Here are all the steps you should take:

It’s easy to overcomplicate the process of choosing a domain. But choosing a branded domain that is short and memorable works better in most cases than trying to shoehorn certain keywords into your domain name.
So if you already have one, go ahead with it. Or if you’re setting one up for your business, your business name works fine too.
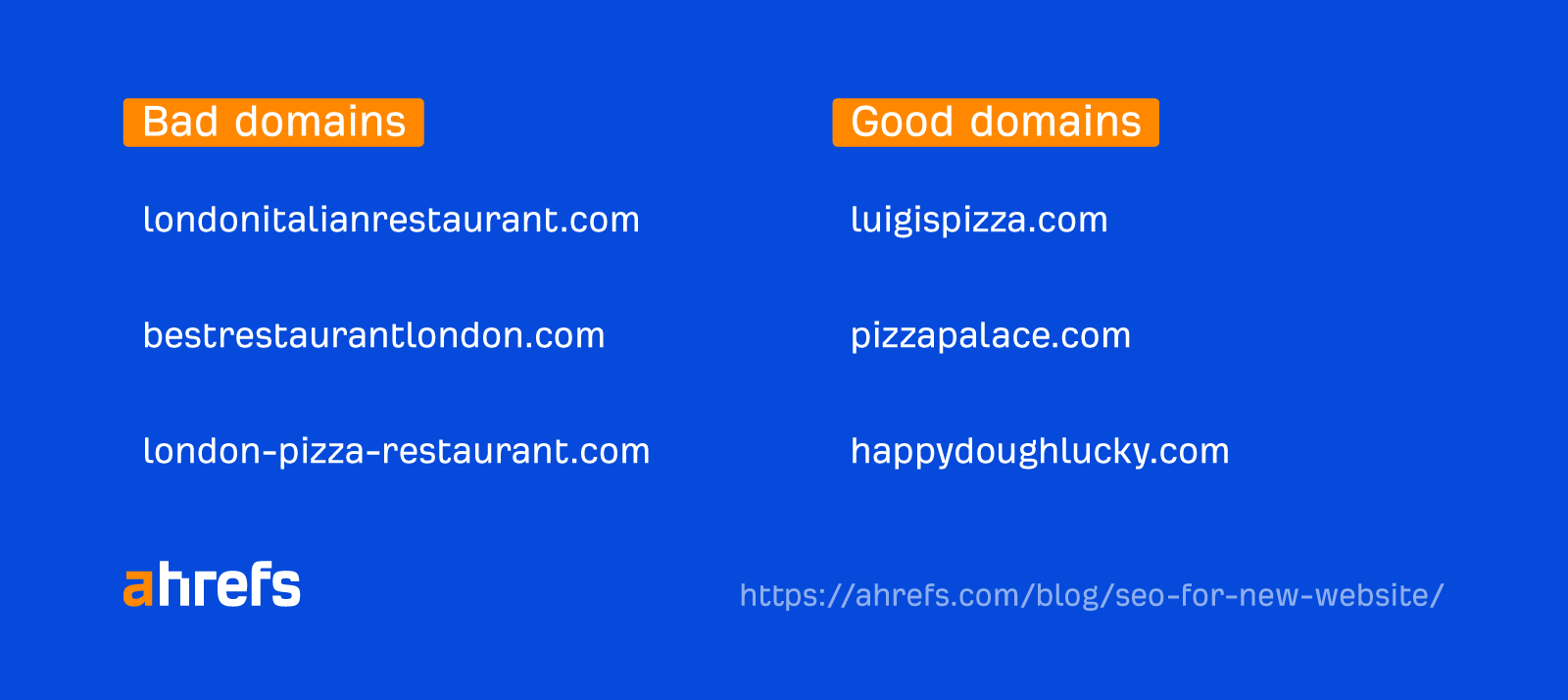
When it comes to the top-level domain (TLD), for example, .com, Google has said that the TLD makes no difference for SEO.
So we treat all of the New Top-level Domains like any other generic top-level domain.
There’s no need to rack your brain over this. .com works fine in most cases, as it’s internationally recognizable.
Once you’ve decided on a domain name, head over to a domain registrar—like Google Domains or Namecheap—to see if it’s available. If it isn’t available, you will need to repeat the process until you find a name that is both available and works for your business.
Website platforms let you create and manage a website easily. There are two types:
- Hosted platforms – They host the site, give you ready-made designs, and let you add and edit content without touching code. Examples are Wix, Squarespace, and Shopify.
- Self-hosted platforms – These allow you to add and edit content with or without code. However, you’ll have to host and install them yourself. Examples are WordPress and Ghost.
Most SEOs recommend WordPress—a self-hosted, open-source platform. SEOs prefer it because it’s customizable—you can edit the code however you like.
But that doesn’t mean you have to be technical to use WordPress. There are millions of plugins you can install that do all sorts of tasks for you. These include SEO plugins too.
You don’t have to know how to code in order to use WordPress.
If you’re using a self-hosted solution, like WordPress.org, you’ll need a web host. We don’t have a particular one to recommend. But as you’re considering your options, look out for the three S’s:
- Security – Hosts should provide you with a free SSL/TLS certificate.
- Server location – It takes time for data to travel between the server and visitor. So it’s best to choose a host with servers in the same country as most of your traffic.
- Support – You’ll want 24/7 support. Consider checking out their reviews in forums like Reddit or test their support out before you sign up.
You now have a basic website you can configure to become SEO-friendly. Here’s what you should do next:
Set up Google Search Console and Ahrefs Webmaster Tools
You’ll need GSC to do a bunch of important SEO tasks, like finding technical errors on your website, submitting sitemaps, and more.
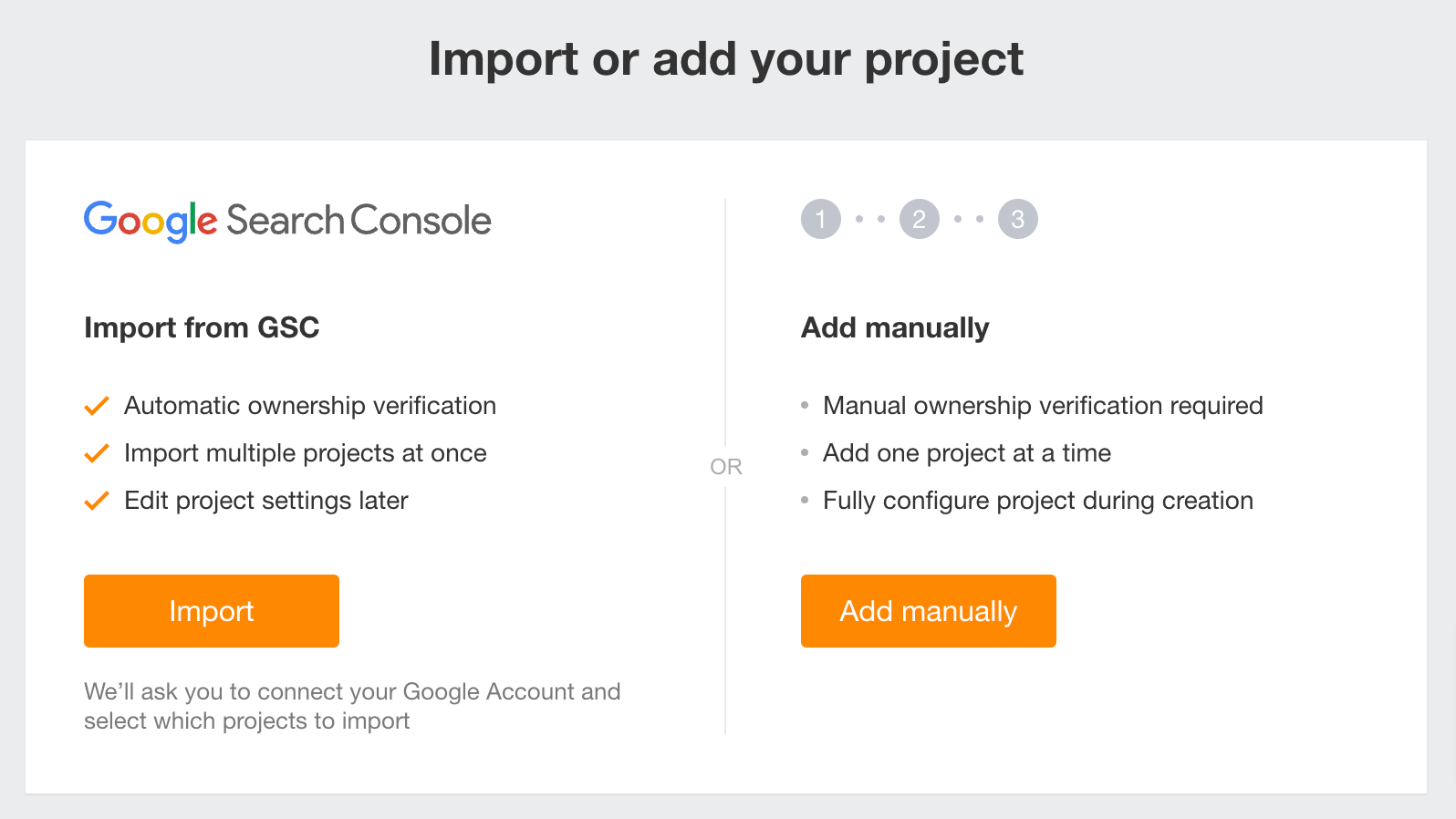
Setting it up is pretty easy. Sign in to GSC with your Google account. You should see this “welcome” screen:
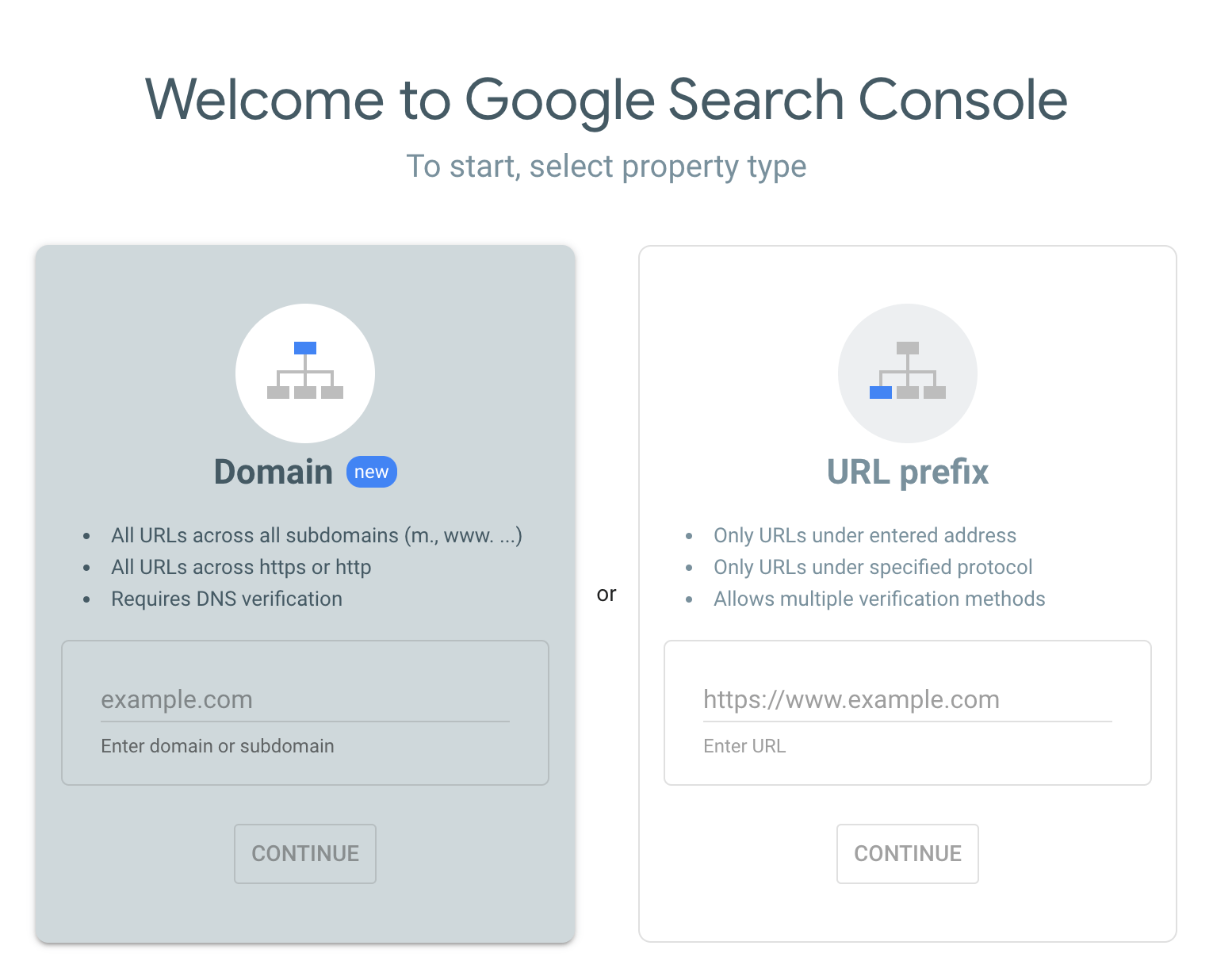
Choose Domain and enter your domain. You’ll then be prompted to verify your domain. Google has explicit step-by-step instructions on how to do this:
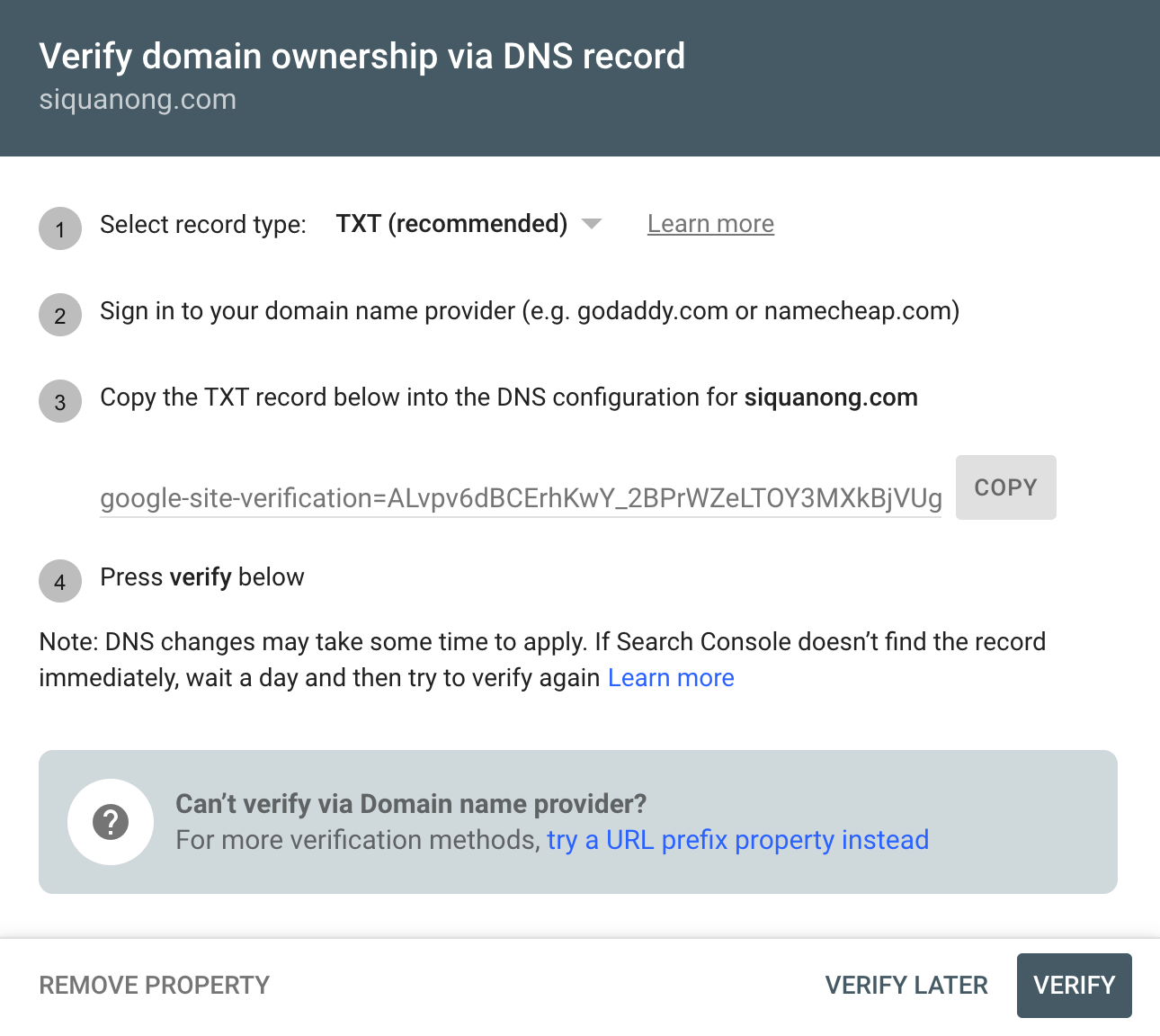
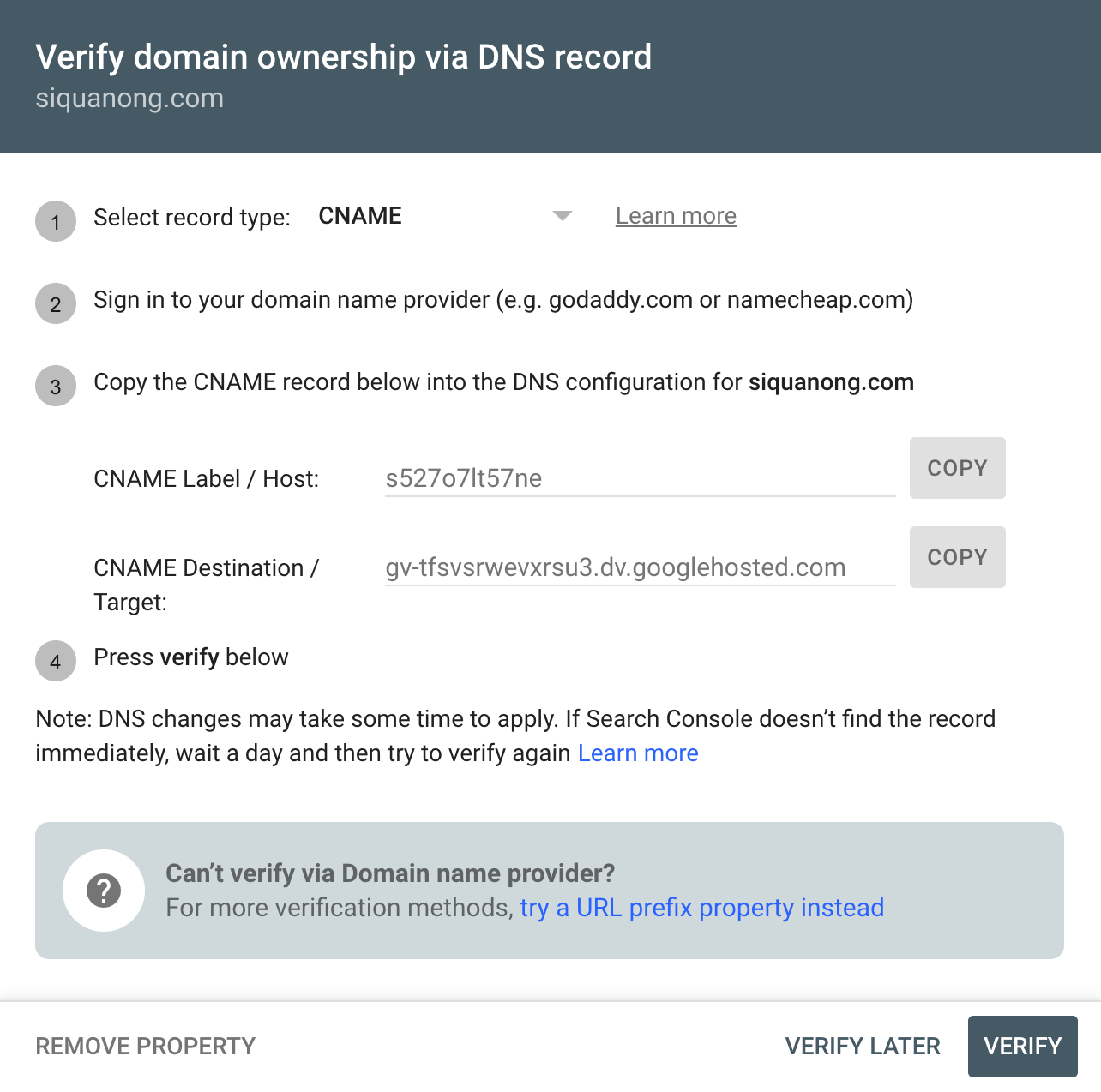
If you’re stuck or unsure, you can check out Google’s help article.
Once that is done, you’ll be able to use GSC and see your search analytics. (You won’t have any data for now since it’s new.)
While GSC is irreplaceable for anyone serious about SEO, it is still lacking in some areas. For example, it only offers some data about the keywords your website ranks for and the sites that link to you.
To compensate for the lacking areas, you should set up Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT). It’s free and allows you to:
- Audit your website for 100+ SEO issues (and explain how to fix them).
- See the websites that are linking to you.
- See the organic keywords your site is ranking for.
- See the amount of organic traffic your site is receiving.
And more.
To use AWT, create a free account. Then add and verify your website. You can use your GSC account to verify too.
Create a logical site structure
It should be easy for visitors and search engines to find content on your site. You’ll need a logical hierarchy for your content, which you can sketch out using a mind map:
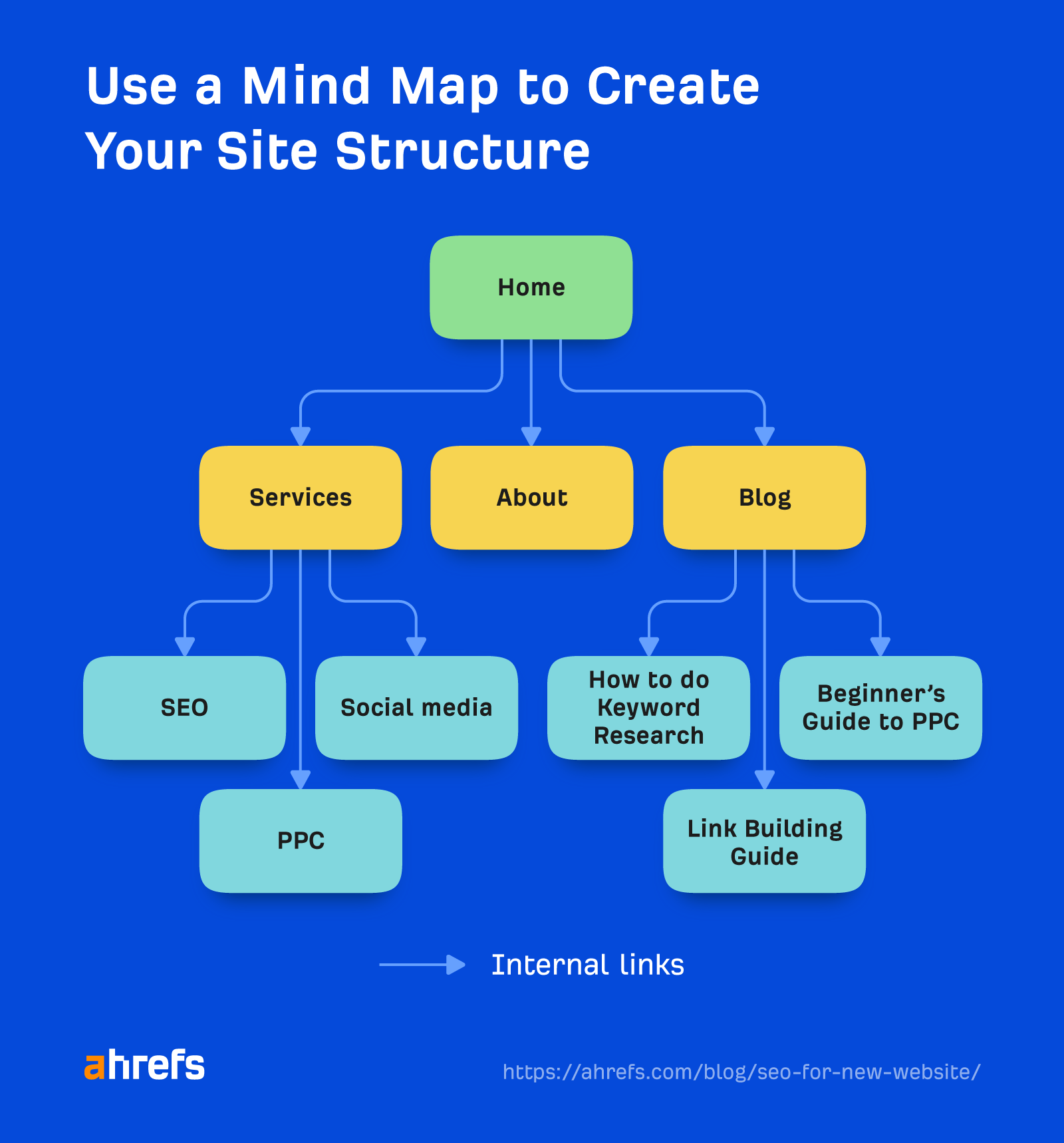
Each brand on the mind map represents an internal link, which is a link from one page on a website to another page.
Internal links are crucial for your website because:
- This is how Google and other search engines find new pages.
- This is also how Google and other search engines understand what your page is about. They do this by looking at the clickable words in the link, known as anchor text.
- Internal links help pass PageRank, which is an important Google ranking factor.
Use a logical URL structure
Our recommendation is to go for something that’s clear and descriptive, so something like website.com/seo-for-new-website/.
Other technical considerations
A positive user experience is important for your business and Google too. You’ll want to make sure you have these things covered:
Use HTTPS
Nobody wants their personal data leaked to hackers. You’ll want to encrypt your site with SSL/TLS. Most decent web hosts should be able to offer this service, or you should be able to enable it yourself with one click.
After that, you should see the padlock on your URLs.
Here’s what it looks like in Google Chrome:
Make sure your site is mobile-friendly
Most people search on mobile these days. Your website should be responsive and work on all devices.
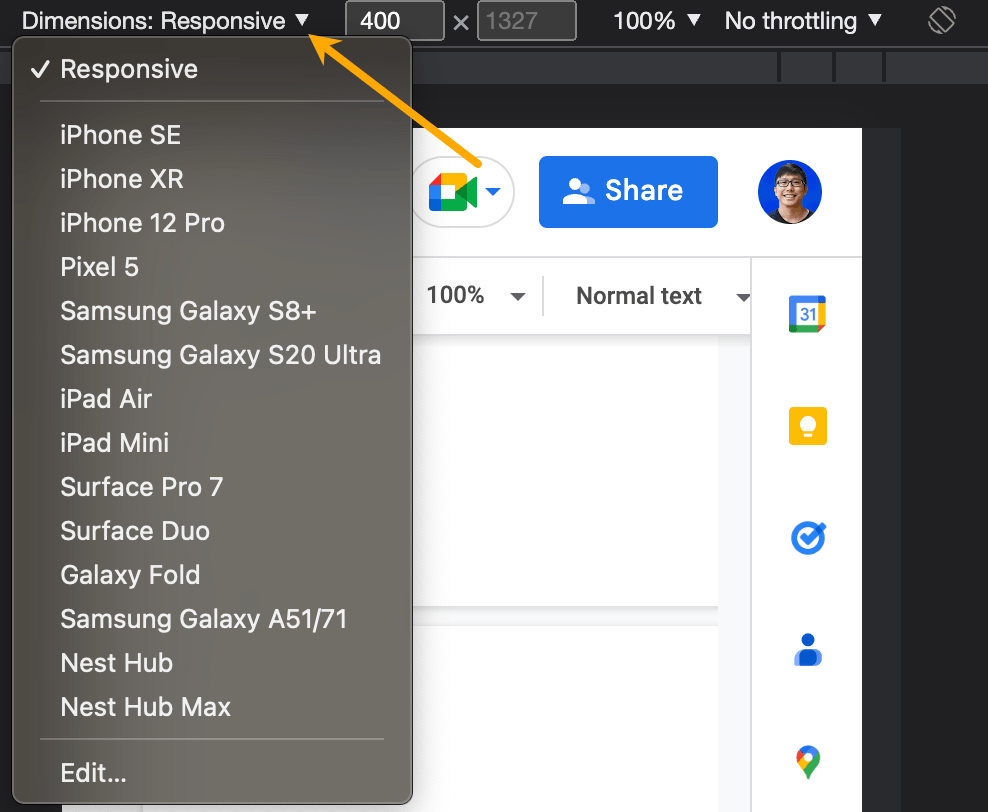
You can check this easily using Developer Tools on Google Chrome:
- Click on the “…” dropdown in the top right corner of the browser
- Select More Tools
- Select Developer Tools
- Click on the mobile button in the top left corner
From here, you’ll be able to select the exact device you want to test for:
Avoid intrusive interstitials
Interstitials are full-screen ads that appear before a webpage’s content is loaded. Nobody likes them. Neither does Google. If there’s no need for such pop-ups on your website, avoid them.
Make sure your site loads fast
Page speed is a Google ranking factor. So it’s definitely important to spend some time making sure your site loads quickly. You can use a tool like PageSpeed Insights to check your page’s performance.
You can’t get organic traffic if no one’s searching for a particular topic. That’s why the first step of any SEO strategy is to find out what your target audience is searching for.
This is known as keyword research.
The easiest way to begin is to use a keyword research tool. Keyword tools are databases of words and phrases with SEO metrics. They show you a list of ideas based on the seed keyword idea you’ve entered.
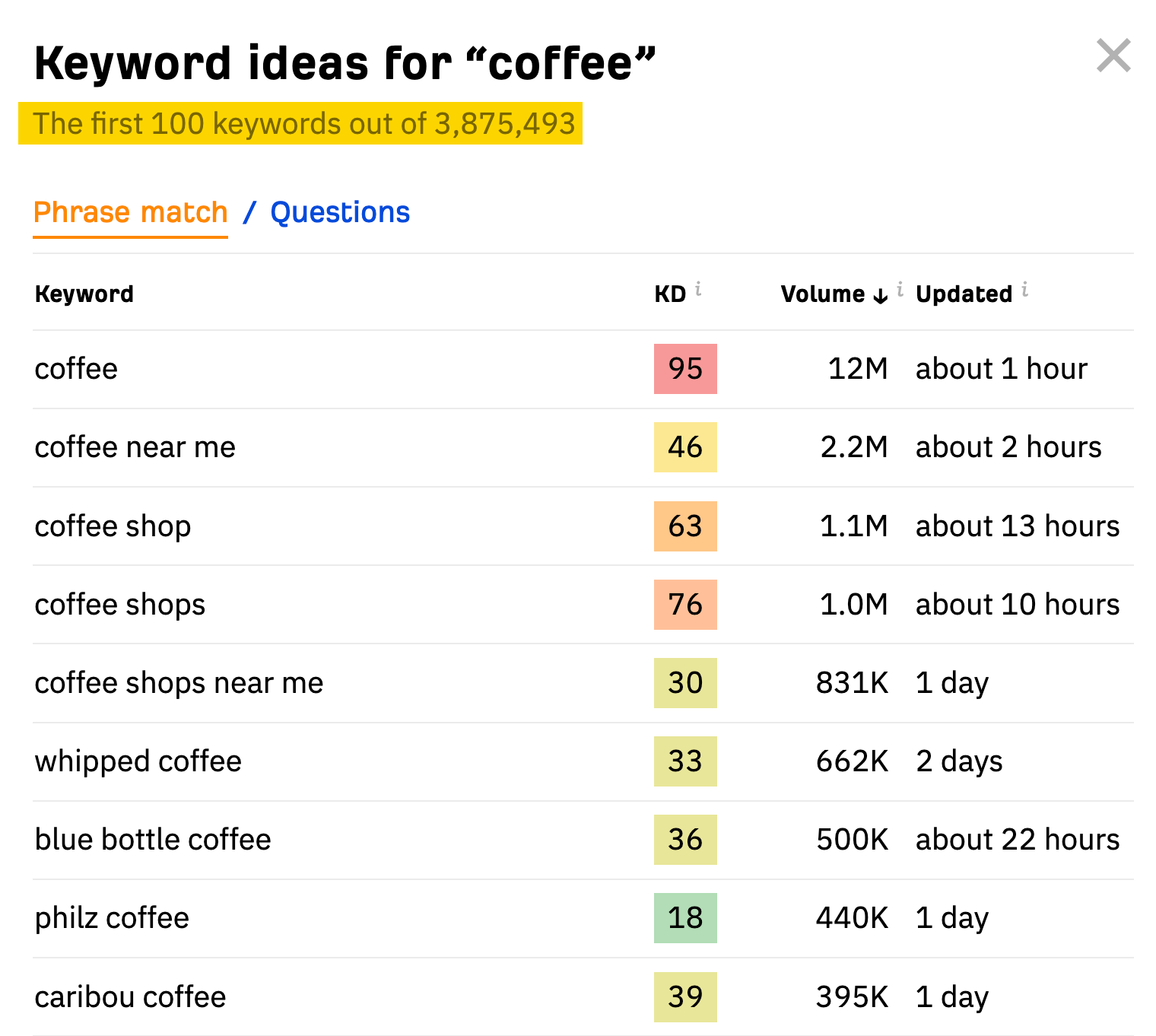
For example, you can get started with a free keyword research tool like Ahrefs’ Keyword Generator.

Enter a single relevant topic and you’ll get up to a hundred keywords back:
If you’re looking for more keywords, you can use a professional keyword tool like Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer. You’ll be able to see the full range of potential topics, plus:
- Important keyword metrics to help you make better decisions.
- Filters to narrow down your search to the best, most relevant keywords.
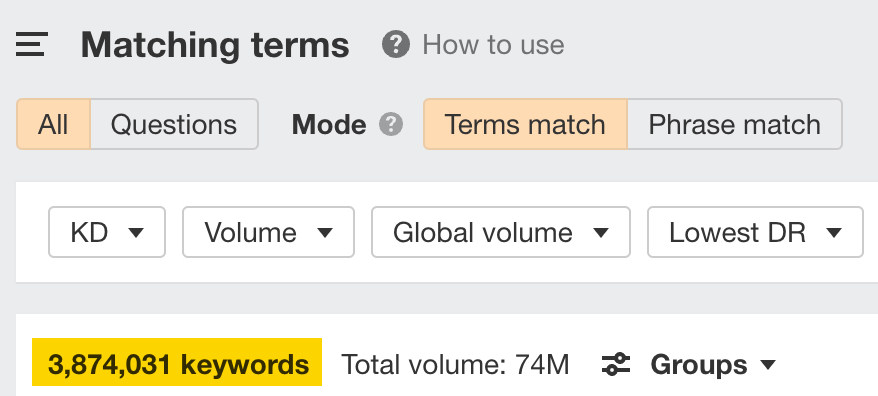
For example, using the same seed keyword as above, “coffee,” Keywords Explorer shows us over 3 million keywords.
But that’s too many. So, let’s drill down by focusing on keywords that we can actually compete with. We can do this by adding a Keyword Difficulty (KD) filter. We’ll also want to make sure these keywords can send us search traffic, so we’ll want to add a Traffic Potential (TP) filter.
Here’s what that looks like:
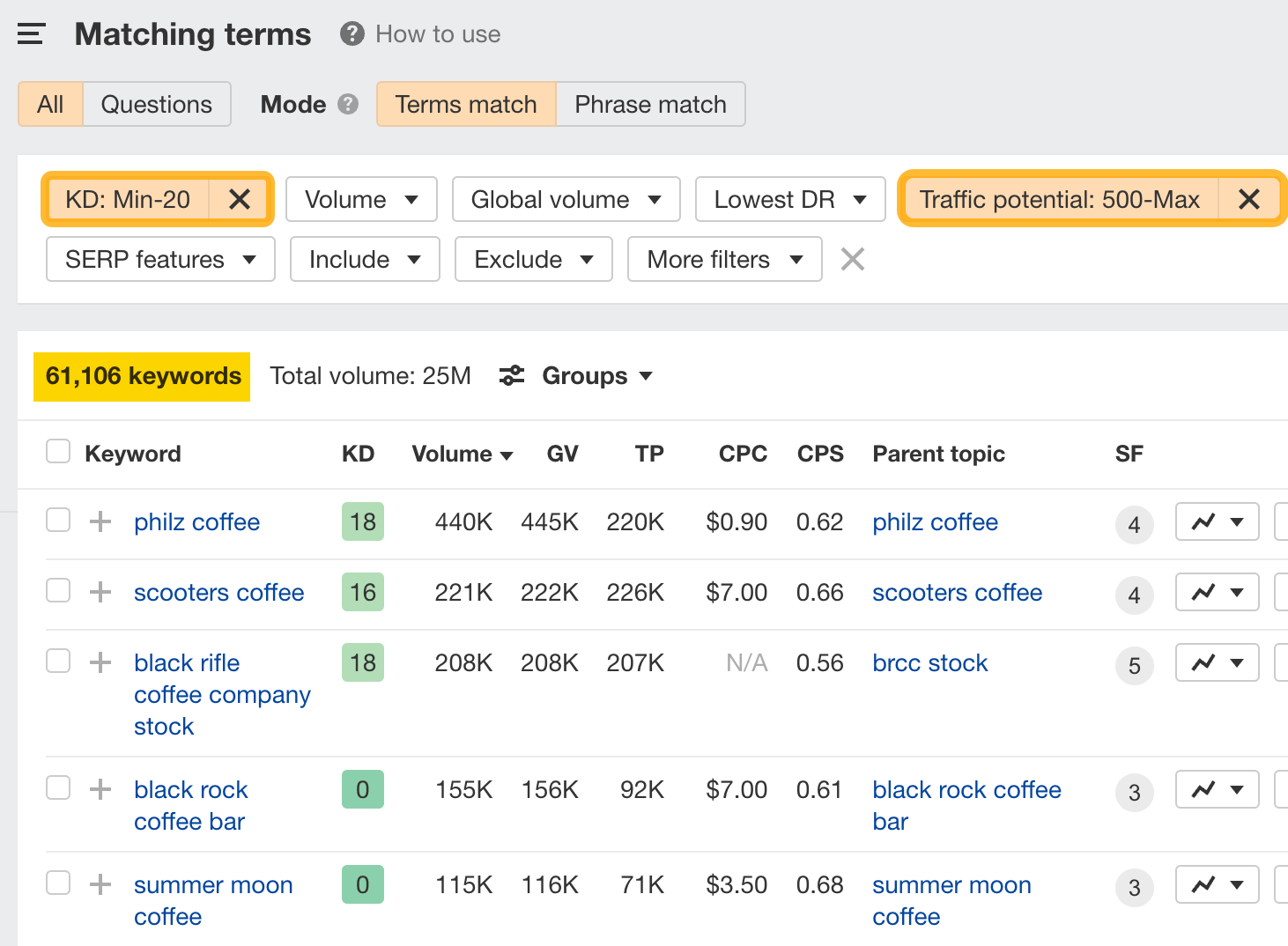
From here, you’ll want to look through the list, pick out those keywords that are relevant, and add them to a keyword list that you can reference. (This can be a simple Google Sheet.)
Just like how product managers design products for their target users, we want to do the same for our content too. In this case, we want to create content that appeals to people searching for our topic.
Here’s how to do it:
Analyze search intent
Search intent is the why behind a search query. In other words, why is the searcher looking for that particular topic?
Knowing search intent is important because:
- Knowing why the searcher is searching means you can create the right piece of content for them.
- Google also wants to know so it can serve the most relevant results.
As a result, by aligning your content with search intent, you can rank higher on Google.
We can identify search intent by looking at the top-ranking pages for your topic and figuring out the three Cs:
- Content type – Are they blog posts, product pages, landing pages, or something else?
- Content format – Are they tutorials, listicles, how-to guides, recipes, free tools, or something else?
- Content angle – Is there a dominant selling point, like low prices or how easy it is?
For example, let’s say we’re targeting the keyword “how to clean coffee maker.” If we take a look at the SERP overview in Ahrefs…
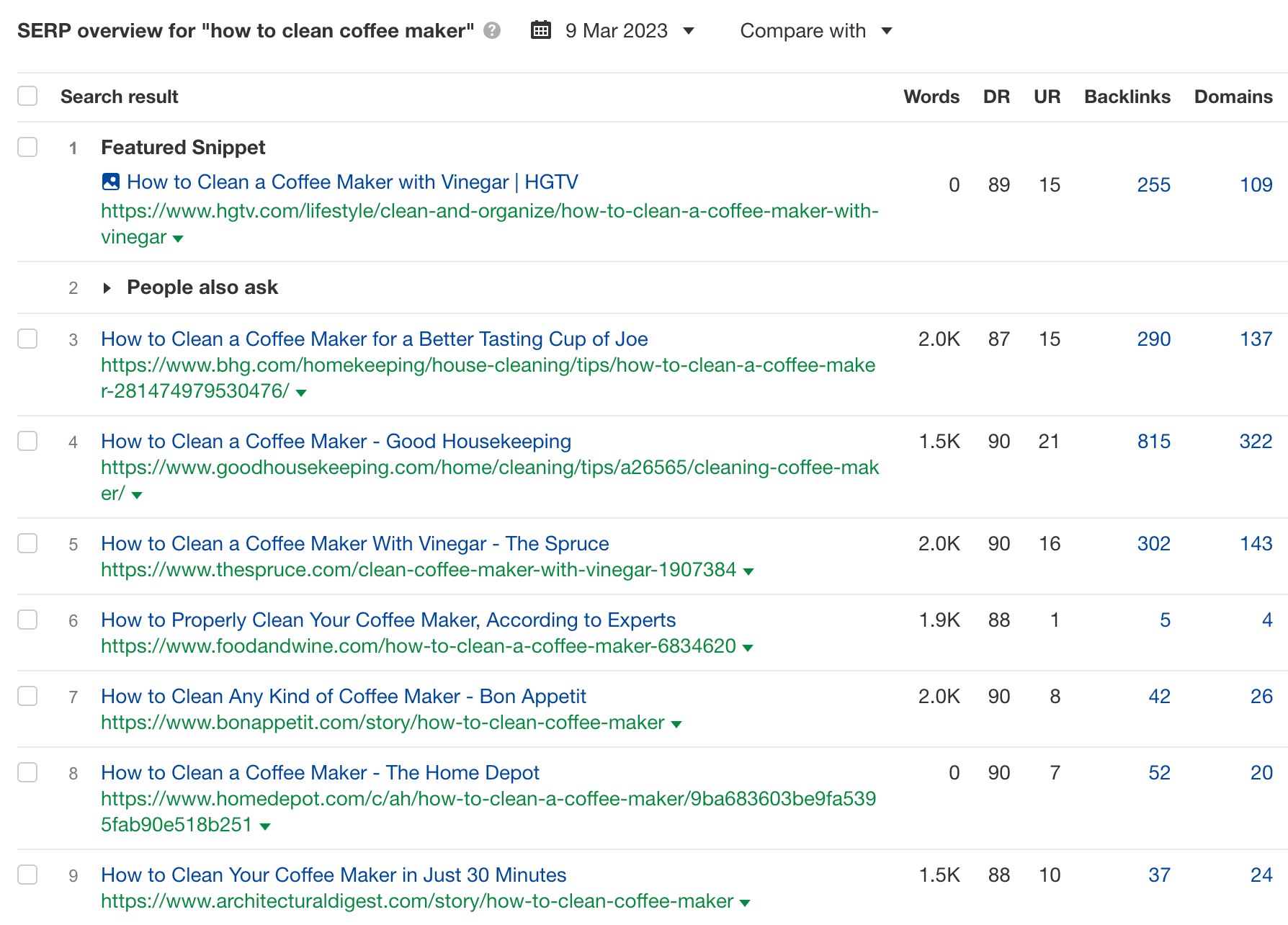
… we can see these:
- Content type – They’re mostly blog posts.
- Content format – They’re mostly how-to guides.
- Content angle – There are a few angles here: “with vinegar,” “better-tasting coffee,” “any kind,” and “in just 30 minutes.”
If we want to rank for this keyword, we’ll have to create a how-to guide on cleaning a coffee maker, with a specific angle targeting a unique know-how we have.
Cover important subtopics
A product manager may have an idea of what their target users want to see, but they won’t want to assume that they know everything.
The same goes for your content too—you won’t want to miss potential subtopics that searchers expect in a piece of content tackling that topic. In this case, we can actually find that out by looking for common keyword rankings among top-ranking pages.
Here’s how:
- Enter your keyword (e.g., “earned media”) into Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Scroll down to the SERP overview
- Select three to five top-ranking articles (make sure they’re similar)
- Click Open in and choose Content gap
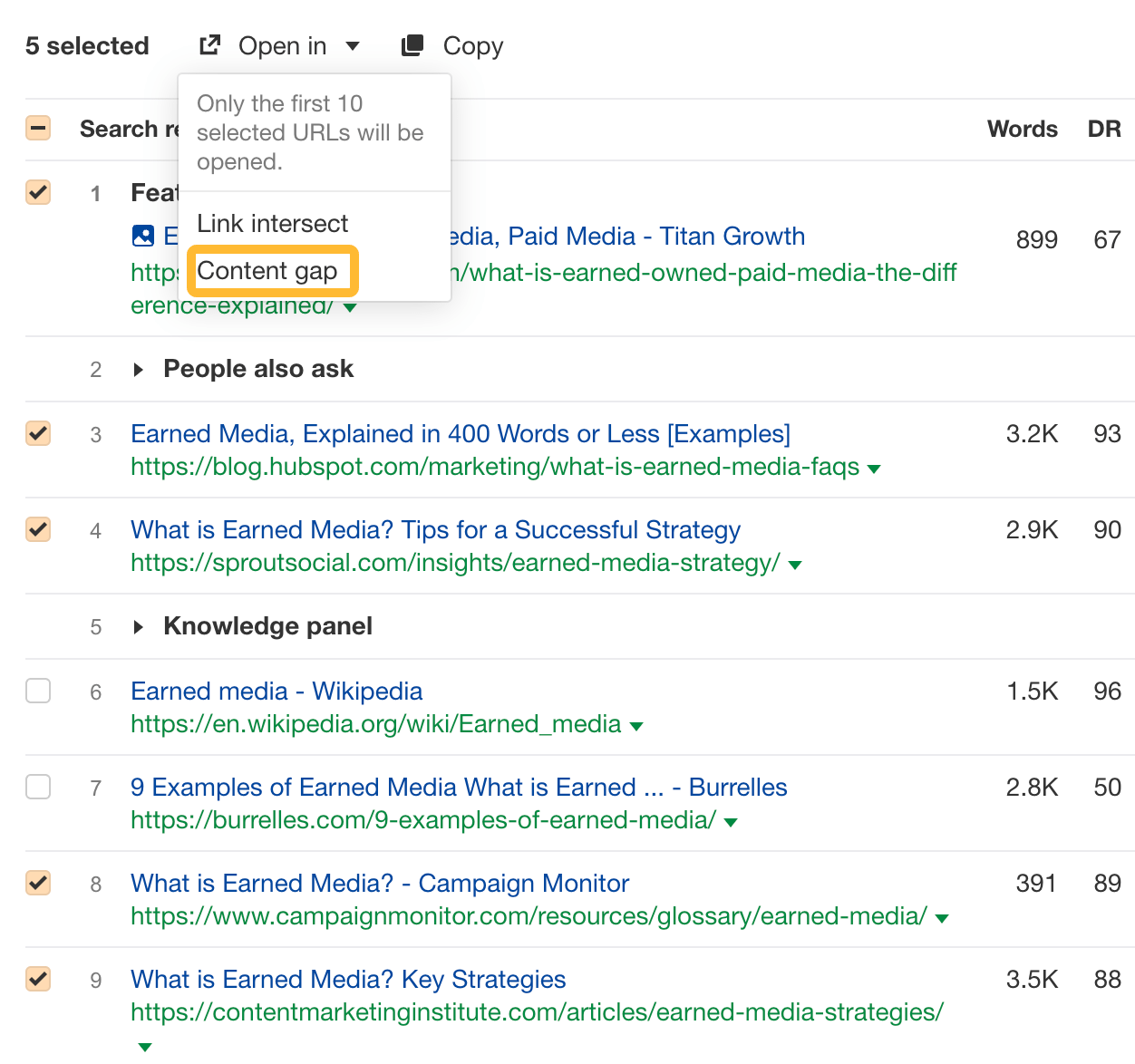
This opens up the Content Gap report, which shows all the keywords these pages are ranking for. We’ll want to select the Intersection dropdown and choose the highest two targets (in this example, 4 and 5).
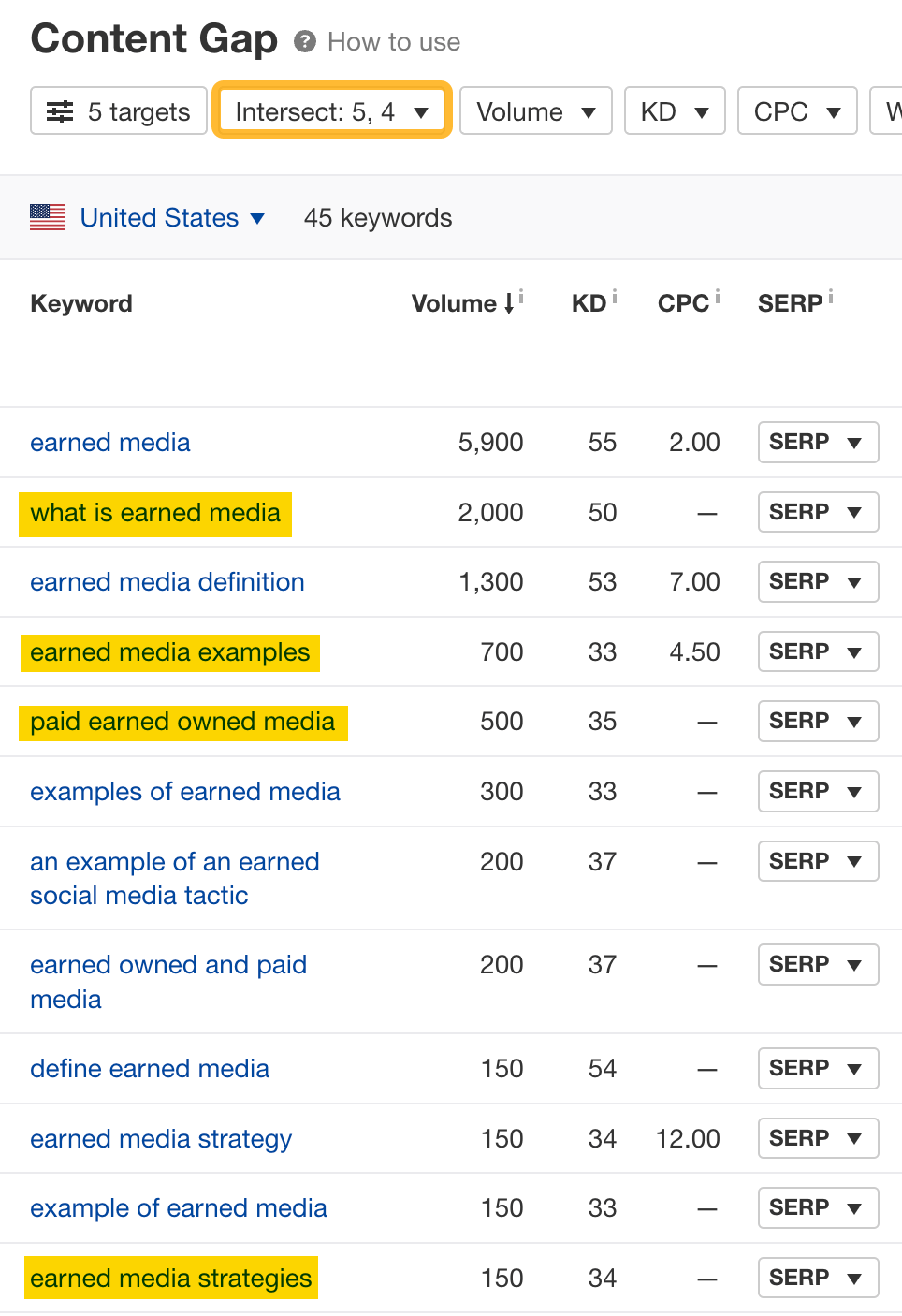
You can see that many of these keywords map to subtopics too. For example, searchers want to know:
- What earned media is.
- Examples of earned media.
- Earned media strategies.
- Other types like paid and owned media.
Make it unique
While you want to be inspired by the current top-ranking pages, your goal is not to “copy” everything that’s already on there. After all, if your content is exactly like everyone else’s, there’s no reason to consume yours particularly.
So you’ll want to give your audience a reason to read, share, or link to your content. The best way to do this is to make sure your content is unique.
Here’s how you can create something unique:
- Write about something from your personal experience – I wrote about my own journey in this post on becoming a content creator.
- Interview experts in your field.
- Crowdsource opinions, expertise, or ideas from multiple experts – We interviewed four link building experts in our post on international link building.
- Create original research from running studies or surveys – We surveyed 439 people for our post on SEO pricing.
- Offer a contrarian opinion – We did this when Joshua argued why Google doesn’t care about AI content.
Make your content easy to read
Your content should be an effortless reading experience for your readers. Follow these tips:
- Use descriptive subheadings (H2–H6) for hierarchy
- Use bullets to help with skimming
- Use images and GIFs (where needed) to break up the text
- Use short sentences and paragraphs to avoid “walls of text”
- Use simple words that everyone can understand
- Write as you speak to make things conversational
- Read your copy out loud (when editing) to smooth the flow
Add your on-page SEO
On-page SEO focuses on helping Google and searchers better understand and digest your content.
Follow these basics:
- Use the keyword in the title (if possible)
- Write a compelling meta description that sells your article on the SERPs
- Add concise and accurate alt text to your images
Just because you’ve created your website doesn’t mean people magically discover it. You have to tell others about your new website.
Here are some starting tips for promoting your website:
- Don’t be shy and tell your friends and family – They’ll be supportive. 😄
- Start building an email list – This will come in handy in the future whenever you publish new content.
- Reach out to people you’ve mentioned in your content – If you’ve linked to and mentioned any resource in your article, tell the authors! Find their contact details and email or DM them.
- Join and participate in relevant niche communities – Whether it’s on Reddit, Slack, Circle, or Discord, become an active member in these communities and share your content when relevant (don’t spam!).
The above tips look deceptively simple, but they will help to get the word out about your website.
There are more ideas to try, of course, but making sure you’re actually promoting your website is more important than the shiny new tactics you can find.
You’ll want to monitor your results so you can figure out what went right or wrong.
The easiest way to do this is to add the keywords you’re targeting to Ahrefs’ Rank Tracker.
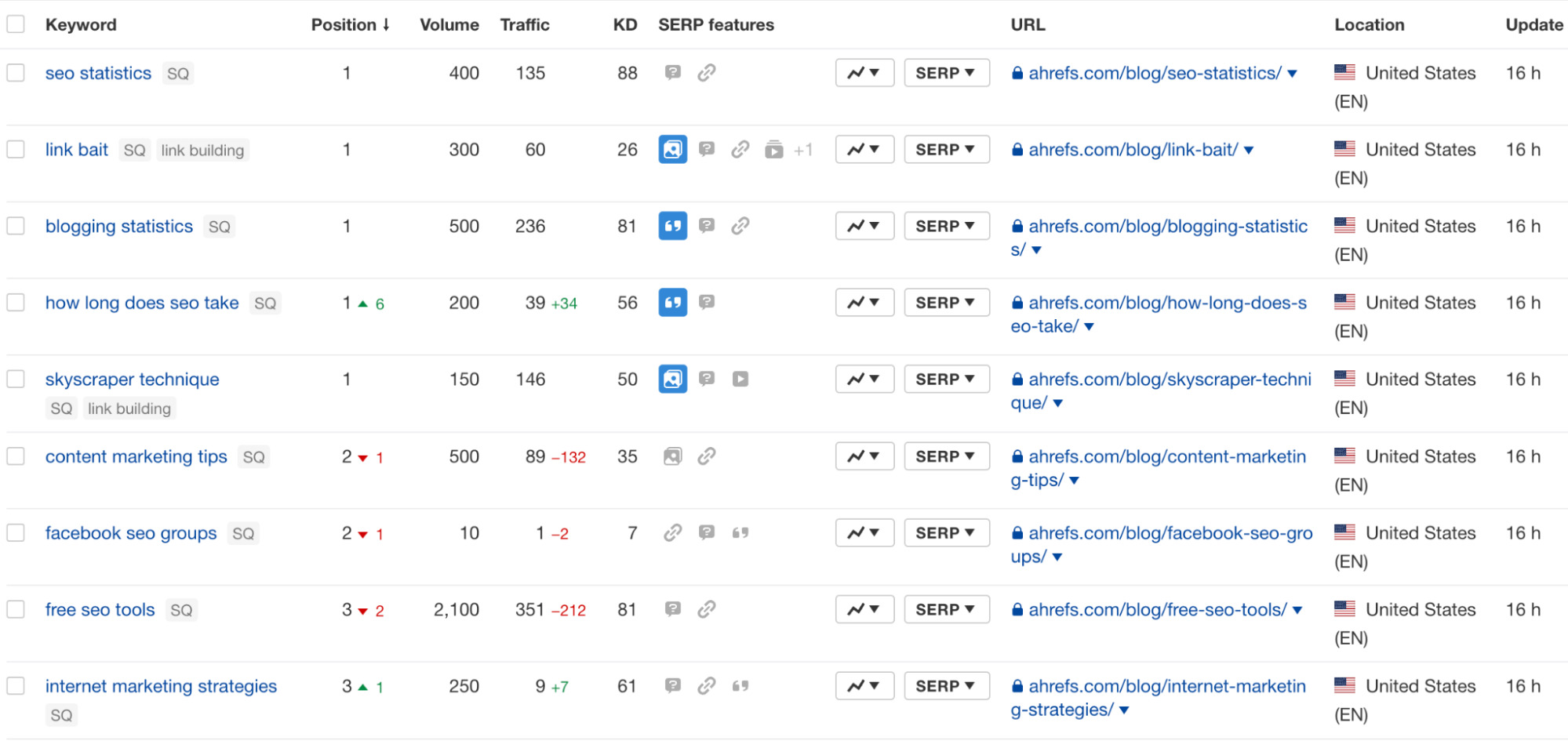
The tool will track your website’s ranking positions for all the keywords you’ve added. This way, you can easily see how well you’re performing across multiple keywords, and whether you need to make any adjustments to your content.
Final thoughts
SEO isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it task. But if you follow the above process, you’ll start to get a consistent flow of organic traffic to your site.
Any questions or comments? Let me know on Twitter.




