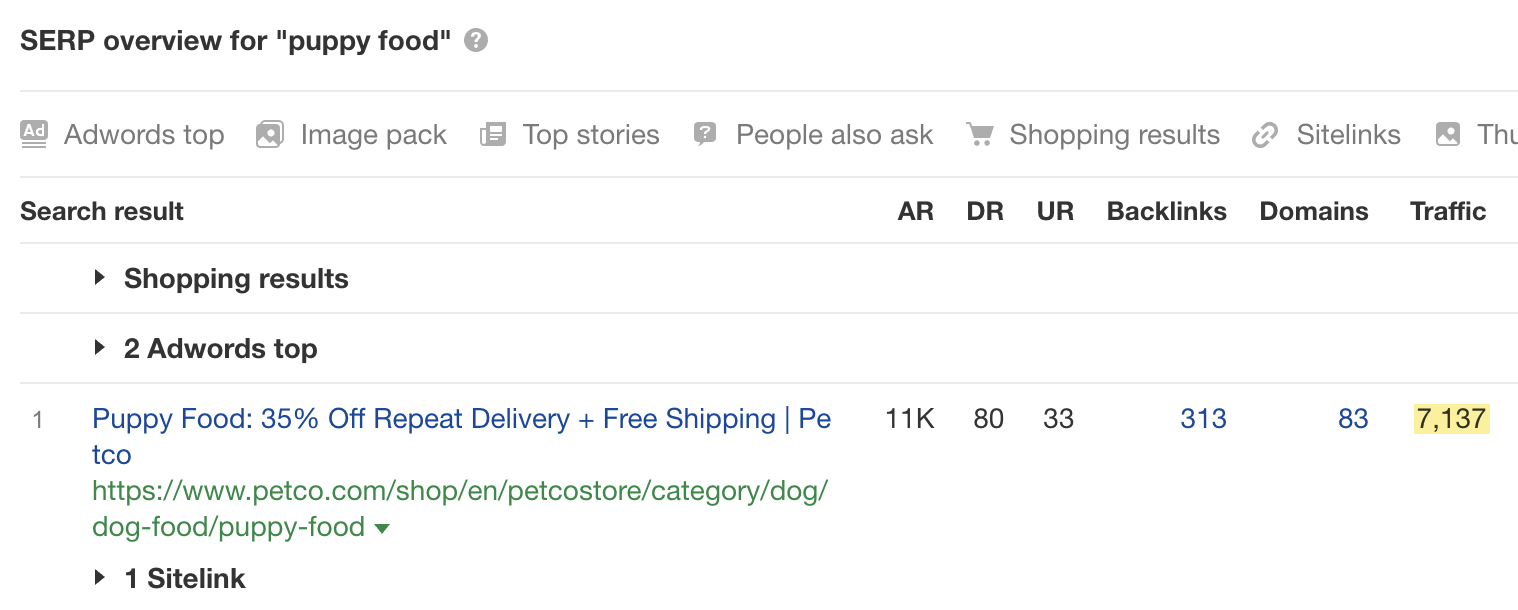
So when you’re looking for keywords with traffic potential, never rely solely on search volume. Check how much traffic the top-ranking page gets as it’s a better estimate of the traffic potential of the topic as a whole.
Broadly speaking, searchers are looking to do one of three things when they type something into Google:
- Learn something
- Buy something
- Find a specific website
This is known as search intent (the intent behind the search).
When choosing keywords to pursue, it’s important to only choose keywords where you’re able to produce content that aligns with search intent. This is because Google simply won’t rank the type of content that searchers aren’t looking for.
For some keywords, search intent is obvious from the keyword itself. If someone types “how to train a dog” into Google, it’s clear that they’re looking to learn, not buy. So you’d probably need to create a blog post to rank for this keyword, not a page selling your dog training services.
For other keywords, intent is a little less… obvious.
Take a keyword like “vegan protein powder,” for example. Is the person searching for this looking to buy vegan protein powder, learn about the best and worst vegan protein powders, or something else?
The best place to look for an answer to this question is in the search results.
If we do this, we see that virtually all of the results are blog posts listing the best protein powders. So it’s clear that these searchers are looking to learn, not buy.
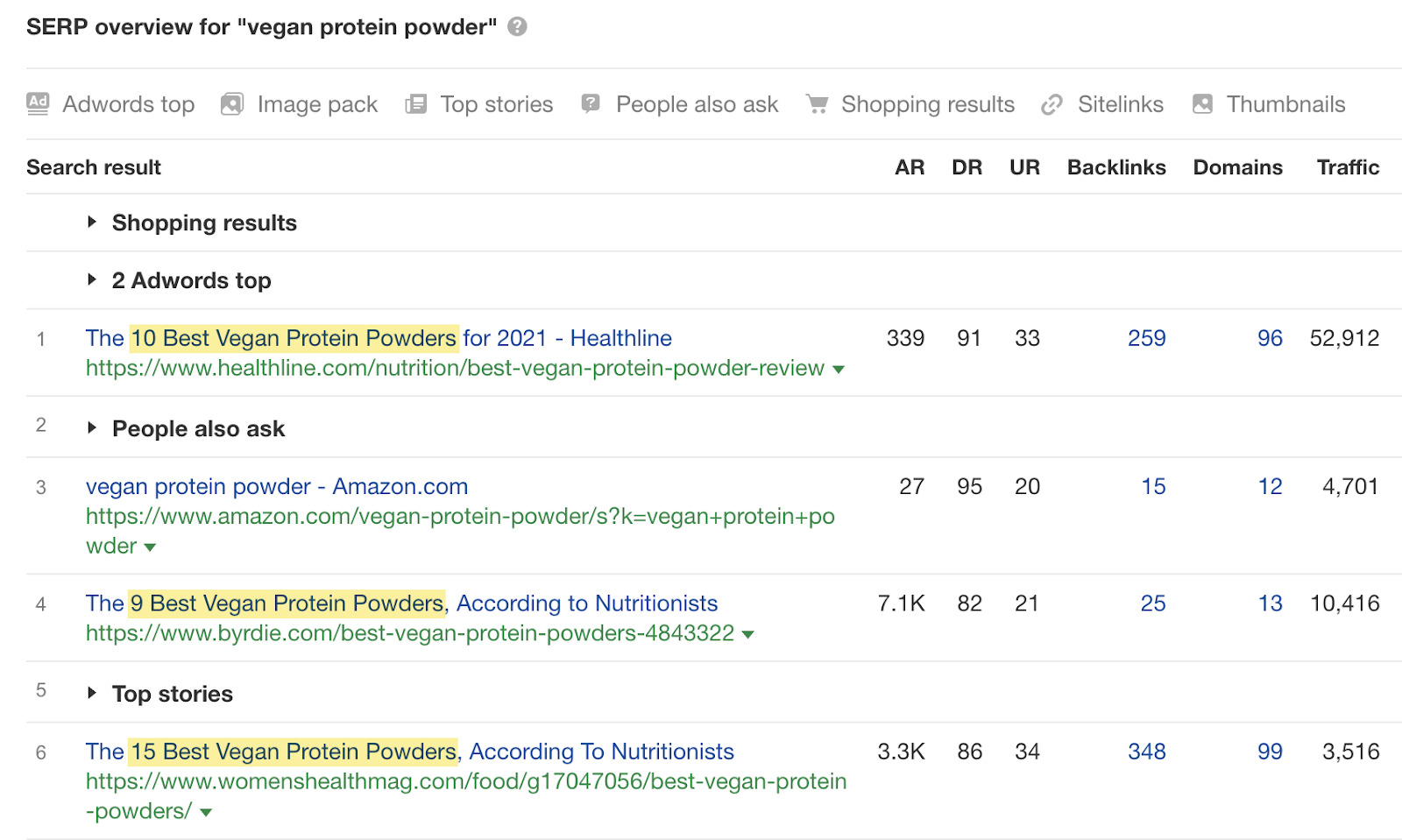
Unless you have a blog, this probably isn’t a great keyword to try to rank for.
Let’s check the search results for another keyword, “dog kennel”:
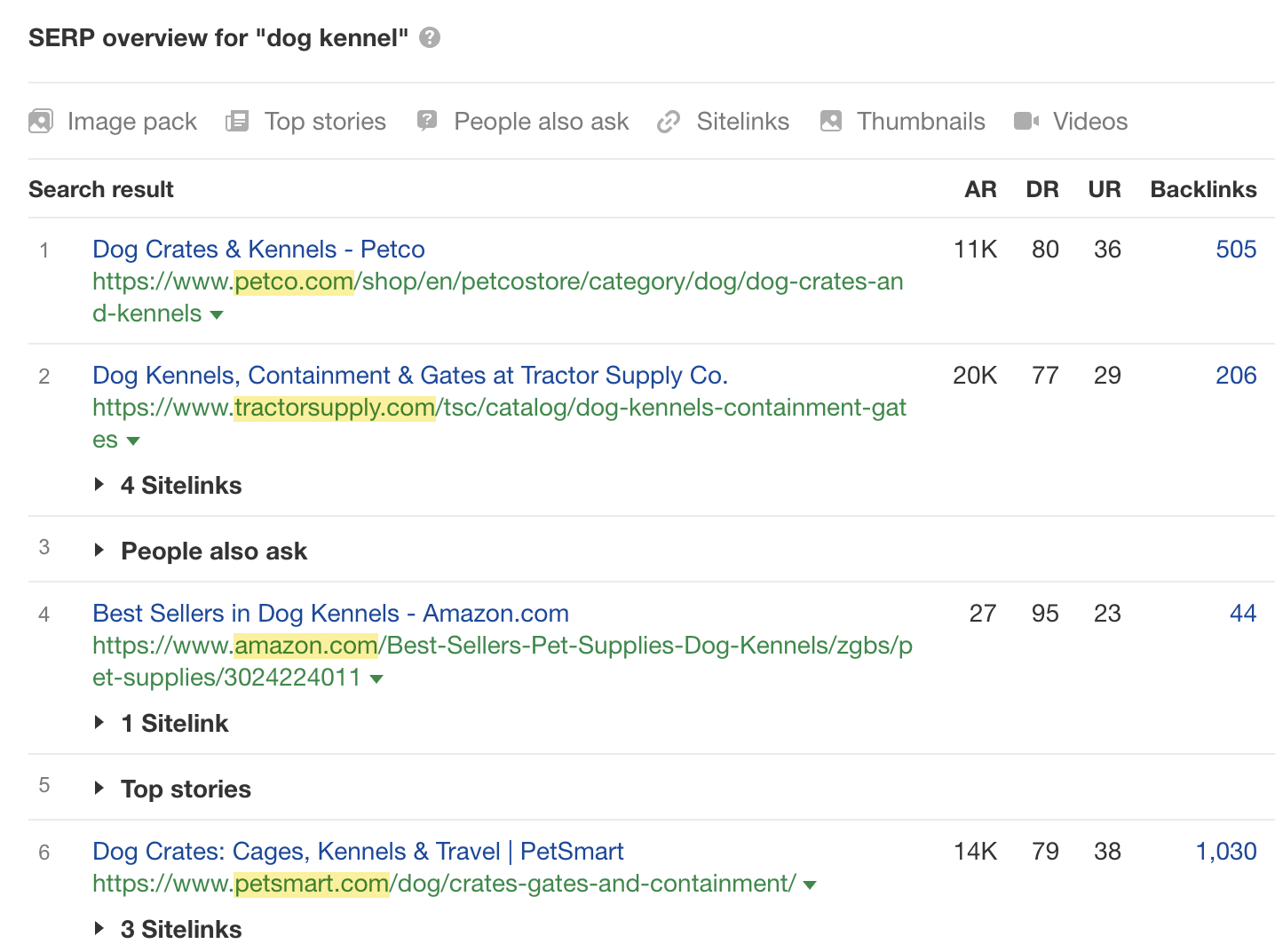
In this case, pretty much all of the top results are category pages from well-known ecommerce stores. So it’s clear that these searchers are looking to buy. Therefore, unless you have an ecommerce store selling dog kennels and can create an ecommerce category page for this type of product on your site, it will be unwise to choose this keyword to pursue.
Let’s look at the results for one more keyword, “chewy dog food.”
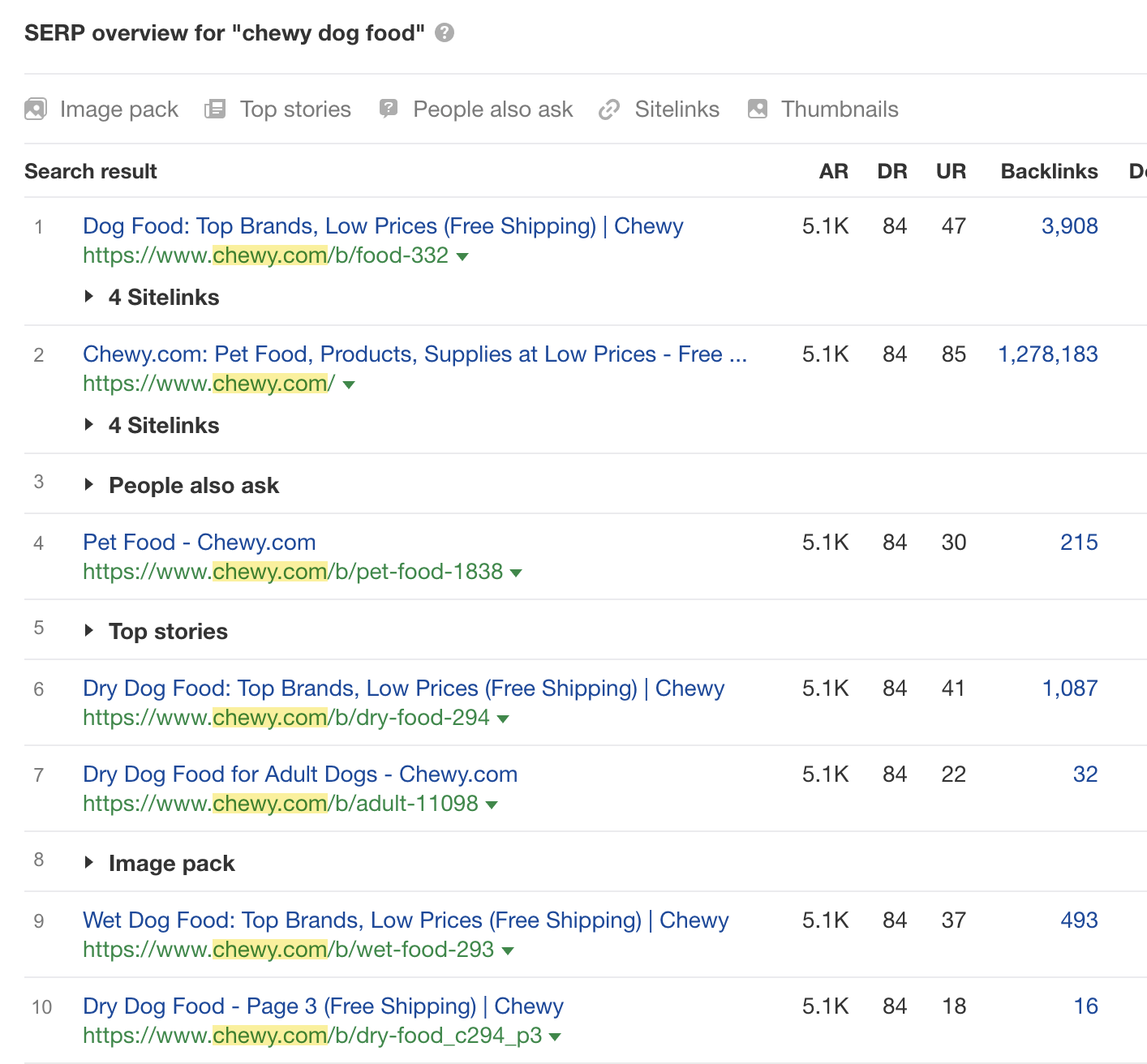
This time, all of the results are from one brand: Chewy. So it’s clear that these searchers are looking for a specific website. Therefore, we probably can’t do anything to rank for this keyword because we’re not that brand.
We’re really only scratching the surface of search intent here, so check out the post below if you want to learn more.
Recommended reading: Search Intent: Complete Beginner’s Guide
“Business potential” describes how lucrative ranking a keyword will be for your business.
If search intent calls for an ecommerce product or category page, answering the question is pretty straightforward. Just ask yourself whether you sell this product or some variation of it. If the answer is yes, the keyword has business potential.
But if search intent calls for a blog post or other informational content, the question is a little more difficult. That’s because you have to consider whether you can naturally pitch your product or service in that content.
For instance, at Ahrefs, a keyword like “how to do keyword research” has high business potential because we sell an SEO tool that helps people do keyword research. It’s easy for us to pitch that tool naturally in a blog post about this topic without seeming pushy. (You’ve probably noticed how we’ve been doing that in this article.)
But a keyword like “how to install Google Analytics” is a “low business potential” topic for Ahrefs. The reason is there’s no way to pitch our product in a blog post about that topic. Our toolset cannot help people install Google Analytics. So although the topic appeals to our target audience, its business value is low.
Here’s the scale we use to assess business potential for blog posts:
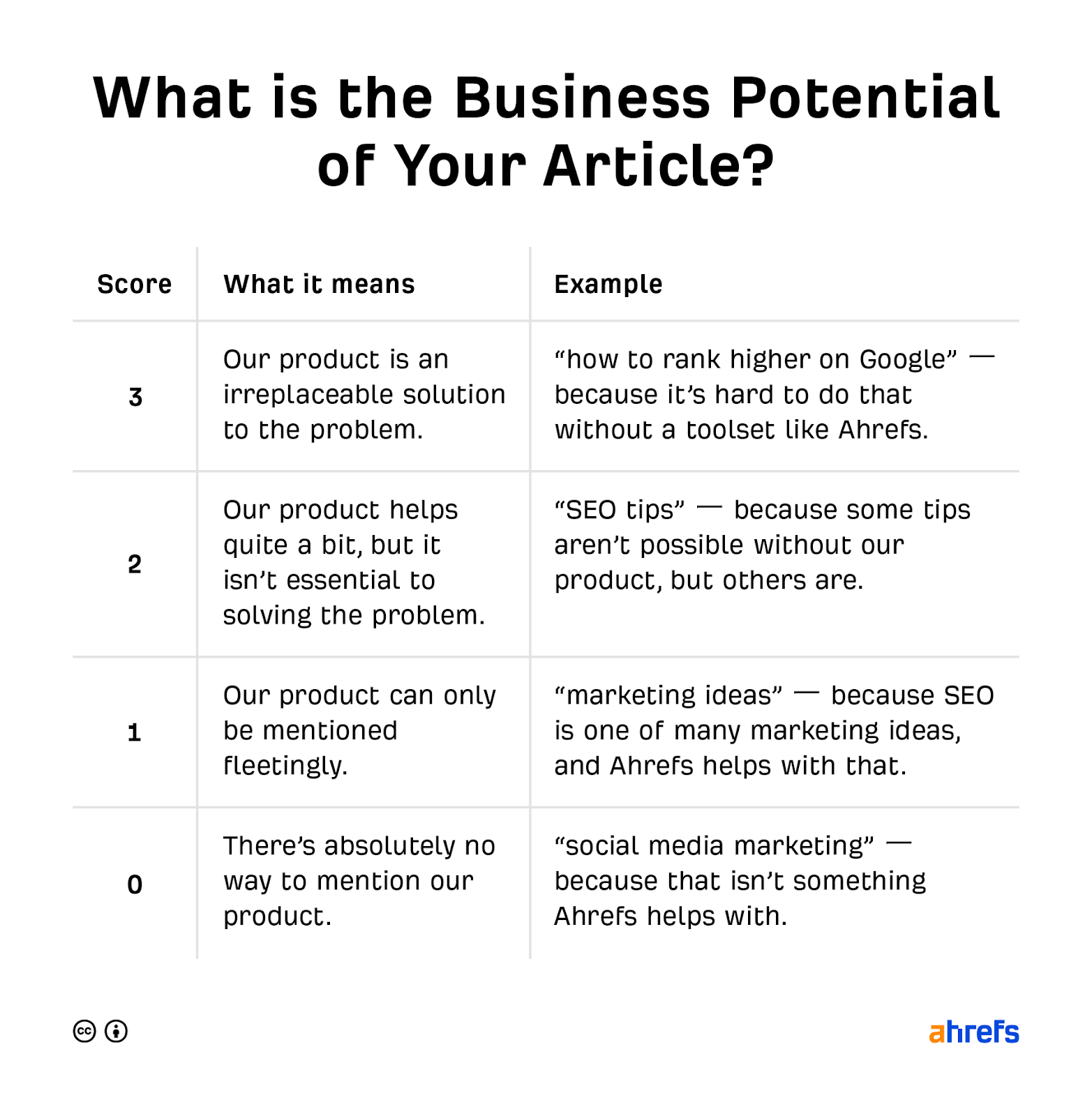
Remember that choosing keywords with business potential doesn’t mean you must make your content sales-y. Quite the opposite, in fact. You’re choosing keywords with high business potential so that any pitches and mentions of your product or service in your content are actually useful and help your audience solve their problem.
In theory, anyone can rank for any keyword with enough effort.
But in the real world, some keywords are going to be harder to rank for than others, especially in the short to medium term. Therefore, you should assess the ranking difficulty of a keyword before you decide whether to go after it.
The simplest way to compare the relative ranking difficulty of potential keywords is by using a keyword difficulty score. Most SEO tools have this, and ours is aptly called Keyword Difficulty (KD).
You’ll see the KD score alongside all keywords in Keywords Explorer:
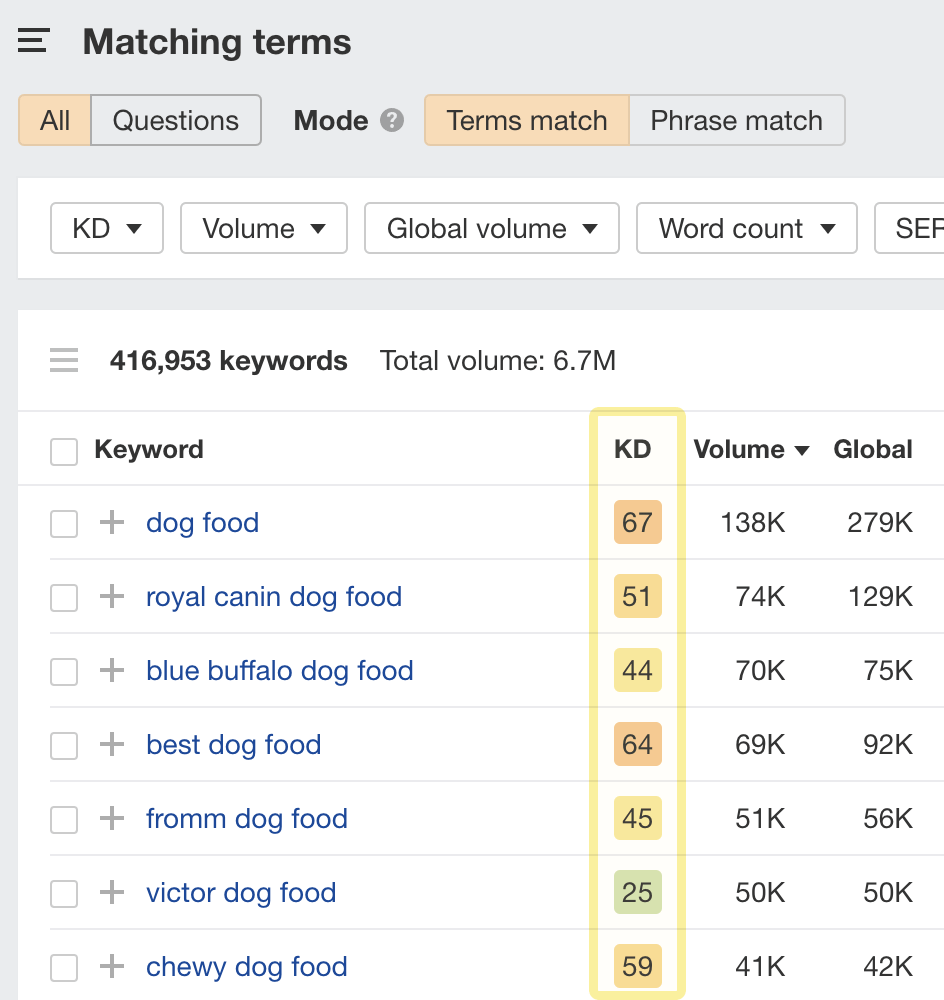
Every SEO tool measures keyword difficulty in its own way. We base ours on the number of backlinks to the current top-ranking pages. In other words, the higher the KD score of a keyword, the more backlinks you’d likely need to rank on the first page of Google.
You can filter for keywords by KD score in Keywords Explorer. So if you only want to see low-difficulty keywords, just set the maximum filter to something low like 10:
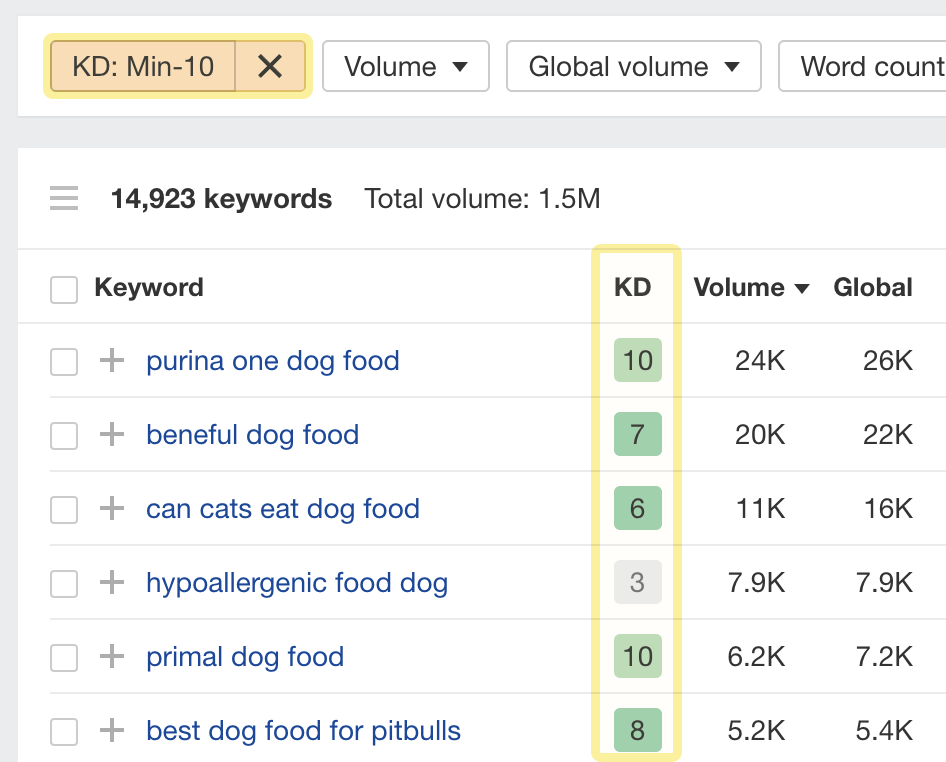
Now it’s important to mention that many other factors affect the true ranking difficulty of a keyword, so you shouldn’t rely entirely on keyword difficulty scores in SEO tools. These scores exist to give you a quick way to find low-difficulty keywords based on some criteria. In our case, that’s the number of backlinks you’d likely need to compete.
If you want to know more about the other factors you should consider when looking for low-competition keywords, check out the resource below.
Recommended reading: How To Find Low-Competition Keywords For SEO
Final thoughts
Choosing keywords for SEO isn’t that complicated. You’re just looking for keywords where:
- Traffic potential is high.
- Business potential is high.
- You can create content that aligns with search intent.
- You actually stand a chance of ranking.
It may take a bit of sifting to find keywords that fit the bill, but it’s certainly doable.
For a complete walkthrough of the keyword research process, watch this video or read our beginner’s guide to keyword research. Both explain the fundamental principles of keyword research and how to do it from start to finish.
Got questions? Ping me on Twitter.